| Revision as of 00:50, 17 August 2006 editජපස (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers60,455 edits →1950 to 1999: cleanup a bit.← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:41, 17 August 2006 edit undoIantresman (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users21,376 edits Can find no citation "discounting" ambiplasma, and no comments on the other timelines entriesNext edit → | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| * ''']''' - Fred Hoyle and ] show that the ] can explain the isotropy of the universe because deviations from isotropy and homogeneity ] in time | * ''']''' - Fred Hoyle and ] show that the ] can explain the isotropy of the universe because deviations from isotropy and homogeneity ] in time | ||
| * ''']''' - Fred Hoyle and ] point out that the primordial ] abundance depends on the number of ]s. | * ''']''' - Fred Hoyle and ] point out that the primordial ] abundance depends on the number of ]s. | ||
| * ''']''' - ] proposes the |
* ''']''' - ] proposes the ] theory to explain ]. | ||
| * '''1965''' - ] and ] analyze ] source count data and discover that the quasar density increases with redshift. | * '''1965''' - ] and ] analyze ] source count data and discover that the quasar density increases with redshift. | ||
| * '''1965''' - ] and ], astronomers at ] discover the 2.7 K ''microwave background radiation'', which earns them the 1978 ] in Physics. ], ], Peter Roll and ] interpret it as relic from the big bang. | * '''1965''' - ] and ], astronomers at ] discover the 2.7 K ''microwave background radiation'', which earns them the 1978 ] in Physics. ], ], Peter Roll and ] interpret it as relic from the big bang. | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 17 August 2006
| Part of a series on | ||||
| Physical cosmology | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
Early universe
|
||||
| Expansion · Future | ||||
Components · Structure
|
||||
| Experiments | ||||
| Scientists | ||||
| Subject history | ||||
The timeline of cosmology lists the sequence of cosmological theories and discoveries in chronological order. The most modern developments follow the scientific development of the discipline of physical cosmology.
Pre-1900
- 2nd century - Ptolemy proposes an Earth-centred Universe, with the Sun and planets revolving around the Earth
- c500 onwards - Several astronomers propose a Sun-centered Universe, including Aryabhata, Bhaskara I, Ibn al-Shatir, and Copernicus
- 1576 - Thomas Digges modifies the Copernican system by removing its outer edge and replacing the edge with a star-filled unbounded space
- 1610 - Johannes Kepler uses the dark night sky to argue for a finite universe
- 1687 - Sir Isaac Newton's laws describe large-scale motion throughout the universe
- 1720 - Edmund Halley puts forth an early form of Olbers' paradox
- 1744 - Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux puts forth an early form of Olbers' paradox
- 1791 - Erasmus Darwin pens the first description of a cyclical expanding and contracting universe
- 1826 - Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers puts forth Olbers' paradox
- 1848 - Edgar Allan Poe offers first correct solution to Olbers' paradox in an essay that also suggests the expansion and collapse of the universe.
1900-1949
- 1905 - Albert Einstein publishes the Special Theory of Relativity, positing that space and time are not separate continuums
- 1915 - Albert Einstein publishes the General Theory of Relativity, showing that an energy density warps spacetime
- 1917 - Willem de Sitter derives an isotropic static cosmology with a cosmological constant as well as an empty expanding cosmology with a cosmological constant, termed a de Sitter universe
- 1922 - Vesto Slipher summarizes his findings on the spiral nebulae's systematic redshifts
- 1922 - Alexander Friedmann finds a solution to the Einstein field equations which suggests a general expansion of space
- 1927 - Georges Lemaître discusses the creation event of an expanding universe governed by the Einstein field equations
- 1928 - Howard Percy Robertson briefly mentions that Vesto Slipher's redshift measurements combined with brightness measurements of the same galaxies indicate a redshift-distance relation
- 1929 - Edwin Hubble demonstrates the linear redshift-distance relation and thus shows the expansion of the universe
- 1933 - Edward Milne names and formalizes the cosmological principle
- 1934 - Georges Lemaître interprets the cosmological constant as due to a vacuum energy with an unusual perfect fluid equation of state
- 1938 - Paul Dirac suggests the large numbers hypothesis, that the gravitational constant may be small because it is decreasing slowly with time
- 1948 - Ralph Alpher, Hans Bethe("in absentia"), and George Gamow examine element synthesis in a rapidly expanding and cooling universe and suggest that the elements were produced by rapid neutron capture
- 1948 - Hermann Bondi, Thomas Gold, and Fred Hoyle propose steady state cosmologies based on the perfect cosmological principle
- 1948 - George Gamow predicts the existence of the cosmic microwave background radiation by considering the behavior of primordial radiation in an expanding universe.
1950 to 1999
- 1950 - Oskar Klein proposes a meta-galaxy model, a first indication of the Alfvén-Klein model.
- 1950 - Fred Hoyle derisively coins the term "Big Bang".
- 1951 - William McCrea shows that the steady state C-field can be accommodated within general relativity by interpreting it as a contribution to the energy-momentum tensor with an unusual equation of state
- 1961 - Robert Dicke argues that carbon-based life can only arise when the gravitational force is small, because this is when burning stars exist; first use of the weak anthropic principle
- 1963 - Fred Hoyle and Jayant Narlikar show that the steady state theory can explain the isotropy of the universe because deviations from isotropy and homogeneity decay exponentially in time
- 1964 - Fred Hoyle and Roger Tayler point out that the primordial helium abundance depends on the number of neutrinos.
- 1965 - Hannes Alfvén proposes the ambiplasma theory to explain baryon asymmetry.
- 1965 - Martin Rees and Dennis Sciama analyze quasar source count data and discover that the quasar density increases with redshift.
- 1965 - Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, astronomers at Bell Labs discover the 2.7 K microwave background radiation, which earns them the 1978 Nobel Prize in Physics. Robert Dicke, James Peebles, Peter Roll and David Todd Wilkinson interpret it as relic from the big bang.
- 1966 - Stephen Hawking and George Ellis show that any plausible general relativistic cosmology is singular
- 1966 - James Peebles shows that the hot Big Bang predicts the correct helium abundance
- 1967 - Andrei Sakharov presents the requirements for baryogenesis, a baryon-antibaryon asymmetry in the universe
- 1967 - John Bahcall, Wal Sargent, and Maarten Schmidt measure the fine-structure splitting of spectral lines in 3C191 and thereby show that the fine-structure constant does not vary significantly with time
- 1968 - Brandon Carter speculates that perhaps the fundamental constants of nature must lie within a restricted range to allow the emergence of life; first use of the strong anthropic principle
- 1969 - Charles Misner formally presents the Big Bang horizon problem
- 1969 - Robert Dicke formally presents the Big Bang flatness problem
- 1973 - Edward Tryon proposes that the universe may be a large scale quantum mechanical vacuum fluctuation where positive mass-energy is balanced by negative gravitational potential energy
- 1974 - Robert Wagoner, William Fowler, and Fred Hoyle show that the hot Big Bang predicts the correct deuterium and lithium abundances
- 1976 - Alex Shlyakhter uses samarium ratios from the Oklo prehistoric natural nuclear fission reactor in Gabon to show that some laws of physics have remained unchanged for over two billion years
- 1977 - Gary Steigman, David Schramm, and James Gunn examine the relation between the primordial helium abundance and number of neutrinos and claim that at most five lepton families can exist.
- 1981 - Alan Guth proposes the inflationary Big Bang universe as a possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems
- 1990 - Preliminary results from NASA's COBE mission confirm the cosmic microwave background radiation is an isotropic blackbody to an astonishing one part in 10 precision, thus eliminating the possibility of an integrated starlight model proposed for the background by steady state enthusiasts.
- 1990s - Ground based cosmic microwave background experiments measure the first peak, determine that the universe is geometrically flat.
- 1998 - Controversial evidence for the fine structure constant varying over the lifetime of the universe is first published.
- 1998 - Adam Riess, Saul Perlmutter and others discover the cosmic acceleration in observations of Type Ia supernovae providing the first evidence for a non-zero cosmological constant. This is confirmed by measurements of the cosmic microwave background radiation by the BOOMERanG experiment
Since 2000
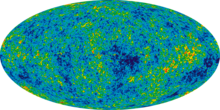
- 2003 - NASA's WMAP takes more detailed pictures of the cosmic microwave background radiation than were obtained by the BOOMERanG experiment. The image can be interpreted to indicate that the universe is 13.7 billion years old (within one percent error) and confirm that the Lambda-CDM model and the inflationary theory are correct.
- 2006 - The long-awaited three-year WMAP results are released, confirming previous analysis, correcting several points, and including polarization data.
See also
Reference
- Bunch, Bryan, and Alexander Hellemans, "The History of Science and Technology: A Browser's Guide to the Great Discoveries, Inventions, and the People Who Made Them from the Dawn of Time to Today". ISBN 0618221239