| Revision as of 11:19, 25 January 2016 editSoetermans (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers59,759 editsm Reverted 1 edit by Lowtrucks (talk) to last revision by Soetermans. (TW)← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:24, 25 January 2016 edit undoLowtrucks (talk | contribs)213 edits Undid revision 701584341 by Soetermans (talk)Next edit → | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
| The creator of Bubble Bobble Fukio Mitsuji (MTJ) went on to create other classics such as Rainbow Islands, Syvalion & Volfied. He died on December 11, 2008. | The creator of Bubble Bobble Fukio Mitsuji (MTJ) went on to create other classics such as Rainbow Islands, Syvalion & Volfied. He died on December 11, 2008. | ||
| == |
==Legacy== | ||
| ] | |||
| ''Bubble Bobble'' |
''Bubble Bobble'' inspired many sequels, including: | ||
| *'']'' (1987) | *'']'' (1987) | ||
| *'']'' (1988) | *'']'' (1988) | ||
| Line 118: | Line 119: | ||
| *{{KLOV game|7222}} | *{{KLOV game|7222}} | ||
| *{{Arcade History|id=343}} | *{{Arcade History|id=343}} | ||
| *{{StrategyWiki}} | |||
| * A detailed level guide (arcade version). | |||
| {{Bubble Bobble series}} | {{Bubble Bobble series}} | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 25 January 2016
| This article is in list format but may read better as prose. You can help by converting this article, if appropriate. Editing help is available. (November 2015) |
| Bubble Bobble | |
|---|---|
 Promotional US flyer for the original arcade iteration of Bubble Bobble Promotional US flyer for the original arcade iteration of Bubble Bobble | |
| Developer(s) | Taito |
| Publisher(s) | Taito and Romstar |
| Designer(s) | Fukio Mitsuji |
| Composer(s) | Tadashi Kimijima |
| Series | Bubble Bobble |
| Platform(s) | Arcade, Various |
| Release | August Template:Vgy |
| Genre(s) | Arcade, comical action platformer |
| Mode(s) | One player or 2 players simultaneously |
| Arcade system | Main CPUs: 2× Z80 (6MHz), Z80 (3MHz), M6801 (1MHz) |
Bubble Bobble (バブルボブル, Baburu Boburu) is an arcade comical action platformer video game by Taito, first released in 1986 and later ported to numerous home computers and game consoles. The game, starring the twin Bubble Dragons Bub (Bubblun) (バブルン, Baburun) and Bob (Bobblun) (ボブルン, Boburun), in which players travel through one hundred different stages, blowing and bursting bubbles, dodging enemies and collecting a variety of items. The game became popular and led to a long series of sequels and spin-offs. The main goal of the game is to rescue Bub and Bob's girlfriends from the Cave of Monsters. It is an early example of an action game with multiple endings, which depend on the player's performance and discovery of secrets.
Gameplay
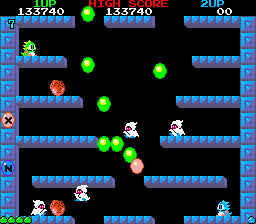
In the game's plot, "Baron Von Blubba" has kidnapped the brothers Bubby and Bobby's girlfriends and turned the brothers into Bubble Dragons, Bub and Bob. Bub and Bob have to finish 100 levels in the Cave of Monsters in order to rescue them.
In the game, each player controls one of the two dragons. Players can move along platforms, fall to lower ones, and jump to higher ones and over gaps. Each level is limited to a single screen, with no scrolling; however, if a screen has gaps in its bottom edge, players can fall through these and reappear at the top. Each level has a certain number of enemies that must be defeated in order to advance. The players must blow bubbles to trap the enemies, then burst these bubbles by colliding with them. Each enemy defeated in this manner turns into a food item that can be picked up for extra points. Defeating multiple enemies at once awards higher scores and causes more valuable food items to appear. All bubbles will float for a certain length of time before bursting on their own; players can jump on these and ride them to otherwise inaccessible areas. Magic items appear from time to time and grant special abilities and advantages when picked up. Special bubbles occasionally appear that can be burst to attack enemies with fire, water, or lightning. Furthermore, if a player collects letter bubbles to form the word EXTEND, he/she earns a bonus life and both players immediately advance to the next level.
A player loses one life upon touching any free enemies or their projectiles (rocks, fireballs, lasers, bottles). Enemies turn "angry"—turning pink in color and moving faster—if they escape from a bubble after being left too long or the players spend a certain amount of time on the current level. They return to normal if either player loses a life. After a further time limit expires, an additional invincible enemy appears for each player, actively chasing them using only vertical and horizontal movements. These disappear once the level is cleared, or when a player loses a life. When there is only one enemy left, it immediately becomes angry and remains in this state until defeated.
In the 100th and final level, players face a boss. This game was one of the first to feature multiple endings. Completing Level 100 in single-player mode reveals a message stating that the game has not truly ended and a hint to the player: "Come here with your friend." If two players complete the game, they see a "Happy End," in which the brothers are transformed to their human selves and reunited with their girlfriends. This ending also includes a code that, when deciphered, allows the game to be played in the faster and more difficult "Super" mode. If this mode is completed with two players, a second "Happy End" is displayed in which Super Drunk is revealed to be the brothers' parents under the control of some outside influence. The brothers return to normal and are reunited with their parents and girlfriends.
Development

The popularity of Bubble Bobble led Taito (or its licensees) to port the game to many home computers and video game consoles. Ports of the game were released for the Commodore 64, Sinclair ZX Spectrum, Amiga, Atari ST, MSX2, Amstrad CPC, Sharp X68000, PC (DOS, 1989 and 1996), Apple II, FM Towns Marty, Sega Master System, Game Boy, Game Boy Color, PlayStation, Sega Saturn, Nintendo Entertainment System, Famicom Disk System, Sega Game Gear, mobile phone (Sprint PCS) and UltraCade's Taito Arcade Classics. The Sega Master System version is noted for having two hundred levels (in effect the normal and super modes consecutively) and is considered one of the best conversions available. Of the original 8 and 16 bit ports, the NES and Game Boy ones were made by Taito themselves. Sega converted Bubble Bobble for the Master System (although this version was not released in North America). The Commodore 64 and Spectrum versions were published by UK-based Firebird Software, and most of the other computer ports by US-based Novalogic.
Commodore 64 coder Steve Ruddy recalled in Retro Gamer:
It wasn't daunting originally, as it looked like a fairly straightforward platform and sprite game. However, once you start playing you noticed how the bubbles followed air flow patterns and how they all gathered in fixed places - lots of sprites on the same line meant a sprite multiplexer wasn't suitable. Fortunately, having worked on the BBC Micro and Mystery of the Nile, I wasn't averse to using software sprites. ... We didn't understand all of the secrets so we just implemented the game to mimic what we did notice. So how the pick-ups appear isn't the same as the arcade on the C64, but it should be very similar to how the pickups appear after the machine is powered up.
The X68000 version of Bubble Bobble includes a secret "Sybubblun" mode, which contains 20 incredibly difficult levels with the characters changed to those from Syvalion, another game designed by Fukio Mitsuji.
In 1996, Taito announced that they lost the original source code. As Probe Entertainment was in charge of the home conversions, Taito sent them a Bubble Bobble arcade PCB so they could play the original game and reproduce its mechanics. This led to the release of Bubble Bobble also featuring Rainbow Islands for Saturn, PlayStation and PC (DOS) in 1996.
In the Game Boy and Game Boy Color versions, since the Game Boy is in its nature a single player device, the storyline involves Bub looking for "Moon Water" to cure his brother, they are known as Bubble Bobble, and Classic Bubble Bobble respectively.
In October 2005, a version was released for the Xbox, PlayStation 2, and PC as part of the Taito Legends compilation of classic arcade games.
At the end of 2006, a new port for mobile phones in Europe and Japan was released.
On December 31, 2007, the NES version of Bubble Bobble was released on Nintendo's Virtual Console service for the Wii. It costs 500 Wii Points, the equivalent of US$5.
The Famicom version of Bubble Bobble was also released for the Nintendo eShop on October 16, 2013 for the Nintendo 3DS and on January 29, 2014 for the Wii U.
The game's music was written by Japanese team Zuntata. Ports for home computer versions were made by Peter Clarke (Commodore 64), David Whittaker (Amiga) and Tim Follin (Atari ST, ZX Spectrum). The music is based upon a popular folk song called "Sing Jemima Sing".
Clones and remakes
The Arcade version of Bubble Bobble was widely bootlegged in its day, but due to a security chip installed by Taito (known as the PS4, based on a Motorola 6800) none of the bootlegs played exactly like the original. Through a technique called "decapping" the MAMEDEV team has been able to reverse engineer the workings of the chip and emulate it perfectly. Following that, project Bubble Bobble REDUX has been able to implement an exact version of Bubble Bobble on bootleg boards.
A version also exists for the BBC Micro in the public domain though never officially released. According to one of the creators it was coded by them independently in 1988 as a clone of the C64 version, but when they approached publishers it was deemed that it would not be financially viable to release a licensed product for the BBC micro at that time.
In 2002 a homebrew version for the Texas Instruments TI-8x series of calculators was released. Template:Computing platform requirements
During Christmas of 2011, a new version for the Amstrad CPC, entitled Bubble Bobble 4 CPC or BB4CPC was released for free by programmer CNGSoft, as an update to the original/official CPC version.
In 2012 a pair of "hackers" released the Bubble Bobble: Lost Cave project where they have created a new version of Bubble Bobble with 100 new levels that runs on the original arcade hardware. The levels are not created from scratch though, they have been selected as the cream of the crop from the various official ports of the game, since Taito granted almost every Bubble Bobble version some kind of unique content.
Reception
Reception| Publication | Score |
|---|---|
| AllGame | |
| Crash | 90% |
| Computer and Video Games | 27/30 |
| Electronic Gaming Monthly | 7.75/10 (GG) |
| Sinclair User | 8/10 |
| Your Sinclair | 90% |
| The Games Machine | 93% |
| Zzap!64 | 97% (C64) |
| Publication | Award |
|---|---|
| Zzap!64 | Gold Medal |
Mean Machines gave the Game Boy port of the game a score of 91%, noting that while some changes had been made, the game played identical to the original arcade port and "provides much addiction and challenge". The four reviewers of Electronic Gaming Monthly stated that the Game Gear version is a faithful conversion of the original which works well in portable form. They particularly praised the simplicity of the gameplay concept and the graphics, and the two-player link option.
The Spectrum version was voted number 58 in the Your Sinclair Readers' Top 100 Games of All Time. GamesRadar ranked it the 24th best NES game ever made. The staff praised its advancements over other platform games of its time and its use of multiple endings.
The creator of Bubble Bobble Fukio Mitsuji (MTJ) went on to create other classics such as Rainbow Islands, Syvalion & Volfied. He died on December 11, 2008.
Legacy
Bubble Bobble inspired many sequels, including:
- Rainbow Islands: The Story of Bubble Bobble 2 (1987)
- Rainbow Islands Extra Version (1988)
- Parasol Stars (1991 originally released for PC-Engine/TurboGrafx-16, converted for NES (Europe only), Amiga, Atari ST, and Game Boy (Europe only)
- Bubble Bobble Part 2 (1993 Nintendo Famicom, Nintendo Entertainment System, Game Boy)
- Bubble Bobble II (World) / Bubble Symphony (Europe, Japan, U.S.) (1994 Arcade, Sega Saturn (Japan only))
- Bubble Memories - The Story of Bubble Bobble III (1995 Arcade)
- Packy's Treasure Slot (1997 Medal Game)
- Bubble'n Roulette (1998 Medal Game)
- Bubblen No KuruKuru Jump! (1999 Medal Game)
- Rainbow Islands - Putty's Party (2000 Bandai Wonderswan)
- Bubble Bobble Old & New* (Remake, 2002 Game Boy Advance)
- Bubble Bobble Revolution (2005 Nintendo DS) a.k.a. Bubble Bobble DS in Japan
- Rainbow Islands Revolution (2005 Nintendo DS)
- Bubble Bobble Evolution (2006 PlayStation Portable)
- Rainbow Islands Evolution (2007 PlayStation Portable)
- Bubble Bobble Plus! (2009 WiiWare on the Wii) a.k.a. Bubble Bobble Neo! (2009 Xbox Live Arcade on Xbox 360)
- Rainbow Islands: Towering Adventure (2009 WiiWare, Xbox Live Arcade)
- Bubble Bobble Double (2010 iOS)
- Bubble Bobble for Kakao (iOS, Android) - 2015 (Notes: This game was published for KakaoTalk messaging app and fully Taito licensed)
- Many of the characters and musical themes of Bubble Bobble were used by Taito in a tile-matching video game Puzzle Bobble (a.k.a. Bust-a-Move) and its sequels.
Other media
- The Bubble Bobble Characters was made cameos for adapted on manga titled Gamest Nª49: Gasmest Island Mokushiroku on October 1992 created by Shinseisha.
- Bubblun, from Bubble Bobble and Chack, from Chack'n'Pop, was adapted for the second manga fans, as titled Cha Kurun Desu (ちゃくるんです) on May 2009.
References
- "Bubble Bobble The Arcade Video Game by Taito Corp". Arcade History.com.
- ^ "Bubble Bobble Video Game by Taito (1986)". The International Arcade Museum. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- "Bubble Bobble & Rainbow Islands games". mobygames.com. Retrieved 2014-06-06.
- ^ Dawkes, Adam (September 2004), "Bubble Trouble", Retro Gamer (8), Imagine Publishing: 36–41, retrieved 2013-01-11
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - ^ "Bubble Memories", Retro Gamer (95), Imagine Publishing: 26–35, October 2011
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - ^ Campbell, Stuart (July 2006), "The Definitive - Bubble Bobble", Retro Gamer (28), Imagine Publishing: 58–68
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - Bevan, Mike (December 2013). "Bubbles, Baseball and Buzz Saws - Software Creations". Retro Gamer. No. 122. Imagine Publishing. pp. 74–79.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - Sybubblun in MAME
- "Bubble Bobble The [Coin-Op] Arcade Video Game by Taito Corp. (1986)". arcade-history.com. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- Salmoria, Nicola. "Completed, at Last". Archived from the original on 2013-05-08. Retrieved 2014-06-25.
- "Bubble Bobble REDUX". Archived from the original on 2013-08-30.
- "Lost and Found". stairwaytohell.com. Retrieved 2014-06-24.
- "Bubble Bobble 8x Project Page". Dwedit.org. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- "Bubble Bobble: Lost Cave Project Page". Lost Cave Project. Retrieved 2014-06-24.
- Couper, Chris. "Bubble Bobble-Review". Allgame. Archived from the original on November 15, 2014. Retrieved April 12, 2013.
- "Bubble Bobble Review". C+VG. October 1987. pp. 14–15. Retrieved 2012-08-10.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - "Bubble Bobble Review", Crash (45): 132–133, October 1987, archived from the original on 2006, retrieved 2012-08-10
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|archivedate=(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - ^ "Review Crew: Bubble Bobble". Electronic Gaming Monthly (63). Ziff Davis: 42. October 1994.
- "Bubble Bobble Review". Sinclair User. October 1987. p. 50. Retrieved 2012-08-10.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - "Bubble Bobble Review", Your Sinclair (69): 56, September 1991, archived from the original on 2006, retrieved 2012-08-10
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|archivedate=(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - "Bubble Bobble Review". The Games Machine. November 1987. p. 66. Retrieved 2012-08-10.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - "Bubble Bobble Review", Zzap!64 (30), Newsfield Publications: 12, October 1987, retrieved 2014-06-23
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - "Bubble Bobble Review". Mean Machines (23). August 1992. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|archivedate=(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - "Let the People Decide", Your Sinclair (93): 11, September 1993, archived from the original on 16 August 2006, retrieved 2014-06-24
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - "Best NES Games of all time", GamesRadar, 2012-04-16, retrieved 2013-12-05
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - ちゃくるんです(ちゃっくんぽっぷ+バブルボブル)TAITOのゲーム Ameblo
External links
- Bubble Bobble at the Killer List of Videogames
- Template:Arcade History
- Template:StrategyWiki
- Bubble Bobble Level Guide A detailed level guide (arcade version).
| Bubble Bobble | |
|---|---|
| Bubble Bobble | |
| Rainbow Islands | |
| Puzzle Bobble | |
| Related games | |
- 1986 video games
- Amiga games
- Amstrad CPC games
- Apple II games
- Arcade games
- Atari ST games
- Commodore 64 games
- Cooperative video games
- DOS games
- Famicom Disk System games
- Game Boy Color games
- Game Boy platform games
- Sega Game Gear games
- Mobile games
- MSX games
- Nintendo Entertainment System games
- FM Towns games
- Platform games
- PlayStation games
- Master System games
- Sharp X68000 games
- Taito games
- Virtual Console games for Wii U
- ZX Spectrum games
- Bubble Bobble
- Video games developed in Japan