| Revision as of 08:49, 22 August 2004 editDer Eberswalder (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,394 editsm →External links← Previous edit | Revision as of 16:12, 5 September 2004 edit undoDragonflySixtyseven (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators88,090 editsm sentence structureNext edit → | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| == History == | == History == | ||
| The territory was established in ] in accordance with the ]. It comprised portions of the ]n ] and the ]. The area was put under the control of the ] for 15 years. After this period a ] was held on ], ]: 90.3% of those voting wished to join ] |
The territory was established in ] in accordance with the ]. It comprised portions of the ]n ] and the ]. The area was put under the control of the ] for 15 years. After this period a ] was held on ], ]: 90.3% of those voting wished to join ]. The Nazis called the area "Westmark". | ||
| After ] the Saarland came under French administration. France and Germany |
After ] the Saarland came under French administration. In ], France and Germany offered to establish an independent Saarland, but a second plebiscite rejected this plan by 67.7%. On ], , the ] established that Saarland should be allowed to rejoin Germany, which it did on ], ], | ||
| The Saar competed in ] ] ] ] qualifying, failling after coming second to ] but ahead of ]. | The Saar competed in ] ] ] ] qualifying, failling after coming second to ] but ahead of ]. | ||
Revision as of 16:12, 5 September 2004
| Flag | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Statistics | |
| Capital: | Saarbrücken |
| Area: | 2570 km² |
| Inhabitants: | 1,080,000 (2000) |
| pop. density: | 420 people/km² |
| Homepage: | http://www.saarland.de/ |
| ISO 3166-2: | DE-SL |
| Politics | |
| Minister-President: | Peter Müller (CDU) |
| Ruling party: | CDU |
| Map | |
| File:Bundeslaender germany sl.png | |
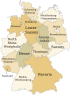
With an area of 2570 km² and 1.08 million inhabitants, Saarland is one of the 16 Bundesländer (federal states) in Germany. The capital is Saarbrücken.
Geography
The state borders France in the south, Luxembourg in the west and Rhineland-Palatinate in the north and the east.
It is named after the Saar River, which is an affluent of the Moselle River and runs through the state from the south to the northwest. Most inhabitants live in a city agglomeration on the French border, surrounding the capital of Saarbrücken.
See also List of places in Saarland.
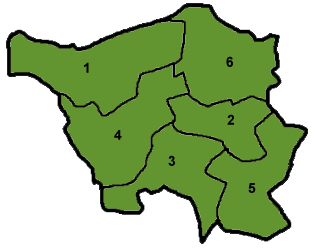
Saarland is divided into six districts:
History
The territory was established in 1920 in accordance with the Treaty of Versailles. It comprised portions of the Prussian Rhine Province and the Rhine Palatinate. The area was put under the control of the League of Nations for 15 years. After this period a plebiscite was held on January 13, 1935: 90.3% of those voting wished to join Germany. The Nazis called the area "Westmark".
After World War II the Saarland came under French administration. In 1954, France and Germany offered to establish an independent Saarland, but a second plebiscite rejected this plan by 67.7%. On October 27, , the Saar Treaty established that Saarland should be allowed to rejoin Germany, which it did on January 1, 1957,
The Saar competed in football's 1954 FIFA World Cup qualifying, failling after coming second to West Germany but ahead of Norway.
From 1920 to 1935, and then from 1947 to 1959, the inhabitants used postage stamps issued specially for the territory; see postage stamps and postal history of the Saar for details.
List of Minister-Presidents of the Saarland
(or equivalent position)
- 1945 - 1946: Hans Neureuther
- 1946 - 1947: Erwin Müller
- 1947 - 1955: Johannes Hoffmann
- 1955 - 1956: Heinrich Welsch
- 1956 - 1957: Hubert Ney
- 1957 - 1959: Egon Reinert
- 1959 - 1979: Franz Josef Röder
- 1979: Werner Klumpp
- 1979 - 1985: Werner Zeyer
- 1985 - 1998: Oskar Lafontaine (SPD)
- 1998 - 1999: Reinhard Klimmt (SPD)
- since 1999: Peter Müller (CDU)
External links
| States of the Federal Republic of Germany | ||
|---|---|---|
| States |
|  |
| City-states | ||
| Former states |
| |