| Revision as of 02:20, 20 April 2015 editMalik Shabazz (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers106,163 edits →Intro: don't "subst" improvement templates← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:59, 20 April 2015 edit undoEntropyandvodka (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,460 edits Added mention of contemporary challenges to Israel stemming from a united monarchy in the intro section. Corrected religion listed in top table.Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{About|the northern kingdom of Israel during the period of divided monarchy|the |
{{About|the northern kingdom of Israel during the biblical period of divided monarchy|the biblical united monarchy|Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy)|other uses|Kingdom of Israel (disambiguation){{!}}Kingdom of Israel}} | ||
| {{Religious text primary|date=April 2015}} | {{Religious text primary|date=April 2015}} | ||
| {{Infobox former country | {{Infobox former country | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
| |capital = ] <small>(930 BCE)</small><br />] <small>(930–909)</small><br />] <small>(909–880)</small><br />] <small>(880–720)</small> | |capital = ] <small>(930 BCE)</small><br />] <small>(930–909)</small><br />] <small>(909–880)</small><br />] <small>(880–720)</small> | ||
| |common_languages = ] | |common_languages = ] | ||
| |religion = ]<br>]<br>]<br>]<ref>https://www.biblegateway.com/passage/?search=Ezekiel+8</ref><ref>http://biblehub.com/1_kings/11-5.htm</ref><ref>http://biblehub.com/2_kings/23-13.htm</ref><ref>http://biblehub.com/jeremiah/11-13.htm</ref><ref>Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman, Free Press, New York, 2001, pages 240-243., ISBN 0-684-86912-8</ref> | |||
| |religion = ]<br />]ism <small>(repressed)</small> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{History of Israel}} | {{History of Israel}} | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| Historians often refer to ancient Israel as the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria to differentiate it from the Southern ]. | Historians often refer to ancient Israel as the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria to differentiate it from the Southern ]. | ||
| Modern scholarship, including ] and ], has challenged the biblical account that the northern kingdom of Israel broke off from a united monarchy with the southern kingdom of Judah, suggesting instead that the northern civilization of Israel developed independently of Judah, a comparatively small and rural area, and that it first reached the political, economic, military and architectural sophistication of a kingdom under the Omride dynasty around 884 BCE. <ref name=Kuhrtp438>{{cite book|last=Kuhrt|first=Amiele|title=The Ancient Near East|year=1995|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-0415167628|page=438}}</ref><ref>Finkelstein, Israel, and Silberman, Neil Asher, ''The Bible Unearthed : Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts'', pages 169-195, Simon & Schuster, 2002. ISBN 0-684-86912-8</ref><ref>http://www.bibleinterp.com/articles/2014/07/wri388001.shtml</ref> | |||
| ==Name== | ==Name== | ||
Revision as of 20:59, 20 April 2015
This article is about the northern kingdom of Israel during the biblical period of divided monarchy. For the biblical united monarchy, see Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy). For other uses, see Kingdom of Israel.| This article uses texts from within a religion or faith system without referring to secondary sources that critically analyze them. Please help improve this article. (April 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Kingdom of Israel | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 930 BCE–720 BCE | |||||||||
 Map of the region in the 9th century BC Map of the region in the 9th century BC | |||||||||
| Capital | Shechem (930 BCE) Penuel (930–909) Tirzah (909–880) Samaria (880–720) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Hebrew | ||||||||
| Religion | Monoaltristic Yahwism Canaanite polytheism Mesopotamian polytheism Folk religion | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Historical era | Classical Antiquity | ||||||||
| • Independence (from United Monarchy) | 930 BCE | ||||||||
| • Destruction (by Assyria) | 720 BCE | ||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | IL | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Part of a series on the | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Israel | ||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||
| Early historyPrehistoric Levant | ||||||||||||||
Ancient Israel and Judah
|
||||||||||||||
Second Temple period
|
||||||||||||||
Late Antiquity and Middle Ages
|
||||||||||||||
|
Modern historyModern history (1517–1948)
State of Israel (1948–present) |
||||||||||||||
| By topic | ||||||||||||||
| Related | ||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||
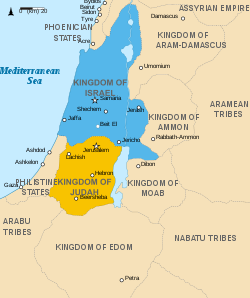
The Kingdom of Israel (Hebrew: מַמְלֶכֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל, Modern: Mamlekhet Yisra'el, Tiberian: Mamléḵeṯ Yiśrāʼēl) was, according to the Bible, one of two successor states to the former United Monarchy (also often called the 'Kingdom of Israel'). It existed roughly from the 930s BCE until about the 720s BCE, when the kingdom was conquered by the Assyrian Empire. The major cities of the kingdom were Shechem, Tirzah, and Shomron (Samaria).
Historians often refer to ancient Israel as the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria to differentiate it from the Southern Kingdom of Judah.
Modern scholarship, including textual criticism and archaeology, has challenged the biblical account that the northern kingdom of Israel broke off from a united monarchy with the southern kingdom of Judah, suggesting instead that the northern civilization of Israel developed independently of Judah, a comparatively small and rural area, and that it first reached the political, economic, military and architectural sophistication of a kingdom under the Omride dynasty around 884 BCE.
Name
In the Hebrew Bible, the Kingdom of Israel has been referred to as "House of Joseph". It is also frequently referenced (particularly in poetry) as Ephraim, the tribe whose territory housed the capital cities and the royal families. It has also been referred to as "Israel in Samaria".
Territory
The territory of the Kingdom of Israel comprised the territories of the tribes of Zebulun, Issachar, Asher, Naphtali, Dan, Manasseh, Ephraim, Reuben and Gad.
Its capital was Samaria according to the Book of Isaiah.
Biblical narrative
United Monarchy
Main article: Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy)The united Kingdom of Israel is said to have existed from about 1030 to about 930 BCE. It was a union of all the twelve Israelite tribes living in the area that presently approximates modern Israel and the Palestinian territories.
Division
After the death of Solomon in about 931 BCE, all the Israelite tribes except for Judah and Benjamin (called the ten northern tribes) refused to accept Rehoboam, the son and successor of Solomon, as their king. The rebellion against Rehoboam arose after he refused to lighten the burden of taxation and services that his father had imposed on his subjects.
Jeroboam, who was not of the Davidic line, was sent for from Egypt by the malcontents. The Tribe of Ephraim and all Israel raised the old cry, "Every man to his tents, O Israel". Rehoboam fled to Jerusalem, and in 930 BCE (some date it in 920 BCE), Jeroboam was proclaimed king over all Israel at Shechem. After the revolt at Shechem at first only the tribe of Judah remained loyal to the house of David. But very soon after the tribe of Benjamin joined Judah. The northern kingdom continued to be called the Kingdom of Israel or Israel, while the southern kingdom was called the kingdom of Judah. 2 Chronicles 15:9 also says that members of the tribes of Ephraim, Manasseh and Simeon fled to Judah during the reign of Asa of Judah.
Both Eusebius and Josephus place the division in 997 BCE - lunar dates of Venus can be mistaken as 64 years later (c. 930 BCE). (Crossing of sun over Mars as Tamuz would be 10 July 997 BCE.)
Shechem was the first capital of the Kingdom of Israel. Afterwards it was Tirzah. King Omri built his capital in Samaria (1 Kings 16:24), which continued as such until the destruction of the Kingdom by the Assyrians (2 Kings 17:5). During the three-year siege of Samaria by the Assyrians, Shalmaneser V died and was succeeded by Sargon II of Assyria, who himself records the capture of that city thus: "Samaria I looked at, I captured; 27,280 men who dwelt in it I carried away" into Assyria. Thus, around 720 BCE, after two centuries, the kingdom of the ten tribes came to an end.
Today, among archaeologists, Samaria is one of the most universally accepted archaeological sites from the biblical period At around 850 BCE, the Mesha Stele, written in Old Hebrew alphabet, records a victory of King Mesha of Moab against king Omri of Israel and his son Ahab.
Relations between the kingdoms
For the first sixty years, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over the northern kingdom, and there was perpetual war between them. For the following eighty years, there was no open war between them, and, for the most part, they were in friendly alliance, co-operating against their common enemies, especially against Damascus.
The conflict between Israel and Judah was resolved when Jehoshaphat, King of Judah, allied himself with the house of Ahab through marriage. Later, Jehosophat's son and successor, Jehoram of Judah, married Ahab's daughter Athaliah, cementing the alliance. However, the sons of Ahab were slaughtered by Jehu following his coup d'état around 840 BCE.
Destruction of the kingdom
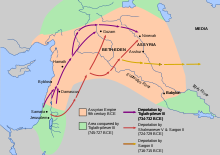
In c. 732 BCE, Pekah of Israel allied with Rezin, king of Aram, threatened Jerusalem, and Ahaz, king of Judah, appealed to Tiglath-Pileser III, the king of Assyria, for help. After Ahaz paid tribute to Tiglath-Pileser Tiglath-Pileser sacked Damascus and Israel, annexing Aram and territory of the tribes of Reuben, Gad and Manasseh in Gilead including the desert outposts of Jetur, Naphish and Nodab. People from these tribes including the Reubenite leader, were taken captive and resettled in the region of the Khabur River system. Tiglath-Pilesar also captured the territory of Naphtali and the city of Janoah in Ephraim and an Assyrian governor was placed over the region of Naphtali. According to 2 Kings 16:9 and 15:29, the population of Aram and the annexed part of Israel was deported to Assyria.
Israel continued to exist within the reduced territory as an independent kingdom until around 720 BCE, when it was again invaded by Assyria and the rest of the population deported. The Bible relates that the population of Israel was exiled, becoming known as The Ten Lost Tribes, leaving only the Tribe of Judah, the Tribe of Simeon (that was "absorbed" into Judah), the Tribe of Benjamin and the people of the Tribe of Levi who lived among them of the original Israelites nation in the southern Kingdom of Judah. However, in their book The Bible Unearthed, authors Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman estimate that only a fifth of the population (about 40,000) were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under Tiglath-Pileser III and Sargon II. Many also fled south to Jerusalem, which appears to have expanded in size fivefold during this period, requiring a new wall to be built, and a new source of water (Siloam) to be provided by King Hezekiah.
The remainder of the northern kingdom was conquered by Sargon II, who captured the capital city Samaria in the territory of Ephraim. He took 27,290 people captive from the city of Samaria resettling some with the Israelites in the Khabur region and the rest in the land of the Medes thus establishing Hebrew communities in Ecbatana and Rages.
The Book of Tobit additionally records that Sargon had taken other captives from the northern kingdom to the Assyrian capital of Nineveh, in particular Tobit from the town of Thisbe in Naphtali.
In medieval Rabbinic fable the concept of the ten tribes who were taken away from the House of David (who continued the rule of the southern kingdom of Judah) becomes confounded with accounts of the Assyrian deportations leading to the myth of the "Ten Lost Tribes". The recorded history differs from this fable: No record exists of the Assyrians having exiled people from Dan, Asher, Issachar, Zebulun or western Manasseh. Descriptions of the deportation of people from Reuben, Gad, Manasseh in Gilead, Ephraim and Naphtali indicate that only a portion of these tribes were deported and the places to which they were deported are known locations given in the accounts. The deported communities are mentioned as still existing at the time of the composition of the books of Kings and Chronicles and did not disappear by assimilation. 2 Chronicles 30:1-11 explicitly mentions northern Israelites who had been spared by the Assyrians in particular people of Ephraim, Manasseh, Asher, Issachar and Zebulun and how members of the latter three returned to worship at the Temple in Jerusalem during the reign of Hezekiah.
Kingdom of Judah
Main article: Kingdom of JudahThe Kingdom of Judah continued to exist as an independent state until 586 BCE, when it was conquered by the Neo-Babylonian Empire.
Culture
Religion
The religious climate of the Kingdom of Israel appears to have followed two major trends. The first, that of YHWH, and the second the cult of Baal as detailed in the Hebrew Bible, and in the Baal cycle discovered at Ugarit.
It is recorded in the Hebrew Bible that Jeroboam built two places of worship, one at Bethel and one at far northern Dan, to be an alternative to the Temple in Jerusalem. He did not want the people of his kingdom to have religious ties to Jerusalem, the capital city of the rival Kingdom of Judah. He erected golden bulls at the entrance to the Temples to represent the national god. The Hebrew Bible, written from the perspective of scribes in Jerusalem, referred to these acts as the way of Jeroboam or the errors of Jeroboam.(1 Kings 12:26–29)
Ahab allowed the cult worship of Baal to become an acceptable religion of the kingdom. His wife Jezebel was a devotee to Baal worship. (1 Kings 16:31)
Prophets
- Elijah, opponent of religious inventions under Ahab and Jezebel
- Elisha, chosen successor of Elijah
- Amos
- Hosea
- Jonah
- Nahum
Royal Houses

| Albright | Thiele | Galil | Kitchen | Common/Biblical name | Regnal Name and style | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The House of Jeroboam | ||||||
| 922–901 | 931–910 | 931–909 | 931–911 | Jeroboam I | ירבעם בן-נבט מלך ישראל Yerav’am ben Nevat, Melekh Yisra’el |
Led the rebellion and divided the kingdoms. Reigned in Israel (Northern Kingdom) for 22 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 901–900 | 910–909 | 909–908 | 911–910 | Nadab | נדב בן-ירבעם מלך ישראל Nadav ben Yerav’am, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned in Israel for 2 years. Death: Killed by Baasha, son of Ahijah of the house of Issachar, along with his whole family. |
The House of Baasha | ||||||
| 900–877 | 909–886 | 908–885 | 910–887 | Baasha | בעשא בן-אחיה מלך ישראל Ba’asha ben Achiyah, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Tirzah for 24 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 877–876 | 886–885 | 885–884 | 887–886 | Elah | אלה בן-בעשא מלך ישראל ’Elah ben Ba’asha, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Tirzah for 2 years. Death: Zimri, one of his officials, got him drunk and killed him at his house in Azra. |
The House of Zimri | ||||||
| 876 | 885 | 884 | 886 | Zimri | זמרי מלך ישראל Zimri, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Tirzah for 7 days. Death: He set his palace on fire when Omri and all the Israelites with him withdrew from Gibbethon and laid siege to Tirzah. |
The House of Omri | ||||||
| 876–869 | 885–874 | 884–873 | 886–875 | Omri | עמרי מלך ישראל ’Omri, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 12 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 869–850 | 874–853 | 873–852 | 875–853 | Ahab | אחאב בן-עמרי מלך ישראל Ah’av ben ’Omri, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 22 years. Death: Shot by an archer during the battle at Ramoth Gilead. He died upon his arrival at Samaria. |
| 850–849 | 853–852 | 852–851 | 853–852 | Ahaziah | אחזיהו בן-אחאב מלך ישראל ’Ahazyahu ben 'Ah’av, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 2 years. Death: He fell through the lattice of his upper room and injured himself. Elijah the prophet told him he would never leave his bed and would die on it. |
| 849–842 | 852–841 | 851–842 | 852–841 | Joram | יורם בן-אחאב מלך ישראל Yehoram ben ’Ah’av, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 12 years. Death: Killed by Jehu, the next king of Israel, |
The House of Jehu | ||||||
| 842–815 | 841–814 | 842–815 | 841–814 | Jehu | יהוא בן-נמשי מלך ישראל Yehu ben Nimshi, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 28 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 815–801 | 814–798 | 819–804 | 814–806 | Jehoahaz | יהואחז בן-יהוא מלך ישראל Yeho’ahaz ben Yehu, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 17 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 801–786 | 798–782 | 805–790 | 806–791 | Jehoash (Joash) |
יואש בן-יואחז מלך ישראל Yeho’ash ben Yeho’ahaz, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 16 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 786–746 | 782–753 | 790–750 | 791–750 | Jeroboam II | ירבעם בן-יואש מלך ישראל Yerav’am ben Yeho’ash, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 41 years. Death: Natural Causes. The Book of Jonah or Jonah's journey to Nineveh (when he was swallowed by a whale or fish) happened at that time. |
| 746 | 753 | 750–749 | 750 | Zachariah | זכריה בן-ירבעם מלך ישראל Zekharyah ben Yerav’am, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 6 months. Death: Shallum son of Jabesh killed him in front of the people and succeeded as king. |
The House of Shallum | ||||||
| 745 | 752 | 749 | 749 | Shallum | שלם בן-יבש מלך ישראל Shallum ben Yavesh, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 1 month. Death: Menahem son of Gadi attacked Shallum and assassinated him. |
The House of Menahem | ||||||
| 745–738 | 752–742 | 749–738 | 749–739 | Menahem | מנחם בן-גדי מלך ישראל Menahem ben Gadi, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 10 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 738–737 | 742–740 | 738–736 | 739–737 | Pekahiah | פקחיה בן-מנחם מלך ישראל Pekahyah ben Menahem, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 2 years. Death: Pekah son of Remaliah, one of the chief officers, took 50 men with him and assassinated the king in his palace at Samaria. |
The House of Pekah | ||||||
| 737–732 | 740–732 | 736–732 | 737–732 | Pekah | פקח בן-רמליהו מלך ישראל Pekah ben Remalyahu, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 20 years. Death: Hoshea son of Elah conspired against him and assassinated him. |
The House of Hoshea | ||||||
| 732–722 | 732–722 | 732–722 | 732–722 | Hoshea | הושע בן-אלה מלך ישראל Hoshe’a ben ’Elah, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 9 years. Death: King Shalmanser attacked and captured Samaria. He charged Hoshea of treason and he put him in prison, then, he deported the Israelites to Assyria. |
List of proposed Assyrian references to Kingdom of Israel (Samaria)
The table below lists all the historical references to Samaria in Assyrian records.
| Assyrian King | Inscription | Year | Transliteration | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shalmaneser III | Kurkh Monoliths | 853 BCE | KUR sir-'i-la-a-a | "Israel" |
| Shalmaneser III | Black Obelisk, Calah Fragment, Kurba'il Stone, Ashur Stone | 841 BCE | mar Hu-um-ri-i | "-Humrite" |
| Adad-nirari III | Tell al-Rimah Stela | 803 BCE | KUR Sa-me-ri-na-a-a | "land of Samaria" |
| Adad-nirari III | Nimrud Slab | 803 BCE | KUR <Bit>-Hu-um-ri-i | "the 'land of Bit-Humri" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | Layard 45b+ III R 9,1 | 740 BCE | ||
| Tiglath-Pileser III | lran Stela | 739–738 BCE | KUR sa-m-ri-i-na-a- | "land of Samaria" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | Layard 50a + 50b + 67a | 738–737 BCE | URU sa-me-ri-na-a-a | "city of Sarnaria" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | Layard 66 | 732–731 BCE | URU Sa-me-ri-na | "city of Sarnaria") |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | III R 10,2 | 731 BCE | KUR E Hu-um-ri-a | "land of Bit-Humri" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | ND 4301 + 4305 | 730 BCE | KUR E Hu-um-ri-a | "land of Bit-Humri" |
| Shalmaneser V | Babylonian Chronicle ABC1 | 725 BCE | URU Sa-ma/ba-ra-'-in | "city of Sarnaria" |
| Sargon II | Nimrud Prism, Great Summary Inscription | 720 BCE | URU Sa-me-ri-na | "city of Samerina" |
| Sargon II | Palace Door, Small Summary Inscription, Cylinder Inscription, Bull Inscription | 720 BCE | KUR Bit-Hu-um-ri-a | "land of Bit-Humri" |
See also
Template:Misplaced Pages books
References
- https://www.biblegateway.com/passage/?search=Ezekiel+8
- http://biblehub.com/1_kings/11-5.htm
- http://biblehub.com/2_kings/23-13.htm
- http://biblehub.com/jeremiah/11-13.htm
- Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman, Free Press, New York, 2001, pages 240-243., ISBN 0-684-86912-8
- Kuhrt, Amiele (1995). The Ancient Near East. Routledge. p. 438. ISBN 978-0415167628.
- Finkelstein, Israel, and Silberman, Neil Asher, The Bible Unearthed : Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts, pages 169-195, Simon & Schuster, 2002. ISBN 0-684-86912-8
- http://www.bibleinterp.com/articles/2014/07/wri388001.shtml
- *Zechariah 10:6
- *II Samuel 2:10
- 1 Kings 22:51 and many subsequent passages
- 1 Kings 12:17–22
- 1 Kings 12:4, 1 Kings 12:14
- 1 Kings 12:2–3
- 2Samuel 20:1
- 1 Kings 12:1–18
- 2 Chronicles 10
- 2 Chronicles 15:9
- 1 Kings 12:25
- 1 Kings 14:17
- See Yohanan Aharoni, et al., The Macmillan Bible Atlas, Macmillan Publishing: New York, 1993, p. 94.; and Amihai Mazar, The Archaeology of the Land of the Bible: 10,000 – 586 B.C.E, New York: Doubleday, 1992, p. 404, see Pp. 406-410 for discussion of archaeological significance of Shomron (Samaria) under Omride Dynasty.
- 2 Kings 3
- 2 Kings 16:7–9
- Lester L. Grabbe, Ancient Israel: What Do We Know and How Do We Know It? (New York: T&T Clark, 2007): 134
- Finkelstein & Silberman 2001, The Bible Unearthed p. 221.
- 2 Chronicles 30:1–18
- ^ http://teldan.wordpress.com/israelite-temple/
- Considered to be a contemporary of the Assyrian King Shalmaneser III (858–824) to whom he paid tribute. This is based on an inscription on The Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III showing "Yaua" son of Omri paying tribute, dated to 841 BCE.
- Paid tribute to the Assyrian King Shalmaneser V (727–722 BCE) but rebelled in 725 BCE. Shalmaneser besieged the capital, Samaria, but died shortly before the fall of the city. His brother Sargon II (722–705 BCE) completed the siege with success in 722. Some of the population of the Northern Kingdom was exiled to other parts of the Assyrian Empire and new population groups were resettled in the new Assyrian province of Samaria. A small group of people fled south to take refuge in Judah.
- * Kelle, Brad (2002), "What's in a Name? Neo-Assyrian Designations for the Northern Kingdom and Their Implications for Israelite History and Biblical Interpretation", Journal of Biblical Literature, 121 (4): 639–646
External links
- About Israel - The Information Center About Israel
- Biblical History The Jewish History Resource Center - Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- Complete Bible Genealogy A synchronized chart of the kings of Israel and Judah
| The Biblical and historical Israelites | |
|---|---|
| Rulers of Israel and Judah | |
|---|---|
| Israel (united monarchy) | |
| Israel (northern kingdom) | |
| Judah (southern kingdom) | |
| Judea (Hasmonean dynasty) | |
| See also | |
Categories: