| Revision as of 18:55, 1 February 2015 editZanhe (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers132,020 edits rm unused sources← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:28, 13 February 2015 edit undoADHZ07111989 (talk | contribs)334 editsm Revert vandal from user id: Zanhe , Stupid you Zanhe look at legal international text and the references.Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| <!-- Please expand this article and discuss with me accordingly, since the authentic's text is rare but still exist in historical record. I do build this article at knowledge per myself since the data is fragmented. Thank's --> | |||
| {{Infobox Former Country | {{Infobox Former Country | ||
| |native_name = {{lang|zh-Hant-CN|楊國}} | |native_name = {{lang|zh-Hant-CN|楊國}} | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
| |status = | |status = | ||
| |government_type = Monarchy | |government_type = Monarchy | ||
| |year_start = 12th Century BC <ref name="zhzp.huhuhu.net">http://zhzp.huhuhu.net/news_view.php?id=235, retrieved 26 September 2014</ref><!-- -Here is the text--汉族杨姓出自姬姓:杨姓得姓氏在西周初,已有 3000多年的历史。周成王封其三弟叔虞在唐,今山西闻喜县东北,史称唐叔虞。周康王封唐叔虞次子杼为杨侯,今山西洪洞县东南,始以杨为氏,从此世上有了杨姓。杨国封地,乃是姜戎族中一支以杨树为图腾的古杨人得居地,今汾河两岸仍多杨树。杨侯传至第六氏杨康,随周宣王北征,阵亡无后。周宣王命第五子涧,即尚父,以承其祧,直到周幽王时尚父才被封杨侯。犬戎虏周幽王,西周灭亡。周平王迁都洛阳是为东周。至东周恒王时,杨国被晋武公所灭。这为第一支杨姓,这支杨姓一直活跃于山西洪洞、陕西咸阳和河南洛阳三角地区,杨国灭后,族人经河南、穿河北、涉湖南、越南岭进入广东。当代湘粤海黔以及部分海外的杨姓都把周武王之孙杼奉为杨氏始祖。 | |||
| |year_start = ? | |||
| 唐叔虞之子燮文由唐侯改封为晋侯,传至十一世晋 昭侯时封其叔成师于曲沃,古城在今山西闻喜东,史称曲沃桓公。至周桓王时,公元前678年曲沃武公统一晋国,史称晋武公。晋武公灭杨国,以杨国古地赐予其少子伯侨,伯侨之曾孙羊舌肸食采于杨邑,其后裔以邑名为杨氏。此为第二支杨氏,这支杨氏也有2700年历史。"""Keyword Shang Fu/Jiang Ziya is times during 12th century"""--> | |||
| |year_end = 677 BC<ref name="zhzp.huhuhu.net"/><!--The original text in Chinese is:至周桓王时,公元前678年曲沃武公统一晋国,史称晋武公。晋武公灭杨国,以杨国古地赐予其少子伯侨,伯侨之曾孙羊舌肸食采于杨邑,其后裔以邑名为杨氏--> | |||
| |p1 = | |p1 = | ||
| |s1 = | |s1 = | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
| |s3 = | |s3 = | ||
| |event_start = | |event_start = | ||
| |event_end = Conquered by ]. | |event_end = Conquered by ] and Yang (State) given to Yang Boqiao.<ref name="zhzp.huhuhu.net"/><!--以杨国古地赐予其少子伯侨,伯侨之曾孙羊舌肸食采于杨邑,其后裔以邑名为杨氏--> | ||
| |event1 = | |event1 = | ||
| |date_event1 = | |date_event1 = | ||
| |event2 = | |event2 = | ||
| |date_event2 = | |date_event2 = | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
| |image_map = | |image_map = | ||
| |image_map_caption = | |image_map_caption = | ||
| |capital = | |capital = ] (絳/绛) | ||
| |common_languages = | |common_languages = | ||
| |religion = | |religion = | ||
| |currency = | |currency = | ||
| |leader1 = Shangfu (尚父) | |leader1 = ] (尚父) | ||
| |leader2 = | |leader2 = ] | ||
| |leader3 = | |leader3 = Yang Xiang | ||
| |leader4 = | |leader4 = Yang Tu | ||
| |year_leader1 = | |year_leader1 = | ||
| |year_leader2 = | |year_leader2 = | ||
| |title_leader = | |title_leader = | ||
| |deputy1 = | |||
| |year_deputy1 = | |||
| |title_deputy = | |||
| |stat_year1 = | |||
| |stat_area1 = | |||
| |stat_pop1 = | |||
| |category= | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Yang''' ({{zh|s=杨|t=楊}}) was a state established during the ] dynasty and the ] of ancient China.<ref name="bamboo">'']'', '']''.</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Schirokauer|first=Conrad|last2=Brown|first2=Miranda | '''Yang''' Clan ({{zh|s=杨|t=楊}}), founded by Yang Boqiao at ancient lands of State of Yang although He is come from Royal Manory of Zhou Dynasty (Ji surname) with mixed members of former peoples of State of Yang and new peoples, State of Yang was a state that established during the ] dynasty and the ] of ancient China.<ref name="bamboo">'']'', '']''.</ref><ref name="Schirokauer 2006">{{cite book|last=Schirokauer|first=Conrad|last2=Brown|first2=Miranda | ||
| |year=2006|title=A Brief History of Chinese Civilization|edition=Second|place=Wadsworth|publisher=Thomson Learning}}</ref><ref>''The Discourses of the States (國語) Chapter Discourses of Zheng (鄭語)''</ref><!-- 鄭語: | |year=2006|title=A Brief History of Chinese Civilization|edition=Second|place=Wadsworth|publisher=Thomson Learning}}</ref><ref>''The Discourses of the States (國語) Chapter Discourses of Zheng (鄭語)''</ref><!-- 鄭語: | ||
| 桓公為司徒,甚得周眾與東土之人,問于史伯曰:「王室多故,余懼及焉,其何所可以逃死?」史伯對曰:「王室將卑,戎狄必昌,不可偪也。當成周者,南有荊、蠻、申、呂、應、鄧、陳、蔡、隨、唐;北有衛、燕、狄、鮮虞、潞、洛、泉、徐、蒲;西有虞、虢、晉、隗、霍、楊、魏、芮;東有齊、魯、曹、宋、滕、薛、鄒、莒;是非王之支子母弟甥舅也,則皆蠻、荊、戎、狄之人也。非親則頑,不可入也。其濟、洛、河、潁之間乎!是其子男之國,虢、鄶、為大,虢叔恃勢,鄶仲恃險,是皆有驕侈怠慢之心,而加之以貪冒。君若以周難之故,寄孥與賄焉,不敢不許。周亂而弊,是驕而貪,必將背君,君若以成周之眾,奉辭伐罪,無不克矣。若克二邑,鄔、弊、補、舟、衣、柔、歷、華,君之土也。若前華後河,右洛左濟,主芣、騩而食溱、洧,修典刑以守之,是可以少固。 --> |
桓公為司徒,甚得周眾與東土之人,問于史伯曰:「王室多故,余懼及焉,其何所可以逃死?」史伯對曰:「王室將卑,戎狄必昌,不可偪也。當成周者,南有荊、蠻、申、呂、應、鄧、陳、蔡、隨、唐;北有衛、燕、狄、鮮虞、潞、洛、泉、徐、蒲;西有虞、虢、晉、隗、霍、楊、魏、芮;東有齊、魯、曹、宋、滕、薛、鄒、莒;是非王之支子母弟甥舅也,則皆蠻、荊、戎、狄之人也。非親則頑,不可入也。其濟、洛、河、潁之間乎!是其子男之國,虢、鄶、為大,虢叔恃勢,鄶仲恃險,是皆有驕侈怠慢之心,而加之以貪冒。君若以周難之故,寄孥與賄焉,不敢不許。周亂而弊,是驕而貪,必將背君,君若以成周之眾,奉辭伐罪,無不克矣。若克二邑,鄔、弊、補、舟、衣、柔、歷、華,君之土也。若前華後河,右洛左濟,主芣、騩而食溱、洧,修典刑以守之,是可以少固。 --> | ||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| ⚫ | King Wu of Zhou granted ] ({{zh|c=唐叔虞|p=Táng Shū Yú}}), a state named Tang. He was the son of ] and the younger brother of ]. The State of Tang would later be renamed ] by Shu Yu's son and successor, Xie.<ref name="han">{{cite book |title=Annotated Shiji |author=Han, Zhaoqi |year=2010 |publisher= Zhonghua Book Company |isbn=978-7-101-07272-3 |language=Chinese |chapter=House of Jin |pages=3093–3094}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | The Yang state was conquered by the Jin state during the reign of ], and ancient lands of the Yang state was given to one of his sons named Boqiao at 13th years old. A clan named Yang (楊) was erected which become a surname in later time.<ref name="zhzp.huhuhu.net"/><ref name="Yang Family History">{{cite web|title=Yang Family History|url=http://www.ancestry.com/name-origin?surname=yang|accessdate=28 March 2014}}</ref> | ||
| ==Legacy== | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| The Yang clan was founded by Boqiao (later become Yang Boqiao, with Yang as usually duchy courtesy name) son of Duke Wu of Jin in the Springs and Autumns Period of the Ji (姬) surname, the surname of the royal family during the Zhou dynasty (c. 8th to 5th Centuries BC) who was enfeoffed a vast land, the Yang kingdom, with it's central in at ancient's Shaanxi.<ref name="han"/><ref name="Yang Family History"/> | |||
| ==Trivia== | |||
| ⚫ | King Wu of Zhou granted ] a state named Tang. He was the son of ] and the younger brother of ]. The State of Tang would later be renamed ] by Shu Yu's son and successor, Xie.<ref name="han">{{cite book |title=Annotated Shiji |author=Han, Zhaoqi |year=2010 |publisher= Zhonghua Book Company |isbn=978-7-101-07272-3 |language=Chinese |chapter=House of Jin |pages=3093–3094}}</ref> | ||
| Boqiao original named Ji Boqiao, later become Yang Boqiao with adoption of duchy fief name replaced the Ji, also known as only Boqiao at modern book during stage named used by later historian. | |||
| ⚫ | The Yang state was conquered by the Jin state during the reign of ], and ancient lands of the Yang state was given to one of his sons named Boqiao at 13th years old. A clan named Yang (楊) was erected which become a surname in later time.<ref>{{cite web|title=Yang Family History|url=http://www.ancestry.com/name-origin?surname=yang|accessdate=28 March 2014}} |
||
| Yang Kingdom has a secret policy since some task already committed to the Kingdom by Zhou Dynasty King, and makes the Yang Surname flourishing around the time. During study of the Annals and text Yang Kingdom has a unique government layer that virtually a Ducal rules and preserved the Zhou Dynasty king along the era.<ref>''尊賢, scroll number 29''</ref><!--楊因見趙簡主曰:「臣居鄉三逐,事君五去,聞君好士,故走來見。」簡主聞之,絕食而歎,跽而行,左右進諫曰:「居鄉三逐,是不容眾也;事君五去,是不忠上也。今君有士見過人矣。」簡主曰:「子不知也。夫美女者,醜婦之仇也;盛德之士,亂世所疏也;正直之行,邪枉所憎也。」遂出見之,因授以為相,而國大治。由是觀之,遠近之人,不可以不察也。--> | |||
| Another Kingdom also blends with the Boqiao's Yang Kingdom. Particularly at Qi, Jing, Qin, Chu. Also Zhao, Wei, and Yan. Since domination of ] and Jin during Spring and Autumn era. Which makes the Boqiao's Yang Kingdom as a stelle hub of ].<ref name="Schirokauer 2006"/><ref>''正諫, part 3''</ref><!--正諫:楚莊王立為君,三年不聽朝,乃令於國曰:「寡人惡為人臣而遽諫其君者,今寡人有國家,立社稷,有諫則死無赦。」蘇從曰:「處君之高爵,食君之厚祿,愛其死而不諫其君,則非忠臣也。」乃入諫。莊王立鼓鐘之間,左伏楊姬,右擁越姬,左裯衽,右朝服,曰:「吾鼓鐘之不暇,何諫之聽!」蘇從曰:「臣聞之,好道者多資,好樂者多迷,好道者多糧,好樂者多亡;荊國亡無日矣,死臣敢以告王。」王曰善。左執蘇從手,右抽陰刃,刎鐘鼓之懸,明日授蘇從為相。--> | |||
| Yang She (Goat Tongue) and another Yang in character blended with Boqiao's Yang Kingdom (楊), as also be the phonetic translation of other Chinese surnames. These include 陽/阳, the Chinese character for "sun"; the very rare Chinese family name 羊, the Chinese character for "goat" or "sheep"; or another character pronounced "Yang", regardless of tone, such as 仰, 養, and 揚.<ref name="Yang Family History"/><ref>''Guo Yu (國語) Chapter 晉語八 Page 90''</ref> <!-- 晉語八:叔魚生,其母視之,曰:「是虎目而豕喙,鳶肩而牛腹,谿壑可盈,是不可饜也,必以賄死。」遂不視。楊食我生,叔向之母聞之,往,及堂,聞其號也,乃還,曰:「其聲,豺狼之聲,終滅羊舌氏之宗者,必是子也?」--> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *{{citation | |||
| |last=Wu | |||
| |first=K. C. | |||
| |year=1982 | |||
| |title=The Chinese Heritage | |||
| |place=New York | |||
| |publisher=Crown Publishers | |||
| |isbn=0-517-54475-X | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{citation | |||
| |last=Shaughnessy | |||
| |first=Edward L. | |||
| |year=1999 | |||
| |editor-last=Loewe | |||
| |editor-first=Michael | |||
| |editor2-last=Shaughnessy | |||
| |editor2-first=Edward L. | |||
| |chapter=Western Zhou History | |||
| |pages=292–351 | |||
| |title=The Cambridge History of Ancient China | |||
| |isbn=978-0-521-47030-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{citation | |||
| |last=Schirokauer | |||
| |first=Conrad | |||
| |last2=Brown | |||
| |first2=Miranda | |||
| |year=2006 | |||
| |title=A Brief History of Chinese Civilization | |||
| |edition=Second | |||
| |place=Wadsworth | |||
| |publisher=Thomson Learning | |||
| }} | |||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Zhou Dynasty topics}} | {{Zhou Dynasty topics}} | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 13 February 2015
| State of Yang楊國 | |
|---|---|
| 12th Century BC –677 BC | |
| Capital | Jiang (絳/绛) |
| Government | Monarchy |
| History | |
| • Established | 12th Century BC |
| • Conquered by Jin and Yang (State) given to Yang Boqiao. | 677 BC |
Yang Clan (simplified Chinese: 杨; traditional Chinese: 楊), founded by Yang Boqiao at ancient lands of State of Yang although He is come from Royal Manory of Zhou Dynasty (Ji surname) with mixed members of former peoples of State of Yang and new peoples, State of Yang was a state that established during the Western Zhou dynasty and the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China.
History
King Wu of Zhou granted Shu Yu of Tang (Chinese: 唐叔虞; pinyin: Táng Shū Yú), a state named Tang. He was the son of King Wu of Zhou and the younger brother of King Cheng of Zhou. The State of Tang would later be renamed Jin by Shu Yu's son and successor, Xie.
The Yang state was conquered by the Jin state during the reign of Duke Wu of Jin, and ancient lands of the Yang state was given to one of his sons named Boqiao at 13th years old. A clan named Yang (楊) was erected which become a surname in later time.
Legacy
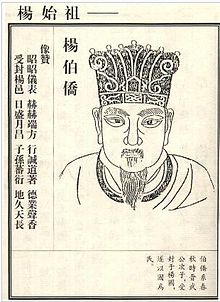
The Yang clan was founded by Boqiao (later become Yang Boqiao, with Yang as usually duchy courtesy name) son of Duke Wu of Jin in the Springs and Autumns Period of the Ji (姬) surname, the surname of the royal family during the Zhou dynasty (c. 8th to 5th Centuries BC) who was enfeoffed a vast land, the Yang kingdom, with it's central in at ancient's Shaanxi.
Trivia
Boqiao original named Ji Boqiao, later become Yang Boqiao with adoption of duchy fief name replaced the Ji, also known as only Boqiao at modern book during stage named used by later historian.
Yang Kingdom has a secret policy since some task already committed to the Kingdom by Zhou Dynasty King, and makes the Yang Surname flourishing around the time. During study of the Annals and text Yang Kingdom has a unique government layer that virtually a Ducal rules and preserved the Zhou Dynasty king along the era.
Another Kingdom also blends with the Boqiao's Yang Kingdom. Particularly at Qi, Jing, Qin, Chu. Also Zhao, Wei, and Yan. Since domination of Quwo and Jin during Spring and Autumn era. Which makes the Boqiao's Yang Kingdom as a stelle hub of Yang Surname.
Yang She (Goat Tongue) and another Yang in character blended with Boqiao's Yang Kingdom (楊), as also be the phonetic translation of other Chinese surnames. These include 陽/阳, the Chinese character for "sun"; the very rare Chinese family name 羊, the Chinese character for "goat" or "sheep"; or another character pronounced "Yang", regardless of tone, such as 仰, 養, and 揚.
References
- Yang Surname
- Spring and Autumn Annals
- Wu, K. C. (1982), The Chinese Heritage, New York: Crown Publishers, ISBN 0-517-54475-X
- Shaughnessy, Edward L. (1999), "Western Zhou History", in Loewe, Michael; Shaughnessy, Edward L. (eds.), The Cambridge History of Ancient China, pp. 292–351, ISBN 978-0-521-47030-8
- Schirokauer, Conrad; Brown, Miranda (2006), A Brief History of Chinese Civilization (Second ed.), Wadsworth: Thomson Learning
- ^ http://zhzp.huhuhu.net/news_view.php?id=235, retrieved 26 September 2014
- Annals of Wei, Bamboo Annals.
- ^ Schirokauer, Conrad; Brown, Miranda (2006). A Brief History of Chinese Civilization (Second ed.). Wadsworth: Thomson Learning.
- The Discourses of the States (國語) Chapter Discourses of Zheng (鄭語)
- ^ Han, Zhaoqi (2010). "House of Jin". Annotated Shiji (in Chinese). Zhonghua Book Company. pp. 3093–3094. ISBN 978-7-101-07272-3.
- ^ "Yang Family History". Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- 尊賢, scroll number 29
- 正諫, part 3
- Guo Yu (國語) Chapter 晉語八 Page 90
External links
| Ancient Chinese states | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou dynasty |
| ||||
| Warring States |
| ||||