| Revision as of 23:29, 13 January 2011 editHans Dunkelberg (talk | contribs)7,265 editsm -superfluous dot after caption which is no full sentence← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:24, 19 January 2011 edit undoWilford Nusser (talk | contribs)485 editsmNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
| |accessdate=2009-12-15}}</ref> Over three successive orbits each Hilda asteroid passes through all of these three points in sequence. The namesake is ], discovered by ] in 1875. There are more than 1,100 known Hilda asteroids including unnumbered objects.<ref name="Ohtsukaetal2008" /><ref name=Broz2008/> | |accessdate=2009-12-15}}</ref> Over three successive orbits each Hilda asteroid passes through all of these three points in sequence. The namesake is ], discovered by ] in 1875. There are more than 1,100 known Hilda asteroids including unnumbered objects.<ref name="Ohtsukaetal2008" /><ref name=Broz2008/> | ||
| Hildas' surface colors often correspond to the low-albedo ] and ], however, a small portion are ]. The surface color of D-type and P-type asteroids such as Hildas and ] found in the outer main asteroid belt, are similar to ], and thus have similar mineralogical surfaces to cometary nuclei. This implies that they share a common origin.<ref name="Ohtsukaetal2008" /> | Hildas' surface colors often correspond to the low-albedo ] and ], however, a small portion are ]. The surface color of D-type and P-type asteroids such as Hildas and ] found in the outer main asteroid belt, are similar to ], and thus have similar mineralogical surfaces to cometary nuclei. This implies that they share a common origin.<ref name="Ohtsukaetal2008" /> | ||
| == Dynamics == | == Dynamics == | ||
Revision as of 19:24, 19 January 2011
| This article may require cleanup to meet Misplaced Pages's quality standards. No cleanup reason has been specified. Please help improve this article if you can. (November 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

The Hilda asteroids consists of asteroids with a semi-major axis between 3.7 AU and 4.2 AU, an eccentricity less than 0.3, and an inclination less than 20°. They do not form a true asteroid family, in the sense that they do not descend from a common parent object. Instead, this is a dynamical group of bodies, made up of asteroids which are in a 2:3 orbital resonance with Jupiter. Hildas move in their elliptical orbits so that their aphelia put them opposite Jupiter, or 60 degrees ahead of or behind Jupiter at the L4 and L5 Lagrangian points. Over three successive orbits each Hilda asteroid passes through all of these three points in sequence. The namesake is 153 Hilda, discovered by Johann Palisa in 1875. There are more than 1,100 known Hilda asteroids including unnumbered objects.
Hildas' surface colors often correspond to the low-albedo D-type and P-type, however, a small portion are C-type. The surface color of D-type and P-type asteroids such as Hildas and Trojans found in the outer main asteroid belt, are similar to cometary nuclei, and thus have similar mineralogical surfaces to cometary nuclei. This implies that they share a common origin.
Dynamics
The asteroids of the Hilda group (Hildas) are in 3:2 mean motion resonance with Jupiter. That is, their orbital periods are 2/3 that of Jupiter. They move along the orbits with a semimajor axis near 4.0 AU and moderate values of eccentricity (up to 0.3) and inclination (up to 20°). Unlike the Trojan asteroids they may have any difference in longitude with Jupiter, nevertheless avoiding dangerous approaches to the planet.
The Hildas taken together constitute a dynamic triangular figure with slightly convex sides and trimmed apexes in the triangular libration points of Jupiter - the "Hildas Triangle". The "asteroidal stream" within the sides of the triangle is about 1 AU wide, and in the apexes this value is 20-40 % greater. Figure 1 shows the positions of the Hildas (black) against a background of all known asteroids (gray) up to Jupiter's orbit at January 1, 2005.
Each of the Hilda objects moves along its own elliptic orbit. However, at any moment the Hildas together constitute this triangular configuration, and all the orbits together form a quite predictable ring. Figure 2 illustrates this with the Hildas positions (black) against a background of their orbits (gray). For the majority of these asteroids their position in orbit may be arbitrary except for the external parts of the apexes (the objects near aphelion) and the middles of the sides (the objects near perihelion). The Hildas Triangle has proven to be dynamically stable for a long time span.
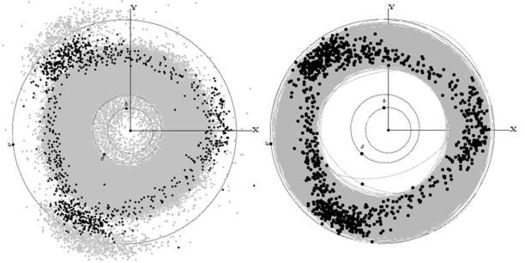
Right: The positions of the Hildas against a background of their orbits.
The typical Hilda object has a retrograde perihelion motion. On average the velocity of perihelion motion is greater as the orbital eccentricity is lesser, while the nodes move more slowly. All typical objects in aphelion would seemingly approach closely to Jupiter, which should be disstabilising for them. But the adjustment of orbital elements over time helps to avoid this, and conjunctions with Jupiter occur only near the perihelion of Hilda asteroids. Moreover the apsidal line oscillates near the line of conjunction with different amplitude and a period of 2.5 to 3.0 centuries.
In addition to the fact that the Hildas triangle revolves in connection to Jupiter the quasi-periodical waves of the stream density of asteroids in every point are noticed, as if the triangle "breathes". At any time the density of objects in the triangle's apexes is more than twice the density within the sides. The Hildas rest at their aphelia in the apexes for an average of 5.0-5.5 years whereas they move along the sides more quickly for 2.5 to 3.0 years. The orbital periods of these asteroids are approximately 7.9 years, or 2/3 that of Jupiter.
Although the triangle is nearly equilateral some asymmetry exists. Due to the eccentricity of Jupiter's orbit the side L4-L5 slightly differs from the two other sides. When Jupiter is in aphelion the mean velocity of the objects moving along this side is somewhat smaller than that of the objects related to the other sides. When Jupiter is in perihelion the picture is reverse.

At the apexes of the triangle corresponding to the points L4 and L5 of Jupiter's orbit the Hildas approach the Trojans. At the mid-sides of the triangle they are close to the asteroids of the external part of the Main Belt. The velocity dispersion of Hildas is more evident than that of Trojans in the regions where they intersect. It should also be noted that the dispersion of Trojans in inclination is twice that of the Hildas. Due to this as much as one quarter of the Trojans cannot intersect with the Hildas, and at all times a great deal of other Trojans are located outside Jupiter's orbit. Therefore the regions of intersection are limited. This is illustrated by Figure 3 that along with Jupiter in the foreground shows the Hildas (black) and the Trojans (gray) along the ecliptic plane with the longitude near 190 degrees at January 1, 2005. One can see the spherical form of the Trojan swarms.
When moving along each side of the triangle the Hildas travel slower than the Trojans but encounter a denser neighborhood of asteroids of the outer Main Belt. But here the velocity dispersion is much smaller.
Research
The observed peculiarities in the Hildas' motion are based on data for a few hundred objects known to date and generate still more questions. Further observations are needed to expand on the list of Hildas. Such observations are most favorable when the Earth is near conjunction with the mid-sides of the Hildas Triangle. These moments occur each 4 and 1/3 months. In these circumstances the brilliance of objects of similar size could run up to 2.5 magnitudes as compared to the apexes.
The Hildas traverse regions of the Solar system from approximately 2 AU up to Jupiter's orbit. This entails a variety of physical conditions and the neighborhood of various groups of asteroids. On further observation some theories on the Hildas may have to be revised.
References
- ^ Ohtsuka, Katsuhito; Yoshikawa, M.; Asher, D. J.; Arakida, H.; Arakida, H. (October 2008). "Quasi-Hilda comet 147P/Kushida-Muramatsu. Another long temporary satellite capture by Jupiter". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 489 (3): 1355–1362. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200810321.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Brož, M. (2008). "Asteroid families in the first-order resonances with Jupiter". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 390 (2): 715–732. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13764.x. Retrieved 2009-12-15.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Matthias Busch. "The triangle formed by the Hilda asteroids". EasySky. Retrieved 2009-12-15.
- L'vov V.N., Smekhacheva R.I., Smirnov S.S., Tsekmejster S.D. Some peculiarities in the Hildas motion. Izv. Pulkovo Astr. Obs., 2004, 217, 318-324 (in Russian)
| Small Solar System bodies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor planets |
| ||||||
| Comets | |||||||
| Other | |||||||