| Revision as of 12:47, 16 October 2011 editRobbot (talk | contribs)94,607 editsm r2.7.2) (Robot: Adding kk:Б. з. д. 331 жыл← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:55, 17 November 2011 edit undoMarkussep (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers, Template editors557,564 edits Epirus (region) --> Epirus using AWBNext edit → | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| == Events == | == Events == | ||
| <onlyinclude> | <onlyinclude> | ||
| === By place === | === By place === | ||
| ==== Macedonia ==== | ==== Macedonia ==== | ||
| * Alexander departs from ] and leads his forces towards ]. He leaves ] as the ruling ] to control Egypt. | * Alexander departs from ] and leads his forces towards ]. He leaves ] as the ruling ] to control Egypt. | ||
| * ] – ] of ]ia is victorious in the ] (near ancient ]) over the ] King ]. Darius turns his chariot and flees, although his subordinates fight on. Alexander pursues the defeated Persian forces to ], but Darius escapes with his ]n cavalry and Greek mercenaries into ]. | * ] – ] of ]ia is victorious in the ] (near ancient ]) over the ] King ]. Darius turns his chariot and flees, although his subordinates fight on. Alexander pursues the defeated Persian forces to ], but Darius escapes with his ]n cavalry and Greek mercenaries into ]. | ||
| * Alexander encounters for the first time ]s, he captures 15 ] after the battle in Daurius' camp. | * Alexander encounters for the first time ]s, he captures 15 ] after the battle in Daurius' camp. | ||
| * Alexander becomes the master of the ], ending the ] dynasty. ] and ] open their gates to him. In the capital, Susa, Alexander gains access to huge treasures amounting to 50,000 gold ]. | * Alexander becomes the master of the ], ending the ] dynasty. ] and ] open their gates to him. In the capital, Susa, Alexander gains access to huge treasures amounting to 50,000 gold ]. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
| == Births == | == Births == | ||
| * | * | ||
| == Deaths == | == Deaths == | ||
| * ], Aeacid dynasty king of ] (b. c. ]) | * ], Aeacid dynasty king of ] (b. c. ]) | ||
| * ], legendary king of ] and last of the ] | * ], legendary king of ] and last of the ] | ||
Revision as of 20:55, 17 November 2011
Calendar year
| Millennium: | 1st millennium BC |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| 331 BC by topic |
| Politics |
|---|
| Categories |
| Gregorian calendar | 331 BC CCCXXXI BC |
| Ab urbe condita | 423 |
| Ancient Egypt era | XXXII dynasty, 2 |
| - Pharaoh | Alexander the Great, 2 |
| Ancient Greek era | 112th Olympiad, year 2 |
| Assyrian calendar | 4420 |
| Balinese saka calendar | N/A |
| Bengali calendar | −923 |
| Berber calendar | 620 |
| Buddhist calendar | 214 |
| Burmese calendar | −968 |
| Byzantine calendar | 5178–5179 |
| Chinese calendar | 己丑年 (Earth Ox) 2367 or 2160 — to — 庚寅年 (Metal Tiger) 2368 or 2161 |
| Coptic calendar | −614 – −613 |
| Discordian calendar | 836 |
| Ethiopian calendar | −338 – −337 |
| Hebrew calendar | 3430–3431 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | −274 – −273 |
| - Shaka Samvat | N/A |
| - Kali Yuga | 2770–2771 |
| Holocene calendar | 9670 |
| Iranian calendar | 952 BP – 951 BP |
| Islamic calendar | 981 BH – 980 BH |
| Javanese calendar | N/A |
| Julian calendar | N/A |
| Korean calendar | 2003 |
| Minguo calendar | 2242 before ROC 民前2242年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −1798 |
| Thai solar calendar | 212–213 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阴土牛年 (female Earth-Ox) −204 or −585 or −1357 — to — 阳金虎年 (male Iron-Tiger) −203 or −584 or −1356 |
Year 331 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Marcellus (or, less frequently, year 423 Ab urbe condita). The denomination 331 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Macedonia
- Alexander departs from Egypt and leads his forces towards Phoenicia. He leaves Cleomenes of Naucratis as the ruling nomarch to control Egypt.
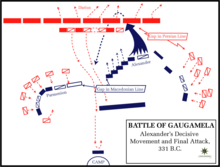
- October 1 – Alexander of Macedonia is victorious in the Battle of Gaugamela (near ancient Ninevah) over the Persian King Darius III. Darius turns his chariot and flees, although his subordinates fight on. Alexander pursues the defeated Persian forces to Arbela, but Darius escapes with his Bactrian cavalry and Greek mercenaries into Media.
- Alexander encounters for the first time war elephants, he captures 15 Persian elephants after the battle in Daurius' camp.
- Alexander becomes the master of the Persian Empire, ending the Achaemenid dynasty. Babylon and Susa open their gates to him. In the capital, Susa, Alexander gains access to huge treasures amounting to 50,000 gold talents.
Greece
- While Alexander is fighting in Asia, Agis III of Sparta, profiting from the Macedonian king's absence from Greece, leads some of the Greek cities in a revolt. With Persian money and 8,000 Greek mercenaries, he holds Crete against Macedonian forces. In the Peloponnesus he routes a force under the Macedonian general Coragus and, although Athens stays neutral, he is joined by Elis, Achaea (except Pellene) and Arcadia, with the exception of Megalopolis, the staunchly anti-Spartan capital of Arcadia, which Agis III's forces besiege.
Italy
- Alexander of Epirus takes Heraclea from the Lucanians, and Terina and Sipontum from the Bruttii.
- Tarentum turn against Alexander of Epirus when they realize that he intends to create a kingdom of his own in southern Italy. Alexander is defeated and killed in the Battle of Pandosia on the banks of the Acheron.
Roman Republic
- The Gallic tribe of the Senones and the Romans conclude a peace and enter upon a period of friendly relations which lasts the rest of the century.
Births
Deaths
- Alexander I of Epirus, Aeacid dynasty king of Epirus (b. c. 370 BC)
- Vahe, legendary king of Armenia and last of the Hyke dynasty