| Revision as of 17:37, 9 December 2015 editWikirictor (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users16,253 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:38, 9 December 2015 edit undoWikirictor (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users16,253 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''''Homo rhodesiensis''''' refers to an extinct ] species of the genus ''Homo'', first described in 1921 by ] in reference to the ''Kabwe skull'' fossil recovered at Broken Hill, or ], in ] (once part of Northern Rhodesia).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gbif.org/occurrence/787018738 |title= GBIF 787018738 Fossil of Homo rhodesiensis Woodward, 1921 | publisher= GBIF org |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> A number of ]-comparable fossil remains came to light in East Africa (Bodo, Ndutu, Eyasi, ]) and North Africa (Salé, Rabat, Dar-es-Soltane, Djbel Irhoud, Sidi Aberrahaman, Tighenif) during the 20th century and were classified as ''Homo rhodesiensis''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.pnas.org/content/99/3/1134.full.pdf |title= The evolution and development of cranial form in Homo | publisher= Department of Anthropology, Harvard University |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> Smith Woodward decided the fossils represented an extinct hominid species as the "... thick skull, sloped forehead and giant brow ridges made the species distinct from living people" The finds were dated between 300,000 and 125,000 years BC. "However, this group of fossils has been known by many other now-obscure names", none ever having been accepted universally including the taxon ''Homo rhodesiensis''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/four-species-of-homo-youve-never-heard-of-part-ii-156735412/?no-ist |title= Four Species of Homo You’ve Never Heard Of, Part II | publisher= smithsonianmag com |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> The ], found in 1954 in South Africa was subject to at least three taxonomic revisions from 1955 to 1996. Consensus is confined to informal taxonomic categories, such as "pre-modern".<ref>{{cite web |url=https://books.google.com.kh/books?id=440TmWXToLAC&pg=PT1354&lpg=PT1354&dq=Homo+rhodesiensis&source=bl&ots=jobjlx_b86&sig=WZdowP4tgdRNifcfwXjyeR8ghEw&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjjr6Kyj8_JAhWm26YKHVbuCCw4PBDoAQhIMAg#v=onepage&q=Homo%20rhodesiensis&f=false |title= Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Human Evolution, 2 Volume Set | publisher= Google Books |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> | '''''Homo rhodesiensis''''' refers to an extinct ] species of the genus ''Homo'', first described in 1921 by ] in reference to the ''Kabwe skull'' fossil recovered at Broken Hill, or ], in ] (once part of Northern Rhodesia).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gbif.org/occurrence/787018738 |title= GBIF 787018738 Fossil of Homo rhodesiensis Woodward, 1921 | publisher= GBIF org |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> A number of ]-comparable fossil remains came to light in East Africa (Bodo, Ndutu, Eyasi, ]) and North Africa (Salé, Rabat, Dar-es-Soltane, Djbel Irhoud, Sidi Aberrahaman, Tighenif) during the 20th century and were classified as ''Homo rhodesiensis''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.pnas.org/content/99/3/1134.full.pdf |title= The evolution and development of cranial form in Homo | publisher= Department of Anthropology, Harvard University |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> Smith Woodward decided the fossils represented an extinct hominid species as the "... thick skull, sloped forehead and giant brow ridges made the species distinct from living people" The finds were dated between 300,000 and 125,000 years BC. "However, this group of fossils has been known by many other now-obscure names", none ever having been accepted universally including the taxon ''Homo rhodesiensis''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/four-species-of-homo-youve-never-heard-of-part-ii-156735412/?no-ist |title= Four Species of Homo You’ve Never Heard Of, Part II | publisher= smithsonianmag com |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> The ], found in 1954 in South Africa was subject to at least three taxonomic revisions from 1955 to 1996. Consensus is confined to informal taxonomic categories, such as "pre-modern".<ref>{{cite web |url=https://books.google.com.kh/books?id=440TmWXToLAC&pg=PT1354&lpg=PT1354&dq=Homo+rhodesiensis&source=bl&ots=jobjlx_b86&sig=WZdowP4tgdRNifcfwXjyeR8ghEw&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjjr6Kyj8_JAhWm26YKHVbuCCw4PBDoAQhIMAg#v=onepage&q=Homo%20rhodesiensis&f=false |title= Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Human Evolution, 2 Volume Set | publisher= Google Books |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> | ||
| Most scientists now regard ''Homo rhodesiensis'' as to be the local (African) representative of '']'' and as such the direct ancestor of anatomically modern humans.<ref name="Kabwe">{{cite web|publisher=The Smithsonian Institution's Human Origin Program|title= Kabwe 1|accessdate=2 November 2010 | url=http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/human-fossils/fossils/kabwe-1}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Chris |last=Stringer|authorlink=Chris Stringer|title=The Origin of our Species|page=202|publisher=Penguin|year=2011|isbn=978-0-141-03720-2}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|page=222|title=From Lucy to Language|first1=Donald|last1=Johansson|first2=Blake|last2=Edgar|publisher=Simon & Schuster|year=2006|isbn=978-0-7432-8064-8}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/five-accidental-hominid-fossil-discoveries-29721935/ |title= Five Accidental Hominid Fossil Discoveries | publisher= smithsonianmag com |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> | Most scientists now regard ''Homo rhodesiensis'' as to be the local (African) representative of '']'' and as such the direct ancestor of anatomically modern humans.<ref name="Kabwe">{{cite web|publisher=The Smithsonian Institution's Human Origin Program|title= Kabwe 1|accessdate=2 November 2010 | url=http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/human-fossils/fossils/kabwe-1}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Chris |last=Stringer|authorlink=Chris Stringer|title=The Origin of our Species|page=202|publisher=Penguin|year=2011|isbn=978-0-141-03720-2}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|page=222|title=From Lucy to Language|first1=Donald|last1=Johansson|first2=Blake|last2=Edgar|publisher=Simon & Schuster|year=2006|isbn=978-0-7432-8064-8}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/five-accidental-hominid-fossil-discoveries-29721935/ |title= Five Accidental Hominid Fossil Discoveries | publisher= smithsonianmag com |date= |accessdate=December 9, 2015}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 17:38, 9 December 2015
| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Homo rhodesiensis Temporal range: Pleistocene, 0.4–0.12 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ | |
|---|---|
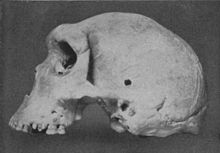
| |
| Skull found in 1921 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Family: | Hominidae |
| Tribe: | Hominini |
| Genus: | Homo |
| Species: | H. rhodesiensis |
| Binomial name | |
| †Homo rhodesiensis Woodward, 1921 | |
Homo rhodesiensis refers to an extinct hominin species of the genus Homo, first described in 1921 by Arthur Smith Woodward in reference to the Kabwe skull fossil recovered at Broken Hill, or Kabwe, in Zambia (once part of Northern Rhodesia). A number of morphologically-comparable fossil remains came to light in East Africa (Bodo, Ndutu, Eyasi, Ileret) and North Africa (Salé, Rabat, Dar-es-Soltane, Djbel Irhoud, Sidi Aberrahaman, Tighenif) during the 20th century and were classified as Homo rhodesiensis. Smith Woodward decided the fossils represented an extinct hominid species as the "... thick skull, sloped forehead and giant brow ridges made the species distinct from living people" The finds were dated between 300,000 and 125,000 years BC. "However, this group of fossils has been known by many other now-obscure names", none ever having been accepted universally including the taxon Homo rhodesiensis. The Saldanha cranium, found in 1954 in South Africa was subject to at least three taxonomic revisions from 1955 to 1996. Consensus is confined to informal taxonomic categories, such as "pre-modern".
Most scientists now regard Homo rhodesiensis as to be the local (African) representative of Homo heidelbergensis and as such the direct ancestor of anatomically modern humans.
Discovery
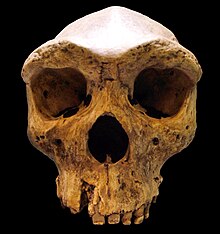
Kabwe 1, also called the Broken Hill skull, was assigned by Arthur Smith Woodward in 1921 as the type specimen for Homo rhodesiensis; today most scientists now assign it to Homo heidelbergensis. The cranium was found in a lead and zinc mine in Broken Hill, Northern Rhodesia (now Kabwe, Zambia) in 1921 by Tom Zwiglaar, a Swiss miner. In addition to the cranium, an upper jaw from another individual, a sacrum, a tibia, and two femur fragments were also found. The skull was dubbed "Rhodesian Man" at the time of the find, but is now commonly referred to as the Broken Hill skull or the Kabwe cranium.
The association between the bones is unclear, but the tibia and femur fossils are usually associated with the skull. Rhodesian Man is dated to be between 125,000 and 300,000 years old. Cranial capacity of the Broken Hill skull has been estimated at 1,230 cm³. Bada, & al., (1974) published the direct date of 110 ka for this specimen measured by aspartic acid racemisation. The destruction of the paleoanthropological site has made layered dating impossible.
The skull is from an extremely robust individual, and has the comparatively largest brow-ridges of any known hominid remains. It was described as having a broad face similar to Homo neanderthalensis (i.e. large nose and thick protruding brow ridges), and has been interpreted as an "African Neanderthal". However, when regarding the skull's extreme robustness, recent research has pointed to several features intermediate between modern Homo sapiens and Neanderthal.
Bodo Cranium
The 600.000 year old Bodo cranium was found in 1976 by members of an expedition led by Jon Kalb at Bodo D'ar in the Awash River valley of Ethiopia. Although the skull is most similar to those of Kabwe, Woodward's nomenclature was discontinued and its discoverers attributed it to H. heidelbergensis.
Another specimen, "the hominid from Lake Ndutu" may approach 400,000 years old; Clarke in 1976 classified it as Homo erectus. Indirect cranial capacity estimate is 1100 ml. Its supratoral sulcus morphology and the presence of protuberance as suggested by Philip Rightmire "give the Nudutu occiput an appearance which is also unlike that of Homo erectus", but Stinger (1986) pointed out that a thickened iliac pillar is typical for Homo erectus.
Classification

In Africa, there is a distinct difference in the Acheulean tools made before and after 600,000 years ago with the older group being thicker and less symmetric and the younger being more extensively trimmed.
Rupert Murrill has studied the relations between Archanthropus skull of Petralona (Chalcidice, Greece) and Rhodesian Man. Most current experts believe Rhodesian Man to be within the group of Homo heidelbergensis though other designations such as Homo sapiens arcaicus and Homo sapiens rhodesiensis have also been proposed.
According to Tim White, it is probable that Rhodesian Man was the ancestor of Homo sapiens idaltu (Herto Man), which itself was the ancestor of Homo sapiens sapiens. The skull has cavities in ten of the upper teeth and is considered one of the oldest known occurrences of cavities. Pitting indicates significant infection before death and implies that the cause of death may have been due to dental disease infection or possibly chronic ear infection.
Present location
The Broken Hill skull is one of the treasures in the collections cared for by the Natural History Museum, London. There is a replica in the Museum in Livingstone, Zambia.
See also
- Homo heidelbergensis
- List of fossil sites (with link directory)
- List of hominina (hominid) fossils (with images)
References
- "GBIF 787018738 Fossil of Homo rhodesiensis Woodward, 1921". GBIF org. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- "The evolution and development of cranial form in Homo" (PDF). Department of Anthropology, Harvard University. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- "Four Species of Homo You've Never Heard Of, Part II". smithsonianmag com. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- "Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Human Evolution, 2 Volume Set". Google Books. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- ^ "Kabwe 1". The Smithsonian Institution's Human Origin Program. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- Stringer, Chris (2011). The Origin of our Species. Penguin. p. 202. ISBN 978-0-141-03720-2.
- Johansson, Donald; Edgar, Blake (2006). From Lucy to Language. Simon & Schuster. p. 222. ISBN 978-0-7432-8064-8.
- "Five Accidental Hominid Fossil Discoveries". smithsonianmag com. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- Begun, David R., ed. (2012). "The African Origin of Homo Sapiens". A Companion to Paleoanthropology. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118332375.
- Rightmire, G. Philip. The Evolution of Homo Erectus: Comparative Anatomical Studies of an Extinct Human Species Cambridge University Press, 1993. ISBN 0-521-44998-7, ISBN 978-0-521-44998-4.
- Bada, Jeffrey L., Roy A. Schroeder, Reiner Protsch, and Rainer Berger. Concordance of Collagen-Based Radiocarbon and Aspartic-Acid Racemization Ages PNAS abstract URL.
- Amino Acid Racemization Dating of Fossil Bones
- "Bodo - Paleoanthropology site information". Fossilized org. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- "Bodo Skull and Jaw". Skulls Unlimited. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- "Bodo fossil". Britannica Encyclopedia. Retrieved December 9, 2015.
- Rightmire, G. Philip (2005). "The Lake Ndutu cranium and early Homo Sapiens in Africa". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 61 (2): 245–254. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330610214. PMID 6410925.
- The Evolution of Homo Erectus: Comparative Anatomical Studies of an Extinct Human Species By G. Philip Rightmire Published by Cambridge University Press, 1993 ISBN 0-521-44998-7, ISBN 978-0-521-44998-4
- H. James Birx (10 June 2010). 21st Century Anthropology: A Reference Handbook. SAGE Publications. p. 48. ISBN 978-1-4522-6630-5.
- Bernard Wood (31 March 2011). Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Human Evolution, 2 Volume Set. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 761–762. ISBN 978-1-4443-4247-5.
- White, Tim D.; Asfaw, B.; DeGusta, D.; Gilbert, H.; Richards, G. D.; Suwa, G.; Howell, F. C. (2003). "Pleistocene Homo sapiens from Middle Awash, Ethiopia". Nature. 423 (6491): 742–747. doi:10.1038/nature01669. PMID 12802332Template:Inconsistent citations
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - http://www.nhm.ac.uk/nature-online/collections-at-the-museum/museum-treasures/broken-hill-skull/index.html
Literature
- Woodward, Arthur Smith (1921). "A New Cave Man from Rhodesia, South Africa". Nature. 108 (2716): 371–372. doi:10.1038/108371a0.
- Singer Robert R. and J. Wymer (1968). "Archaeological Investigation at the Saldanha Skull Site in South Africa". The South African Archaeological Bulletin. 23 (3). The South African Archaeological Bulletin, Vol. 23, No. 91: 63–73. doi:10.2307/3888485. JSTOR 3888485.
- Murrill, Rupert I. (1975). "A comparison of the Rhodesian and Petralona upper jaws in relation to other Pleistocene hominids". Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Anthropologie. 66: 176–187..
- Murrill, Rupert Ivan (1981). Ed. Charles C. Thomas (ed.). Petralona Man. A Descriptive and Comparative Study, with New Information on Rhodesian Man. Springfield, Illinois: Thomas. ISBN 0-398-04550-X.
- Rightmire, G. Philip (2005). "The Lake Ndutu cranium and early Homo Sapiens in Africa". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 61 (2): 245–254. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330610214. PMID 6410925..
- Asfaw, Berhane (2005). "A new hominid parietal from Bodo, middle Awash Valley, Ethiopia". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 61 (3): 367–371. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330610311. PMID 6412559..
| Human evolution | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxonomy (Hominins) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ancestors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Models |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Timelines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||