| Revision as of 14:27, 27 November 2011 edit194.254.137.115 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:28, 27 November 2011 edit undo194.254.137.115 (talk)No edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| * <math>\eta \geq 1\,</math> the probability density function has its mode at 0. | * <math>\eta \geq 1\,</math> the probability density function has its mode at 0. | ||
| * <math>\eta < 1\,</math> the probability density function has its mode at | * <math>\eta < 1\,</math> the probability density function has its mode at | ||
| ::<math>\ |
::<math>\x*}=-\frac{\ln(z^\star)}{b}\, \qquad 0 < z^\star < 1</math> | ||
| :where <math>z^\star\,</math> is the smallest root of | :where <math>z^\star\,</math> is the smallest root of | ||
| ::<math>\eta^2z^2 - \eta(3 + \eta)z + \eta + 1 = 0\,,</math> | ::<math>\eta^2z^2 - \eta(3 + \eta)z + \eta + 1 = 0\,,</math> | ||
Revision as of 14:28, 27 November 2011
Probability density function | |||
Cumulative distribution function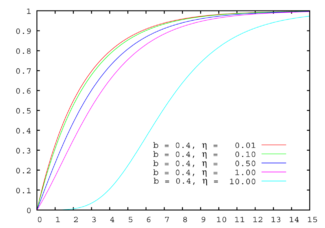 | |||
| Parameters |
scale (real) shape (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean |
where and | ||
| Mode | for , for where | ||
| Variance |
where and | ||
The Gompertz distribution is an extreme value (reverted Gumbel distribution) distribution which is truncated at zero. It has been used as a model of customer lifetime.
Specification
Probability density function
The probability density function of the Gompertz distribution is:
where is the scale parameter and is the shape parameter of the Gompertz distribution.
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function of the Gompertz distribution is:
Properties
The Gompertz distribution is right-skewed for all values of .
Shapes
The Gompertz density function can take on different shapes depending on the values of the shape parameter :
- the probability density function has its mode at 0.
- the probability density function has its mode at
- Failed to parse (unknown function "\x"): {\displaystyle \x*}=-\frac{\ln(z^\star)}{b}\, \qquad 0 < z^\star < 1}
- where is the smallest root of
- which is
Related distributions
The Gompertz distribution is a natural conjugate to a gamma distribution. If varies according to a gamma distribution with shape parameter and scale parameter (mean = ), the cumulative distribution function is Gamma/Gompertz (G/G).





 where
where  and
and

 for
for  ,
,  for
for  where
where




 .
.
 the probability density function has its mode at 0.
the probability density function has its mode at 0. the probability density function has its mode at
the probability density function has its mode at is the smallest root of
is the smallest root of


 and scale parameter
and scale parameter  (mean =
(mean =  ), the cumulative distribution function is Gamma/Gompertz (G/G).
), the cumulative distribution function is Gamma/Gompertz (G/G).