| Revision as of 00:29, 7 November 2016 edit220.233.98.238 (talk) →1810← Previous edit | Revision as of 00:31, 7 November 2016 edit undoTitodutta (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators156,709 editsm Reverted 1 edit by 220.233.98.238 identified as test/vandalism using STikiNext edit → | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| ===1810=== | ===1810=== | ||
| :] is annexed by ] | :] is annexed by ] | ||
| hey there;p | |||
| ===16 July 1825=== | ===16 July 1825=== | ||
Revision as of 00:31, 7 November 2016
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Territorial evolution of Australia" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
This is a list of the evolution of the borders of the colonies and later states of Australia. It lists each change to the internal and external borders of Australia before and after Federation.

Pre-Federation
7 February 1788

- The colony of New South Wales is founded. New South Wales, according to Arthur Phillip's amended Commission dated 25 April 1787, includes "all the islands adjacent in the Pacific Ocean" and running westward to the 135th meridian east. This included the islands of New Zealand. When drawing up the territorial boundaries of the colony of New South Wales, established in 1788, the British government set its western boundary at the meridian of 135° East of Greenwich, as it appeared on Melchisédech Thévenot's chart, Hollandia Nova‒‒Terre Australe, published in Relations de Divers Voyages Curieux (Paris, 1663).
1810
- Macquarie Island is annexed by New South Wales
16 July 1825
- New South Wales' western border is extended to 129° E.
- 3 December 1825
- The colony of Van Diemen's Land is proclaimed.
2 May 1829
- Swan River Colony is declared by Charles Fremantle for Britain.
6 February 1832
- Swan River Colony has its name changed to Western Australia.
28 December 1836
- The colony of South Australia is proclaimed with its western border set at 132° E.
21 May 1840
- New Zealand is formally annexed to New South Wales.
16 November 1840
- The colony of New Zealand is proclaimed by Letters Patent. Although not represented on a map here, New South Wales was significantly reduced in size by this proclamation. Separation was effected on 3 May 1841.
17 February 1846

- The colony of North Australia was proclaimed by Letters Patent on 17 February. This was all of New South Wales north of 26° S.
15 April 1847

- The colony of North Australia was revoked and reincorporated into New South Wales.
1 July 1851
- The colony of Victoria is proclaimed.
1 January 1856
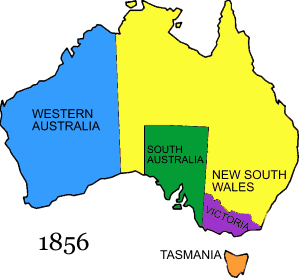
- Van Diemen's Land name is changed to Tasmania.
6 June 1859
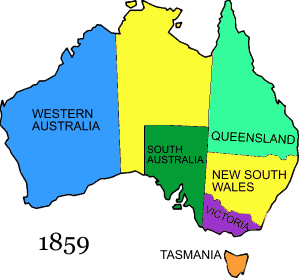
- The colony of Queensland is proclaimed by Letters Patent, with its western border set at 141° E, and settlement began on 10 December that year.
1860

- South Australia border changed from 132° E to 129° E.
1862

- Queensland's western border is moved to 139° E.
6 July 1863

- That part of New South Wales to the north of South Australia was annexed to South Australia by Letters Patent.
1890
- Macquarie Island is transferred from New South Wales to Tasmania.
Post-Federation
1 January 1901

- The Commonwealth of Australia was formed, uniting the British colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia. Note that the Northern Territory was under South Australian administration at Federation.
1 January 1911
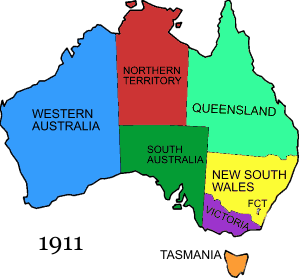
- The Federal Capital Territory was created within New South Wales, and the Northern Territory was split off from South Australia.
12 July 1915

- The coastal area now known as the Jervis Bay Territory is added to the Federal Capital Territory.
1 March 1927

- The Northern Territory was split into the territories of North Australia and Central Australia.
12 June 1931
- North Australia and Central Australia were reunited as the Northern Territory.
29 July 1938
- The Federal Capital Territory's changed its name to the Australian Capital Territory.
11 May 1989
- The Jervis Bay Territory becomes Australia's third mainland territory when the Australian Capital Territory is granted self government.
External Territories
1 July 1914
- Norfolk Island is transferred from New South Wales to the Commonwealth of Australia
23 July 1931
- Ashmore Island and the Cartier Islands are transferred from Britain to Australia
13 June 1933
- The Australian Antarctic Territory is transferred from Britain
26 June 1947
- Heard Island and the McDonald Islands are transferred from Britain
23 November 1955
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are transferred from Singapore to Australia
1 October 1958
- Christmas Island is transferred from Britain
30 September 1969
- The Coral Sea Islands Territory is transferred from Queensland to the Commonwealth of Australia
Former External Territories
- Territory of Papua (1906–42)
- Territory of New Guinea (1920–42)
- Territory of Nauru (1920–68)
- Territory of Papua and New Guinea (1942–71)
- Territory of Papua New Guinea (1971–75)
See also
- States and territories of Australia
- Proposals for new Australian States
- Northern Territory borders
- South Australian borders
- Western Australia border
References
- ^ "A Nation sub-divided". Australian Heritage. Heritage Australia Publishing. 2011. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- Sir Joseph Banks, 'Draft of proposed Introduction to Captn Flinders Voyages', November 1811; State Library of New South Wales, The Papers of Sir Joseph Banks, Series 70.16; quoted in Robert J. King, "Terra Australis, New Holland and New South Wales: the Treaty of Tordesillas and Australia", The Globe, no.47, 1998, pp.35–55, p.35.
- Acting under instructions from England, Captain Fremantle took possession of the Swan River, to found a new colony; and formally laid claim to "all that part of New Holland which is not included within the territory of New South Wales".
External links
- States of Australia – Statoids.com
| Territorial evolution of the world | |
|---|---|
| By country | |
| By former country | |
| By subdivision |
|
| By region |
|
| By country, people, region or period | |
| By international organisation | |