| Revision as of 12:58, 4 December 2009 editMondalorBot (talk | contribs)14,786 editsm Robot adding: ru:Барбаро; cosmetic changes← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:12, 8 December 2009 edit undoHistoriananna (talk | contribs)3 edits flagging topic for "coi"- stronge evidence on the internet that a major contributor, "Edward 321" , has a coi with this topic.Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{coi|date=December 2009}} | |||
| ]]] | ]]] | ||
Revision as of 20:12, 8 December 2009
| A major contributor to this article appears to have a close connection with its subject. It may require cleanup to comply with Misplaced Pages's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. Please discuss further on the talk page. (December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

The Barbaro family was a patrician family of Venice. Various members were noted as church leaders, diplomats, patrons of the arts, military commanders, philosophers, scholars, and scientists.
History
Antonio Barbaro was Procuratore of San Marco in 968. The Barbaro family’s wealth came from the salt trade.
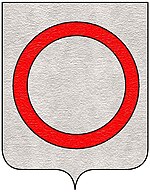
The Barbaro coat of arms was a red circle on a white field. It was granted in 1125 in remembrance of Admiral Marco Barbaro cutting off the hand of a Moor during the Battle of Ascalon and using the bleeding stump to draw a circle onto a turban- which he flew as a pennant from his masthead.
The family fortunes diminished after Napoleon's defeat of Venice and they had to turn most of the Palazzo Barbaro into apartments. The last of the family died in the mid-nineteenth century.
Notable members
Famous members included the brothers Daniele Barbaro and Marcantonio Barbaro, who were patrons of the architect Andrea Palladio and the painter Paolo Veronese.. Barbaro-family members acted as deans and professors of the University of Padua. Several members were also Patriarchs of Aquileia.
- Donato Barbaro (fl. c. 1259), Venetian admiral
- Francesco Barbaro (1390–1454), humanist
- Ermolao Barbaro (1410–1471/1474), Bishop of Treviso and Verona
- Giosafat Barbaro (1413–1494), ambassador
- Ermolao Barbaro (1454–1493/1495), philosopher, Patriarch of Aquileia 1491–1493
- Marco Barbaro (1511–1570), genealogist
- Daniele Barbaro (1513–70), scholar, cardinal and co-owner of Villa Barbaro; Patriarch of Aquileia 1550–1570
- Marcantonio Barbaro (1518–1595), ambassador and co-owner of Villa Barbaro
- Francesco Barbaro – Bishop of Aquileia 1585–1593, Patriarch of Aquileia 1593–1616
- Ermolao II Barbaro – Bishop of Aquileia 1596–1616, Patriarch of Aquileia 1616–1622
- Antonio Barbaro (d. 1679), Venetian soldier and colonial official
Patronage
The Barbaro family was connected to several buildings within and around Venice, some of which include:
- The Palazzi Barbaro are located near the Ponte dell'Accademia. The first building dates from the 14th century. It belonged to Piero Spiera in the early 15th century, passing though several hand before being acquired by Zaccaria Barbaro, Procuratore of San Marco. The other building was originally two stories and belonged to the Tagliapietra family. In the 16th century, they gave the Barbaro family permission to build on top. In 1524, the sister of the Alfonso I d'Este, Duke of Ferrara was living at the Palazzi Barbaro. In 1797 the Palazzi belonged to Senator Zuanne Barbaro and were later purchased by Daniel Sargent Curtis. The buildings are also known as the Palazzo Barbaro-Curtis.
- Another Palazzo Barbaro owned by a Daniele Barbaro and in 1797 by a Marco Barbaro.
- Yet another Palazzo Barbaro, near the Palazzo Barbarigo. It was owned in 1661 by a Lorenzo Barbaro and in 1712 by a Francesco Antonio Barbaro, but had by 1740 it belonged to the Barbarigo family.
- The Palazzo Dario was built about 1450 by Zuanne Dario. After the death of diplomat Giovanni Dario in 1494, his daughter inherited. She was married to Vincenzo Barbaro, the son of Giacomo Barbaro and owner of the neighboring Palazzo Barbaro.
- Another Palazzo Barbaro, now known as the Palazzo Barbaro-Volkoff or Barbaro-Wolkoff. This 14th century Gothic palace was owned by an Antonio Barbaro in 1797. Eleonora Duse later lived there.
- rebuilding the Rialto Bridge.
- creating a Barbaro-family chapel within San Francesco della Vigna.
- The church of Santa Maria Zobenigo, also known as the Santa Maria de Giglio was built around 900 by the Zubenigo family, who died out in 1124. It was rebuilt between 1680 and 1700 by Guiseppe Sardi. The rebuilding was funded by the Barbaro family and the churh contains statues of four members of the family. The façade shows plans for Rome, Corfu, Padua, Candia,Spalatro, and Pavia.
- creating Villa Barbaro.
References
- ^ “The City of Falling Angels, John Berendt, Penguin Books, 2006, pg.150 , ISBN 1-59420-058-0
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 346
- website.
- “Una famiglia veneziana nella storia: i Barbaro”, Michela Marangoni, Manlio Pastore Stocchi, Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti, 1996, pg. 135 , ISBN 88-86166-34-6
- “Venice”, Augustus John Cuthbert Hare, Ballantyne Press, 1896, pg. 149
- “Delle inscrizioni veneziane, Volume 4”, Emmanuele Antonio Cicogna, Fonni, 1969, pg. 520
- “A literary companion to Venice”, Ian Littlewood, Ballantyne Press, 1995, pg. 150
- “Guida per la città di Venezia all'amico delle belle arti, Volume”, Giannantonio Moschini, Giovanni Antonio Moschini, Tip. di Alvisopoli, 1815, pg. 468
- Hobson, Anthony, "Villa Barbaro", in Great Houses of Europe, ed. Sacheverell Sitwell (London: Weidenfeld, 1961), pp. 89–97. ISBN 0-600-33843-6
- ""The Patriarchate of Aquileia"". Retrieved 2007-10-07.
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 278
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 282
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 58
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 298
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 329
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 330
- “ Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places”, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907, pg. 54