| Revision as of 00:11, 28 May 2012 editJonny Bee Goo (talk | contribs)324 edits Restoring referenced version by TRAJAN 117 bsed upon BRITANNICA and OHIO UNIVERSITY per WP:SOURCES and WP:CONSENSUS← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:09, 29 May 2012 edit undoHmains (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers1,214,057 editsm copyedit, clarity edits, MOS implementation, and/or AWB general fixes using AWB (8062)Next edit → | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
| | | | | ||
| |national anthem = ], ] | |national anthem = ], ] | ||
| |capital = ]<ref>] from |
|capital = ]<ref>] from 1799 to 1814, during the ].</ref> | ||
| |common_languages = ], ]<br>], ], ], ], ], ], ] | |common_languages = ], ]<br>], ], ], ], ], ], ] | ||
| |religion = ] | |religion = ] | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
| |stat_area1= 70000 | |stat_area1= 70000 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Kingdom of Sardinia''', also '''Piedmont–Sardinia''' or '''Sardinia–Piedmont''', refers to the possessions of the ] from 1720 or 1723 onwards<ref> A 2 penny ''(2 denari)'' coin minted in 1722, still using the title of King of Sicily for Victor Amadeus II.</ref><ref name=col>{{Cite book|title=]|chapter=Sardinia, kingdom of|edition=6|publisher=Columbia University Press|year=2007|url=http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/history/A0843673.html#axzz0yhEdFv00}}</ref><ref name=brit>{{Cite web|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/524132/Sardinia|title=Sardinia (historical kingdom, Italy)|work=]|accessdate=6 September 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Benigni|first=Umberto|chapter=Sardinia|title=]|volume=13|place=New York|publisher=Robert Appleton Company|year=1912|accessdate=6 September 2010|url=http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/13473b.htm}}</ref><ref>Thuesen, 2002, p. 506.</ref><ref>The Savoyard State continued to be styled as ''Kingdom of Sicily, Jerusalem and Cyprus'' on official acts until 1723, when the king ended his protests against the forced changeover between Sicily and Sardinia.</ref> |
'''Kingdom of Sardinia''', also '''Piedmont–Sardinia''' or '''Sardinia–Piedmont''', refers to the possessions of the ] from 1720 or 1723 onwards,<ref> A 2 penny ''(2 denari)'' coin minted in 1722, still using the title of King of Sicily for Victor Amadeus II.</ref><ref name=col>{{Cite book|title=]|chapter=Sardinia, kingdom of|edition=6|publisher=Columbia University Press|year=2007|url=http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/history/A0843673.html#axzz0yhEdFv00}}</ref><ref name=brit>{{Cite web|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/524132/Sardinia|title=Sardinia (historical kingdom, Italy)|work=]|accessdate=6 September 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Benigni|first=Umberto|chapter=Sardinia|title=]|volume=13|place=New York|publisher=Robert Appleton Company|year=1912|accessdate=6 September 2010|url=http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/13473b.htm}}</ref><ref>Thuesen, 2002, p. 506.</ref><ref>The Savoyard State continued to be styled as ''Kingdom of Sicily, Jerusalem and Cyprus'' on official acts until 1723, when the king ended his protests against the forced changeover between Sicily and Sardinia.</ref> following the award of the crown of ] to ] under the ]. This compensated him for the loss of the crown of ] to ] and allowed him to retain the title of king, as the title "King of Sardinia" had existed since the 14th century. Besides Sardinia, the new kingdom included ], ], and ]; ], including ], was added by the ] in 1815. Officially, the nation's name became ''Kingdom of Sardinia, Cyprus and Jerusalem'', the House of Savoy maintaining a national claim to the thrones of ] and ], although both had long been under ] rule. During most of the 18th and 19th centuries, the political and economic capital of the kingdom was ] in Piedmont on the Italian mainland. In 1860, Nice and Savoy were ceded to France in return for French consent and assistance in ]. In 1861, the Kingdom of Sardinia became the founding state of the new ], ] all other Italian states. The Kingdom thus continued in legal continuity with the new Italian state, to which it transferred all its institutions. | ||
| ==Early history of Piedmont== | ==Early history of Piedmont== | ||
| {{Main|Duchy of Savoy}} | {{Main|Duchy of Savoy}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Piedmont was inhabited in early historic times by Celtic-] tribes such as the ] and the ]. They later submitted to the ] (c. |
Piedmont was inhabited in early historic times by Celtic-] tribes such as the ] and the ]. They later submitted to the ] (c. 220 BC), who founded several colonies there including ''Augusta Taurinorum ''(Turin) and ''Eporedia'' (]). After the fall of the ], the region was repeatedly invaded by the ], the ] (5th century), ], ] (6th century), ] (773). In the 9th–10th centuries there were further incursions by the ] and ]. At the time Piedmont, as part of the ] within the ], was subdivided into several marks and counties. | ||
| In 1046, ] added Piedmont to their main segment of ], with a capital at ] (now in ]). Other areas remained independent, such as the powerful communes of ] and ] and the marquisates of ] and ]. The County of Savoy was elevated to a duke in 1416, and Duke ] moved the seat to ] in 1563. | In 1046, ] added Piedmont to their main segment of ], with a capital at ] (now in ]). Other areas remained independent, such as the powerful communes of ] and ] and the marquisates of ] and ]. The County of Savoy was elevated to a duke in 1416, and Duke ] moved the seat to ] in 1563. | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
| ==Exchange of Sardinia for Sicily== | ==Exchange of Sardinia for Sicily== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The Spanish domination of Sardinia ended at the beginning of the 18th century, as a result of ]. By the ] of 1713, ]'s European empire was divided: ] received ] and parts of the ], while ] (the ] and ]), received the ], the ], ], and the bulk of the ]. During the ], ], duke of Savoy and sovereign of Piedmont, had to agree to yield Sicily to the Austrian Habsburgs and receive Sardinia in exchange. The exchange was formally ratified in the ] of February 17, 1720. Because a ] had existed since the 14th century, the exchange allowed Victor Amadeus to retain the title of king in spite of the loss of Sicily.<ref name=col |
The Spanish domination of Sardinia ended at the beginning of the 18th century, as a result of ]. By the ] of 1713, ]'s European empire was divided: ] received ] and parts of the ], while ] (the ] and ]), received the ], the ], ], and the bulk of the ]. During the ], ], duke of Savoy and sovereign of Piedmont, had to agree to yield Sicily to the Austrian Habsburgs and receive Sardinia in exchange. The exchange was formally ratified in the ] of February 17, 1720. Because a ] had existed since the 14th century, the exchange allowed Victor Amadeus to retain the title of king in spite of the loss of Sicily.<ref name="col"/><ref name="brit"/> | ||
| Victor Amadeus initially resisted the exchange, and until 1723 continued to style himself King of Sicily rather than King of Sardinia.<ref>See for example Thuesen, 2002, p. 506. A minted in 1722 still uses the title of King of Sicily for Victor Amadeus II.</ref> The state took the official title of ''Kingdom of Sardinia, Cyprus and Jerusalem'', as the house of ] still claimed the thrones of ] and ], although both had long been under ] rule. | Victor Amadeus initially resisted the exchange, and until 1723 continued to style himself King of Sicily rather than King of Sardinia.<ref>See for example Thuesen, 2002, p. 506. A minted in 1722 still uses the title of King of Sicily for Victor Amadeus II.</ref> The state took the official title of ''Kingdom of Sardinia, Cyprus and Jerusalem'', as the house of ] still claimed the thrones of ] and ], although both had long been under ] rule. | ||
| In |
In 1767–1769, ] conquered the ] in the ] from the ], who ruled it with the island of ], and since then the archipelago is still part of the ]. | ||
| ==Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna== | ==Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| In 1792 Piedmont-Sardinia joined the ] against the ], but was beaten in 1796 by Napoleon and forced to conclude the disadvantageous ], giving the French army free passage through Piedmont. On December 6, 1798 ] occupied Turin and forced ] to abdicate and leave for the island of Sardinia. The provisionary government voted to unite Piedmont with France. In 1799 the Austro-Russians briefly occupied the city, but with the ] (1800), the French regained control. The island of Sardinia stayed out of the reach of the French for the rest of the war. | In 1792, Piedmont-Sardinia joined the ] against the ], but was beaten in 1796 by Napoleon and forced to conclude the disadvantageous ], giving the French army free passage through Piedmont. On December 6, 1798 ] occupied Turin and forced ] to abdicate and leave for the island of Sardinia. The provisionary government voted to unite Piedmont with France. In 1799 the Austro-Russians briefly occupied the city, but with the ] (1800), the French regained control. The island of Sardinia stayed out of the reach of the French for the rest of the war. | ||
| In 1814 the kingdom was restored and enlarged with the addition of the former ], now a duchy, and it served as a ] against ]. This was confirmed by the ]. | In 1814, the kingdom was restored and enlarged with the addition of the former ], now a duchy, and it served as a ] against ]. This was confirmed by the ]. | ||
| In the reaction after Napoleon, the country was ruled by conservative monarchs: ] (1802–21), ] (1821–31) and ] (1831–49), who fought at the head of a contingent of his own troops at the ], which set the reactionary ] on the Spanish throne. Victor Emanuel I disbanded the entire Code Napoléon and returned the lands and power to the nobility and the Church. This reactionary policy went as far as discouraging the use of roads built by the French. These changes typified Piedmont. | In the reaction after Napoleon, the country was ruled by conservative monarchs: ] (1802–21), ] (1821–31) and ] (1831–49), who fought at the head of a contingent of his own troops at the ], which set the reactionary ] on the Spanish throne. Victor Emanuel I disbanded the entire Code Napoléon and returned the lands and power to the nobility and the Church. This reactionary policy went as far as discouraging the use of roads built by the French. These changes typified Piedmont. | ||
| The Kingdom of Sardinia industrialized from 1830 onward. A constitution, the '']'', was enacted in ], under liberal pressure, and under the same pressure Charles Albert declared war on Austria. After initial success the war took a turn for the worse and Charles Albert was defeated by ] at ]. | The Kingdom of Sardinia industrialized from 1830 onward. A constitution, the '']'', was enacted in ], under liberal pressure, and under the same pressure Charles Albert declared war on Austria. After initial success the war took a turn for the worse and Charles Albert was defeated by ] at ]. | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
| Like all of Italy, the Kingdom of Sardinia was troubled with political instability, under alternating governments. After a very short and disastrous renewal of the war with Austria in 1849, Charles Albert abdicated on March 23, 1849, in favour of his son ]. | Like all of Italy, the Kingdom of Sardinia was troubled with political instability, under alternating governments. After a very short and disastrous renewal of the war with Austria in 1849, Charles Albert abdicated on March 23, 1849, in favour of his son ]. | ||
| In 1852 a liberal ministry under ] was installed, and the Kingdom of Sardinia became the engine driving the ]. The Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) took part in the ], allied with the ], ], and ], and fighting against ]. | In 1852, a liberal ministry under ] was installed, and the Kingdom of Sardinia became the engine driving the ]. The Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) took part in the ], allied with the ], ], and ], and fighting against ]. | ||
| In 1859 France sided with the Kingdom of Sardinia in a war against ], the ]. ] didn't keep his promises to Cavour to fight until all of the ] had been conquered. Following the bloody battles of ] and ], both French victories, Napoleon thought the war too costly to continue and made a separate peace behind Cavour's back in which only Lombardy would be ceded. Due to the Austrian government's refusal to cede any lands to the Kingdom of Sardinia, they agreed to cede ] to Napoleon who in turn then ceded the territory to the Kingdom of Sardinia to avoid 'embarrassing' the defeated Austrians. Cavour angrily resigned from office when it became clear that Victor Emmanuel would accept the deal. | In 1859, France sided with the Kingdom of Sardinia in a war against ], the ]. ] didn't keep his promises to Cavour to fight until all of the ] had been conquered. Following the bloody battles of ] and ], both French victories, Napoleon thought the war too costly to continue and made a separate peace behind Cavour's back in which only Lombardy would be ceded. Due to the Austrian government's refusal to cede any lands to the Kingdom of Sardinia, they agreed to cede ] to Napoleon who in turn then ceded the territory to the Kingdom of Sardinia to avoid 'embarrassing' the defeated Austrians. Cavour angrily resigned from office when it became clear that Victor Emmanuel would accept the deal. | ||
| ===Garibaldi and the Thousand=== | ===Garibaldi and the Thousand=== | ||
| On March 5, 1860 ], ], ], and ] voted in ]s to join the Kingdom of Sardinia. This alarmed Napoleon who feared a strong Savoyard state on his southeastern border and he insisted that if the Kingdom of Sardinia were to keep the new acquisitions they would have to cede Savoy and Nice to France. This was done after dubious referendums showed over 99.5% majorities in both areas in favour of joining France. <!-- not sure how to fix this, but I don't understand why the referenda in Savoy and Nice were "dubious" but the ones in central Italy were not. --> | On March 5, 1860, ], ], ], and ] voted in ]s to join the Kingdom of Sardinia. This alarmed Napoleon who feared a strong Savoyard state on his southeastern border and he insisted that if the Kingdom of Sardinia were to keep the new acquisitions they would have to cede Savoy and Nice to France. This was done after dubious referendums showed over 99.5% majorities in both areas in favour of joining France. <!-- not sure how to fix this, but I don't understand why the referenda in Savoy and Nice were "dubious" but the ones in central Italy were not. --> | ||
| In 1860 ] started his campaign to conquer southern Italy in the name of the Kingdom of Sardinia. He quickly toppled the ] and marched to ]. Cavour was actually the most satisfied with the unification while Garibaldi wanted to conquer Rome. Garibaldi was too revolutionary for the king and his prime minister. | In 1860, ] started his campaign to conquer southern Italy in the name of the Kingdom of Sardinia. He quickly toppled the ] and marched to ]. Cavour was actually the most satisfied with the unification while Garibaldi wanted to conquer Rome. Garibaldi was too revolutionary for the king and his prime minister. | ||
| ===Towards Kingdom of Italy=== | ===Towards Kingdom of Italy=== | ||
| On March 17, 1861 the ] was proclaimed by the Parliament, so ratifying the ]s of all other Italian states to Piedmont. The institutions and laws of the Kingdom were quickly extended to all Italy, brutally abolishing the administrations of the other regions. Piedmont would become the most dominant and wealthiest region in Italy and the capital of Piedmont, Turin, would remain the Italian capital until 1865 when the capital was moved to ]; but in contrast, many revolts exploded through the peninsula, ]. The ] would rule Italy until 1946 when Italy was declared a ] by ]. | On March 17, 1861, the ] was proclaimed by the Parliament, so ratifying the ]s of all other Italian states to Piedmont. The institutions and laws of the Kingdom were quickly extended to all Italy, brutally abolishing the administrations of the other regions. Piedmont would become the most dominant and wealthiest region in Italy and the capital of Piedmont, Turin, would remain the Italian capital until 1865 when the capital was moved to ]; but in contrast, many revolts exploded through the peninsula, ]. The ] would rule Italy until 1946 when Italy was declared a ] by ]. | ||
| ==Flags== | ==Flags== | ||
Revision as of 03:09, 29 May 2012
This article is about the Savoyard state of Piedmont-Sardinia. For the older realm which gave its name to that state, see Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica.Kingdom of Sardinia, also Piedmont–Sardinia or Sardinia–Piedmont, refers to the possessions of the House of Savoy from 1720 or 1723 onwards, following the award of the crown of Sardinia to King Victor Amadeus II of Savoy under the Treaty of The Hague (1720). This compensated him for the loss of the crown of Sicily to Austria and allowed him to retain the title of king, as the title "King of Sardinia" had existed since the 14th century. Besides Sardinia, the new kingdom included Savoy, Piedmont, and Nice; Liguria, including Genoa, was added by the Congress of Vienna in 1815. Officially, the nation's name became Kingdom of Sardinia, Cyprus and Jerusalem, the House of Savoy maintaining a national claim to the thrones of Cyprus and Jerusalem, although both had long been under Ottoman rule. During most of the 18th and 19th centuries, the political and economic capital of the kingdom was Turin in Piedmont on the Italian mainland. In 1860, Nice and Savoy were ceded to France in return for French consent and assistance in Italian unification. In 1861, the Kingdom of Sardinia became the founding state of the new Kingdom of Italy, annexing all other Italian states. The Kingdom thus continued in legal continuity with the new Italian state, to which it transferred all its institutions.
Early history of Piedmont
Main article: Duchy of Savoy
Piedmont was inhabited in early historic times by Celtic-Ligurian tribes such as the Taurini and the Salassi. They later submitted to the Romans (c. 220 BC), who founded several colonies there including Augusta Taurinorum (Turin) and Eporedia (Ivrea). After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the region was repeatedly invaded by the Burgundians, the Goths (5th century), Byzantines, Lombards (6th century), Franks (773). In the 9th–10th centuries there were further incursions by the Magyars and Saracens. At the time Piedmont, as part of the Kingdom of Italy within the Holy Roman Empire, was subdivided into several marks and counties.
In 1046, Oddo of Savoy added Piedmont to their main segment of Savoy, with a capital at Chambéry (now in France). Other areas remained independent, such as the powerful communes of Asti and Alessandria and the marquisates of Saluzzo and Montferrat. The County of Savoy was elevated to a duke in 1416, and Duke Emanuele Filiberto moved the seat to Turin in 1563.
Early history of Sardinia
Main articles: History of Sardinia and Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica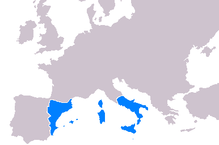
In 1297, Pope Boniface VIII, intervening between the Houses of Anjou and Aragon, established on paper a regnum Sardiniae et Corsicae that would be a fief of the Papacy. Then the Pope offered his newly-invented fief to James II of Aragon, promising him papal support should he wish to conquer Pisan Sardinia in exchange for Sicily. In 1323 James II formed an alliance with Hugh II of Arborea and, following a military campaign which lasted a year or so, occupied the Pisan territories of Cagliari and Gallura along with the city of Sassari, claiming the territory as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica. In 1353 Aragon made war on Arborea, then fought with its leader Marianus IV of Arborea,of the Cappai de Bas family, but did not reduce the last of the autochthonous giudicati (indigenous kingdoms of Sardinia) until 1410. The Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica retained its separate character as part of the Crown of Aragon and was not merely incorporated into the Kingdom of Aragon. At the time of his struggles with Arborea, Peter IV of Aragon granted an autonomous legislature to the Kingdom, which had one of Europe's most advanced legal traditions. The Kingdom was governed in the king's name by a viceroy. When in 1409, Martin the younger, king of Sicily and heir to Aragon, defeated the last Sardinian giudicato but then died in Cagliari of malaria, without issue, Sardinia passed with the Crown of Aragon to a united Spain. Corsica, which had never been conquered, was dropped from the formal title. The loss of the autochthonous' independence, the firm Aragonese (later Spanish) rule, with the introduction of a sterile feudalism, as well as the discovery of the Americas, provoked an unstoppable decline of Kingdom of Sardinia. A short period of resurgence occurred under the local noble Leonardo de Alagon, marquess of Oristano, who managed to defeat the viceroy's army in the 1470s but was later crushed at the Battle of Macomer (1478), ending any further hope of independence for the island. The unceasing attacks from North African pirates and a series of plagues (from 1582, 1652 and 1655) further worsened the situation.
Exchange of Sardinia for Sicily

The Spanish domination of Sardinia ended at the beginning of the 18th century, as a result of War of the Spanish succession. By the Treaty of Utrecht of 1713, Spain's European empire was divided: Savoy received Sicily and parts of the Duchy of Milan, while Charles VI (the Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria), received the Spanish Netherlands, the Kingdom of Naples, Sardinia, and the bulk of the Duchy of Milan. During the War of the Quadruple Alliance, Victor Amadeus II, duke of Savoy and sovereign of Piedmont, had to agree to yield Sicily to the Austrian Habsburgs and receive Sardinia in exchange. The exchange was formally ratified in the Treaty of The Hague of February 17, 1720. Because a kingdom of Sardinia had existed since the 14th century, the exchange allowed Victor Amadeus to retain the title of king in spite of the loss of Sicily.
Victor Amadeus initially resisted the exchange, and until 1723 continued to style himself King of Sicily rather than King of Sardinia. The state took the official title of Kingdom of Sardinia, Cyprus and Jerusalem, as the house of Savoy still claimed the thrones of Cyprus and Jerusalem, although both had long been under Ottoman rule.
In 1767–1769, Charles Emmanuel III conquered the Maddalena archipelago in the Strait of Bonifacio from the Republic of Genoa, who ruled it with the island of Corsica, and since then the archipelago is still part of the Sardinian region.
Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna

In 1792, Piedmont-Sardinia joined the First Coalition against the French First Republic, but was beaten in 1796 by Napoleon and forced to conclude the disadvantageous Treaty of Paris (1796), giving the French army free passage through Piedmont. On December 6, 1798 Joubert occupied Turin and forced Charles Emmanuel IV to abdicate and leave for the island of Sardinia. The provisionary government voted to unite Piedmont with France. In 1799 the Austro-Russians briefly occupied the city, but with the Battle of Marengo (1800), the French regained control. The island of Sardinia stayed out of the reach of the French for the rest of the war.
In 1814, the kingdom was restored and enlarged with the addition of the former Republic of Genoa, now a duchy, and it served as a buffer state against France. This was confirmed by the Congress of Vienna. In the reaction after Napoleon, the country was ruled by conservative monarchs: Victor Emmanuel I (1802–21), Charles Felix (1821–31) and Charles Albert (1831–49), who fought at the head of a contingent of his own troops at the Battle of Trocadero, which set the reactionary Ferdinand VII on the Spanish throne. Victor Emanuel I disbanded the entire Code Napoléon and returned the lands and power to the nobility and the Church. This reactionary policy went as far as discouraging the use of roads built by the French. These changes typified Piedmont. The Kingdom of Sardinia industrialized from 1830 onward. A constitution, the Statuto Albertino, was enacted in the year of revolutions, 1848, under liberal pressure, and under the same pressure Charles Albert declared war on Austria. After initial success the war took a turn for the worse and Charles Albert was defeated by Marshal Radetzky at Custozza.
Italian unification


Like all of Italy, the Kingdom of Sardinia was troubled with political instability, under alternating governments. After a very short and disastrous renewal of the war with Austria in 1849, Charles Albert abdicated on March 23, 1849, in favour of his son Victor Emmanuel II.
In 1852, a liberal ministry under Count Camillo Benso di Cavour was installed, and the Kingdom of Sardinia became the engine driving the Italian Unification. The Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) took part in the Crimean War, allied with the Ottoman Empire, Britain, and France, and fighting against Russia.
In 1859, France sided with the Kingdom of Sardinia in a war against Austria, the Austro-Sardinian War. Napoleon III didn't keep his promises to Cavour to fight until all of the Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia had been conquered. Following the bloody battles of Magenta and Solferino, both French victories, Napoleon thought the war too costly to continue and made a separate peace behind Cavour's back in which only Lombardy would be ceded. Due to the Austrian government's refusal to cede any lands to the Kingdom of Sardinia, they agreed to cede Lombardy to Napoleon who in turn then ceded the territory to the Kingdom of Sardinia to avoid 'embarrassing' the defeated Austrians. Cavour angrily resigned from office when it became clear that Victor Emmanuel would accept the deal.
Garibaldi and the Thousand
On March 5, 1860, Parma, Tuscany, Modena, and Romagna voted in referendums to join the Kingdom of Sardinia. This alarmed Napoleon who feared a strong Savoyard state on his southeastern border and he insisted that if the Kingdom of Sardinia were to keep the new acquisitions they would have to cede Savoy and Nice to France. This was done after dubious referendums showed over 99.5% majorities in both areas in favour of joining France.
In 1860, Giuseppe Garibaldi started his campaign to conquer southern Italy in the name of the Kingdom of Sardinia. He quickly toppled the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies and marched to Gaeta. Cavour was actually the most satisfied with the unification while Garibaldi wanted to conquer Rome. Garibaldi was too revolutionary for the king and his prime minister.
Towards Kingdom of Italy
On March 17, 1861, the Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed by the Parliament, so ratifying the annexations of all other Italian states to Piedmont. The institutions and laws of the Kingdom were quickly extended to all Italy, brutally abolishing the administrations of the other regions. Piedmont would become the most dominant and wealthiest region in Italy and the capital of Piedmont, Turin, would remain the Italian capital until 1865 when the capital was moved to Florence; but in contrast, many revolts exploded through the peninsula, especially in Southern Italy. The House of Savoy would rule Italy until 1946 when Italy was declared a republic by referendum.
Flags
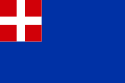
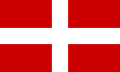
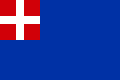
When the Duchy of Savoy changed its name into Kingdom of Sicily in 1713 and Kingdom of Sardinia in 1723, it maintained its traditional flag depicting a white cross on a red field. But a problem arose: if the Duchy owned the small harbour of Nice only, the union with Sicily and then Sardinia gave to the Kingdom a quite big fleet, which had the same flag of Malta. To disambiguate the ships of the two different States, the House of Savoy added a blue border to its flag, and then it reduced the cross in a single quarter.
The flag had following minor changes until 1848, when a revolution happened: to follow the liberal revolutions which were exploding in all Europe, King Charles Albert adopted the Napoleonic Italian tricolour, surmonted by the Savoyard shield, as national flag. This flag became the flag of Italy until 1946.
Maps
-
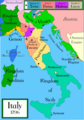 1796: Kingdom of Sardinia Republic of Genoa Duchy of Parma Duchy of Modena Republic of Lucca Grand Duchy of Tuscany Papal States Republic of Venice Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
1796: Kingdom of Sardinia Republic of Genoa Duchy of Parma Duchy of Modena Republic of Lucca Grand Duchy of Tuscany Papal States Republic of Venice Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
-
 1859: Kingdom of Sardinia Kgdm Lombardy–Veneto Duchies Parma–Modena Papal States Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
1859: Kingdom of Sardinia Kgdm Lombardy–Veneto Duchies Parma–Modena Papal States Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
-
 1860: Kingdom of Sardinia Kgdm Lombardy–Veneto Papal States Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
1860: Kingdom of Sardinia Kgdm Lombardy–Veneto Papal States Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
After the annexation of Lombardy, the Grand Duchy of Tuscany, and the Duchies of Emiliani and Romagna pontificia. -
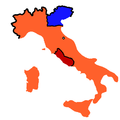 1861: Kingdom of Italy Kgdm Lombardy–Veneto Papal States
1861: Kingdom of Italy Kgdm Lombardy–Veneto Papal States
After the Expedition of the Thousand.
Constituent countries
Until the perfect fusion of 1848, the Savoyard State was formed by different constituent countries:
- The Duchy of Savoy
- The Principality of Piedmont
- The County of Nice
- The Duchy of Genoa
- The Viceroyalty of Sardinia
References
- Cagliari from 1799 to 1814, during the French occupation.
- A 2 penny (2 denari) coin minted in 1722, still using the title of King of Sicily for Victor Amadeus II.
- ^ "Sardinia, kingdom of". [[Columbia Encyclopedia|The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia]] (6 ed.). Columbia University Press. 2007.
{{cite book}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^ "Sardinia (historical kingdom, Italy)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- Benigni, Umberto (1912). "Sardinia". [[The Catholic Encyclopedia]]. Vol. 13. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
{{cite book}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - Thuesen, 2002, p. 506.
- The Savoyard State continued to be styled as Kingdom of Sicily, Jerusalem and Cyprus on official acts until 1723, when the king ended his protests against the forced changeover between Sicily and Sardinia.
- See for example Thuesen, 2002, p. 506. A coin minted in 1722 still uses the title of King of Sicily for Victor Amadeus II.
Sources
- Hearder, Harry (1986). Italy in the Age of the Risorgimento, 1790–1870. London: Longman. ISBN 0-582-49146-0.
- Martin, George Whitney (1969). The Red Shirt and the Cross of Savoy. New York: Dodd, Mead and Co. ISBN 0-396-05908-2.
- Storrs, Christopher (1999). War, Diplomacy and the Rise of Savoy, 1690–1720. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-55146-3.
- Thuesen, Nils Petter (2002). Verdens historie i årstall. Orion. ISBN 978-82-458-0517-8.
External links
| List of historic states of Italy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Roman period | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ancient Rome |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medieval and Early Modern states |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| French Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras (1792–1815) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-Napoleonic states |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||