| Revision as of 15:48, 13 February 2010 editSwerfvalk (talk | contribs)201 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:19, 13 February 2010 edit undoFreedom2live (talk | contribs)26 edits →External linksNext edit → | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| * graphically illustrates component options in long and short butterflies. | * graphically illustrates component options in long and short butterflies. | ||
| * things you should know about Butterfly Spreads | |||
| {{Derivatives market}} | {{Derivatives market}} | ||
Revision as of 21:19, 13 February 2010

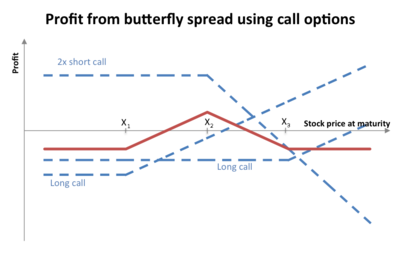
A butterfly options strategy consists of the following options:
- Long 1 call with a strike price of (X − a)
- Short 2 calls with a strike price of X
- Long 1 call with a strike price of (X + a)
where a > 0.
All the options has the same expiration date.
At expiration of the options the value (but not the profit) of the option strategy will be zero if the price of the underlying is below (X−a) or above (X+a). If the price of the underlying is between (X-a) and (X+ a) the option strategy will be worth a positive amount. The expiry payoff function is shaped like an upside-down V, and the maximum value occurs at X (see diagram).
Using put–call parity a butterfly can also be created as follows:
- Long 1 put with a strike price of (X + a)
- Short 2 puts with a strike price of X
- Long 1 put with a strike price of (X − a)
where a>0
The double option position in the middle is called the body, while the two other positions are called the wings. A related strategy where the middle two positions have differing strike values is known as an Iron condor.
In an unbalanced butterfly the variable "a" can have 2 different values.
Long butterfly
The butterfly spread is a neutral options trading strategy that is a combination of a bull spread and a bear spread. It is a limited profit, limited risk options strategy. There are 3 striking prices involved in a butterfly spread and it can be constructed using calls or puts.
Long butterflies are entered when the investor thinks that the underlying stock will not rise or fall much by expiration (i.e. when the investor is bearish on volatility). Using calls, the long butterfly can be constructed by buying one lower striking in-the-money call, writing two at-the-money calls and buying another higher striking out-of-the-money call. A resulting net debit is taken to enter the trade, hence it is also a debit spread.
A long butterfly spread can also be constructed using puts and is known as a long put butterfly. The long put butterfly spread is a neutral options trading strategy that is a combination of a bull put spread and a bear put spread. It is a limited profit, limited risk options trading strategy that is taken when the options trader thinks that the underlying stock will not rise or fall much by expiration. There are 3 striking prices involved in a long put butterfly spread and it is constructed by buying one lower striking put, writing two at-the-money puts and buying another higher striking put for a net debit.
Short butterfly
Short butterfly is the name of a neutral-outlook, options trading strategy that involves trading options at three different strike prices. The short butterfly is a neutral strategy like the long butterfly spread but bullish on volatility. It is a limited profit, limited risk options trading strategy and it can be constructed using calls or puts.
Using calls, the short butterfly can be constructed by writing one lower striking call, buying two at-the-money calls and writing another higher striking call. A net credit is received upon entering this spread. Hence, the short butterfly is also a credit spread.
References
- McMillan, Lawrence G. (2002). Options as a Strategic Investment (4th ed. ed.). New York : New York Institute of Finance. ISBN 0-7352-0197-8.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help)
External links
- Long and Short Butterflies graphically illustrates component options in long and short butterflies.
- Butterfly Spreads - Spread Your Wings & Profit things you should know about Butterfly Spreads