| Revision as of 08:48, 9 August 2011 editBeetstra (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Administrators172,055 edits Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEBI').← Previous edit | Revision as of 08:58, 9 August 2011 edit undoCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:WikiProject_ChemNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 443836485 | ||
| | Name = <small>D</small>-Gluconic acid | | Name = <small>D</small>-Gluconic acid | ||
| | ImageFile = D-Gluconsäure Keilstrich.svg | | ImageFile = D-Gluconsäure Keilstrich.svg | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| | ChEMBL = 464345 | | ChEMBL = 464345 | ||
| | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| | ChEBI = 33198 | | ChEBI = 33198 | ||
| | SMILES = O=C(O)(O)(O)(O)(O)CO | | SMILES = O=C(O)(O)(O)(O)(O)CO | ||
Revision as of 08:58, 9 August 2011
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name D-Gluconic acid | |
| Other names Dextronic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.639 |
| E number | E574 (acidity regulators, ...) |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H12O7 |
| Molar mass | 196.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 131 °C (268 °F; 404 K) |
| Solubility in water | Good |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.86 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
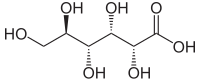
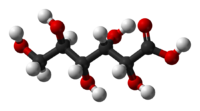
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4COOH. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoic acid.
In aqueous solution at delicately acidic pH, gluconic acid forms the gluconate ion. The salts of gluconic acid are known as "gluconates". Gluconic acid, gluconate salts, and gluconate esters occur widely in nature because such species arise from the oxidation of glucose. Some drugs are injected in the form of gluconates.
Chemical structure
The chemical structure of gluconic acid consists of a six-carbon chain with five hydroxyl groups terminating in a carboxylic acid group. In aqueous solution, gluconic acid exists in equilibrium with the cyclic ester glucono delta-lactone.
Occurrence and uses
Gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit, honey, kombucha tea, and wine. As a food additive (E574), it is an acidity regulator. It is also used in cleaning products where it dissolves mineral deposits especially in alkaline solution. The gluconate anion chelates Ca, Fe, Al, and other metals. In 1929 Horace Terhune Herrick developed a process for producing the salt by fermentation.
Calcium gluconate, in the form of a gel, is used to treat burns from hydrofluoric acid; calcium gluconate injections may be used for more severe cases to avoid necrosis of deep tissues. Quinine gluconate is a salt between gluconic acid and quinine, which is used for intramuscular injection in the treatment of malaria. Zinc gluconate injections are used to neuter male dogs. Iron gluconate injections have been proposed in the past to treat anemia.
References
- Bjerrum, J., et al. Stability Constants, Chemical Society, London, 1958.
- Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers. Food Standards Agency
- "All Chemistry". Time magazine. May 13, 1929. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
Dr. Horace T. Herrick (U. S. Department of Agriculture) told of experiments aiming to produce tartaric acid from mold. They did not succeed in their aim, but a way was found of procuring gluconic acid. This acid formerly cost $100 per lb., can now be made for less than 35¢. It can be used in dyestuff manufacture at the new price; also, to make calcium gluconate, valuable medicinally in the treatment of hemorrhages.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) -
el Saadi MS, Hall AH, Hall PK, Riggs BS, Augenstein WL, Rumack BH (1989). "Hydrofluoric acid dermal exposure". Vet Hum Toxicol. 31 (3): 243–7. PMID 2741315.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) -
Roblin I, Urban M, Flicoteau D, Martin C, Pradeau D (2006). "Topical treatment of experimental hydrofluoric acid skin burns by 2.5% calcium gluconate". J Burn Care Res. 27 (6): 889–94. doi:10.1097/01.BCR.0000245767.54278.09. PMID 17091088.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - D. Thomas, U. Jaeger, I. Sagoschen, C. Lamberti and K. Wilhelm (2009), Intra-Arterial Calcium Gluconate Treatment After Hydrofluoric Acid Burn of the Hand. CardioVascular and Interventional Radiology, Volume 32, Number 1, pages 155-158, DOI 10.1007/s00270-008-9361-1
- Julie K. Levy, P. Cynda Crawford, Leslie D. Appel, Emma L. Clifford (2008), Comparison of intratesticular injection of zinc gluconate versus surgical castration to sterilize male dogs. American Journal of Veterinary Research Vol. 69, No. 1, Pages 140-143. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.69.1.140
- Paul Reznikoff and Walther F. Goebel (1937), The preparation of ferrous gluconate and its use in the treatment of hypochromic anelia in rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Thereapy, volume 59 issue 2, page 182.