| Revision as of 20:23, 3 June 2015 editDN-boards1 (talk | contribs)1,949 edits Added note on its orbit.← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:04, 4 June 2015 edit undoArtman40 (talk | contribs)2,039 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| | density = (unknown) | | density = (unknown) | ||
| | single_temperature = 33–55 ] | | single_temperature = 33–55 ] | ||
| | rotation = Chaotic <ref>http://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-s-hubble-finds-pluto-s-moons-tumbling-in-absolute-chaos</ref> | |||
| | rotation = (unknown) | |||
| | axial_tilt = (unknown) | | axial_tilt = (unknown) | ||
| | albedo = 0.04–0.35 (assumed)<ref name="Stern06b" /> | | albedo = 0.04–0.35 (assumed)<ref name="Stern06b" /> | ||
Revision as of 03:04, 4 June 2015
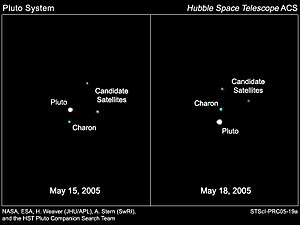 Discovery images of Nix (and Hydra) Discovery images of Nix (and Hydra) | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Hubble Space Telescope Pluto Companion Search Team |
| Discovery date | June 2005 |
| Designations | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈnɪks/ |
| Named after | Nyx |
| Alternative names | (134340) Pluto II |
| Adjectives | Nictian |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Semi-major axis | 48708 km |
| Eccentricity | 0.0030 |
| Orbital period (sidereal) | 24.856±0.001 d |
| Inclination | 0.195° |
| Satellite of | Pluto |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean radius | 23–68 km |
| Mass | 5×10 to 2×10 kg |
| Mean density | (unknown) |
| Synodic rotation period | Chaotic |
| Axial tilt | (unknown) |
| Albedo | 0.04–0.35 (assumed) |
| Temperature | 33–55 K |
| Apparent magnitude | 23.38–23.7 (measured) |
Nix is a natural satellite of Pluto. It was discovered along with Hydra in June 2005, and is to be imaged along with Pluto and Charon by the New Horizons mission in July 2015. Of the four small Plutonian moons, New Horizons is expected to get the best pictures of Nix.
Discovery
Nix was found by the Hubble Space Telescope Pluto Companion Search Team, composed of Hal A. Weaver, S. Alan Stern, Max J. Mutchler, Andrew J. Steffl, Marc W. Buie, William J. Merline, John R. Spencer, Eliot F. Young, and Leslie A. Young. The discovery images were taken on May 15, 2005, and May 18, 2005; Nix and Hydra were independently discovered by Max J. Mutchler on June 15, 2005, and Andrew J. Steffl on August 15, 2005. The discoveries were announced on October 31, 2005, after confirmation by precoveries from 2002. They were provisionally designated S/2005 P 1 (Hydra) and S/2005 P 2 (Nix).
Orbit

Nix follows a circular orbit in the same plane as Charon. Its orbital period of 24.9 days is close to a 1:4 orbital resonance with Charon, but the timing discrepancy is 2.7%, which suggests that there is no active resonance. A hypothesis explaining such a near-resonance is that it originated before the outward migration of Charon following the formation of all five known moons, and is maintained by the periodic local fluctuation of 9% in the Pluto–Charon gravitational field strength.
As it orbits, it flips up and down on its axis, with the north pole becoming the south pole and vice versa, periodically.
Physical characteristics
Although its size has not been directly measured, Nix has been calculated to have a diameter of between 46 and 137 kilometers (29 and 85 mi). To meet the lower end of the range, its geometric albedo would have to be similar to Charon's 35%. For it to be the at the higher end of the range, it would have to have a reflectivity of 4%, like the darkest Kuiper belt objects. Nix is slightly fainter than Hydra, suggesting that it is somewhat smaller in size. In the discovery image, Nix is 6,300 times fainter than Pluto.
Early research appeared to show that Nix was reddish like Pluto and unlike the other moons, but more recent reports have been that it is grey like the remaining satellites.
Name
The formal name "Nix", from the Greek goddess of darkness and night and mother of Charon, was announced on June 21, 2006 on IAU Circular 8723, where the designation Pluto II is also given. Together with Hydra (Pluto's third moon) the initials are those of the unmanned New Horizons spaceprobe. The initial proposal was to use the classical spelling Nyx, but to avoid confusion with the asteroid 3908 Nyx the spelling was changed to Nix. The USGS Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature states that Nix is the "Egyptian spelling", while Jürgen Blunck explains it as the "Spanish translation" of the Greek name.
See also
References
- Jennifer Blue (2009-11-09). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". IAU Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). Retrieved 2010-08-30.
- ^
Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi: 10.1086/504422 , please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi= 10.1086/504422instead.. a, i, e per JPL (site updated 2008 Aug 25) - ^
H. A. Weaver; S. A. Stern; M. J. Mutchler; A. J. Steffl; et al. (23 February 2006). "Discovery of two new satellites of Pluto". Nature. 439 (7079): 943–945. arXiv:astro-ph/0601018. Bibcode:2006Natur.439..943W. doi:10.1038/nature04547. PMID 16495991.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - Based on the range of diameters from Buie et al. (2006), and densities ranging from 1 g/cm (ice) to 2 g/cm (Pluto).
- http://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-s-hubble-finds-pluto-s-moons-tumbling-in-absolute-chaos
- ^ Stern, S. A.; Mutchler, M. J.; Weaver, H. A.; Steffl, A. J. (2006). "The Positions, Colors, and Photometric Variability of Pluto's Small Satellites from HST Observations 2005–2006". Astronomical Journal. 132 (3): submitted. arXiv:astro-ph/0607507. Bibcode:2006AJ....132.1405S. doi:10.1086/506347. (Final preprint)
- Cain, Fraser (2008). "Pluto's Moon Nix".
- IAU Circular No. 8625 describing the discovery
- ^ IAU Circular No. 8723 naming the moons
- Boyle, Alan. "Pluto's Moons Raise New Puzzles for NASA's New Horizons Mission". NBC News.com. NBC News. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- Brightness Difference on 2005-05-15: (5th root of 100) ^ (Nix APmag 23.38 – Pluto APmag 13.87) = 6,368x
- "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology. July 21, 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
- Blunck, Jürgen, Solar System Moons: Discovery and Mythology (2009), p. 129.
- Steffl, A. J.; Mutchler, M. J.; Weaver, H. A.; Stern, S. A.; et al. (2006). "New Constraints on Additional Satellites of the Pluto System". The Astronomical Journal. 132 (2): 614–619. arXiv:astro-ph/0511837. Bibcode:2006AJ....132..614S. doi:10.1086/505424.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help)(Final preprint)
External links
- Nix Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- Background Information Regarding Our Two Newly Discovered Satellites of Pluto – The discoverers' website
- NASA's Hubble Reveals Possible New Moons Around Pluto – Hubble press release
- Two More Moons Discovered Orbiting Pluto (SPACE.com)
- Pluto's Newest Moons Named Hydra and Nix (SPACE.com)
| Pluto | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geography (features) |
|   | ||||||||||||
| Moons | ||||||||||||||
| Exploration | ||||||||||||||
| Astronomy |
| |||||||||||||
| Related | ||||||||||||||
| Moons of likely dwarf planets | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Trans-Neptunian objects | |
|---|---|
| TNO classes | |
| Dwarf planets (moons) | |
| Sednoids | |