| Revision as of 13:08, 30 September 2017 editRui Gabriel Correia (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers11,371 edits →Varieties: unrelated, unsourced, OR← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:33, 1 October 2017 edit undo83.137.1.199 (talk) →Cationic fabric softenersTag: references removedNext edit → | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| As softeners are often hydrophobic, they commonly occur in the form of an ]. In the early formulations, manufactures used ]s as ]s. The emulsions are usually opaque, milky fluids. However, there are also ]s, where the droplets of the hydrophobic phase are substantially smaller{{Nonspecific|date=August 2011}}. Microemulsions provide the advantage of increased ability of smaller particles to penetrate into the fibers. Manufactures often use a mixture of cationic and non-ionic surfactants as an emulsifier. Another approach is a polymeric network, an emulsion polymer. | As softeners are often hydrophobic, they commonly occur in the form of an ]. In the early formulations, manufactures used ]s as ]s. The emulsions are usually opaque, milky fluids. However, there are also ]s, where the droplets of the hydrophobic phase are substantially smaller{{Nonspecific|date=August 2011}}. Microemulsions provide the advantage of increased ability of smaller particles to penetrate into the fibers. Manufactures often use a mixture of cationic and non-ionic surfactants as an emulsifier. Another approach is a polymeric network, an emulsion polymer. | ||
| ===Cationic fabric softeners=== | === Cationic fabric softeners === | ||
| Rinse-cycle softeners usually contain ]s of the quaternary ammonium type as the main active ingredient. Cationic surfactants adhere well to natural fibers (wool, cotton), but less so to synthetic fibers. Cationic softeners are incompatible with ]s in detergents because they combine with them to form a solid precipitate. This requires that the softener be added in the rinse cycle. Overuse of fabric softener reduces the absorbency of textiles, which adversely effects the function of towels. | |||
| In the 1950s, manufactures introduced ] (DHTDMAC) as a fabric softener, initially to counteract the harsh feel that the machine washing imparted to nappies (cloth diapers). They had to discontinue using this compound because the cation biodegrades very slowly. Contemporary fabric softeners are most often based on salts of ] cations. Characteristically, the cations contain one or two long ] chains derived from fatty acids.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.henkelconsumerinfo.com |title=Henkel Consumer Info |publisher=Henkelconsumerinfo.com |date= |accessdate=2009-06-04}}</ref> Other cationic compounds can be derived from ], substituted amine salts, or quaternary ] ammonium salts.<ref name=Ullmann>E. Smulders, E. Sung "Laundry Detergents, 2. Ingredients and Products" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. {{DOI|10.1002/14356007.o15_013}}</ref> | |||
| Formerly, the active material of most softeners in Europe, the USA, and Japan, was ] (]). Due to its poor biodegradability it has been replaced by the readily biodegradable ]s in the 1980s and 1990s. | |||
| Conventional softeners, which contain 4–8 % active material, have been partially replaced in many countries by softener concentrates having some 12–30 % active material. | |||
| <gallery caption="Cationic surfactants used as fabric softeners" widths="220" heights="100"> | <gallery caption="Cationic surfactants used as fabric softeners" widths="220" heights="100"> | ||
Revision as of 23:33, 1 October 2017
A fabric softener (recently called fabric conditioner by some producers for marketing purposes ) is a chemical compound that is typically applied to laundry during the rinse cycle in a washing machine.
Fabric softeners are available as solutions and solids, and may also be permeated in dryer sheets used in a clothes dryer.
Varieties
Many modern washing machines have a dispenser that adds liquid fabric softener automatically on the final rinse. Users of launderette machines may need to add it manually. Some washing powder brands have fabric conditioning mixed in, which manufacturers claim saves money compared to buying separate washing powder and fabric softener. Some manufacturers claim their products make ironing easier or make clothes dry faster. All liquid fabric softeners are added to water—either by adding the product directly to the final rinse water or by 2:1 (water:softener) dilution in an automatic dispenser. Even diluted fabric softener can cause spotting when poured directly onto clothes, and can ruin them.
Dry fabric softeners are typically supplied in the form of dryer sheets added in the clothes dryer to soften the fabric and prevent buildup of static electricity in susceptible fabrics.
Mechanism of action
Fabric softeners coat the surface of a fabric with chemical compounds that are electrically charged, causing threads to "stand up" from the surface so the fabric feels softer and makes it fluffier. Cationic softeners bind by electrostatic attraction to the negatively charged groups on the surface of the fibers and neutralize their charge. The long aliphatic chains then line up towards the outside of the fiber, imparting lubricity.
Electrically conductive fabric softener chemicals may also prevent static charge buildup in clothes dryers. Other functions manufacturers claim include less friction during ironing, increased stain resistance, reduced wrinkling and pilling, and lower drying time. Most contain fragrances. Cationic fabric softeners are added during the rinse cycle rather than the wash cycle because they can interfere with detergent cleaning action. In addition to fabric softening chemicals, fabric softeners may include acids or bases to maintain optimal pH for absorption, silicone-based anti-foaming agents, emulsion stabilizers, fragrances, and colors.
Composition
Early cotton softeners were typically based on a water emulsion of soap and olive oil, corn oil, or tallow oil. Softening compounds differ in affinity to various fabrics. Some work better on cellulose-based fibers (i.e., cotton), others have higher affinity to hydrophobic materials like nylon, polyethylene terephthalate, polyacrylonitrile, etc. New silicone-based compounds, such as polydimethylsiloxane, work by lubricating the fibers. Manufacturers use derivatives with amine- or amide-containing functional groups as well. These groups improve the softener's binding to fabrics.
As softeners are often hydrophobic, they commonly occur in the form of an emulsion. In the early formulations, manufactures used soaps as emulsifiers. The emulsions are usually opaque, milky fluids. However, there are also microemulsions, where the droplets of the hydrophobic phase are substantially smaller. Microemulsions provide the advantage of increased ability of smaller particles to penetrate into the fibers. Manufactures often use a mixture of cationic and non-ionic surfactants as an emulsifier. Another approach is a polymeric network, an emulsion polymer.
Cationic fabric softeners
Rinse-cycle softeners usually contain cationic surfactants of the quaternary ammonium type as the main active ingredient. Cationic surfactants adhere well to natural fibers (wool, cotton), but less so to synthetic fibers. Cationic softeners are incompatible with anionic surfactants in detergents because they combine with them to form a solid precipitate. This requires that the softener be added in the rinse cycle. Overuse of fabric softener reduces the absorbency of textiles, which adversely effects the function of towels.
Formerly, the active material of most softeners in Europe, the USA, and Japan, was distearyldimethylammonium chloride (DSDMAC). Due to its poor biodegradability it has been replaced by the readily biodegradable esterquats in the 1980s and 1990s.
Conventional softeners, which contain 4–8 % active material, have been partially replaced in many countries by softener concentrates having some 12–30 % active material.
- Cationic surfactants used as fabric softeners
-
 "Monoesterquat" used as fabric softener.
"Monoesterquat" used as fabric softener.
-
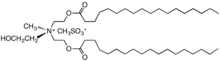 "Diesterquat" used as a fabric softener.
"Diesterquat" used as a fabric softener.
-
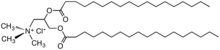 A diesterquat derivative of trimethylamine used as a fabric softener, chloride salt.
A diesterquat derivative of trimethylamine used as a fabric softener, chloride salt.
-
 Distearyldimethylammonium chloride, a fabric softener with low biodegradability, has been phased out.
Distearyldimethylammonium chloride, a fabric softener with low biodegradability, has been phased out.
Anionic fabric softeners
Anionic softeners and antistatic agents can be, for example, salts of monoesters and diesters of phosphoric acid and the fatty alcohols. These are often used together with the conventional cationic softeners. Cationic softeners are incompatible with anionic surfactants in detergents because they combine with them to form a solid precipitate. This requires that they be added in the rinse cycle. Anionic softeners can combine with anionic surfactants directly. Other anionic softeners can be based on smectite clays. Some compounds, such as ethoxylated phosphate esters, have softening, anti-static, and surfactant properties.
Risks
As with soaps and detergents, fabric softeners may cause irritant dermatitis. Manufacturers produce some fabric softeners without dyes and perfumes to reduce the risk of skin irritation. Fabric softener overuse may make clothes more flammable, due to the fat-based nature of most softeners. Several deaths have been attributed to this phenomenon, and fabric softener makers recommend not using them on clothes labeled as flame-resistant.
References
- Terlep, Sharon (16 December 2016). "Millennials Are Fine Without Fabric Softener; P&G Looks to Fix That". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- Cite error: The named reference
Ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - "Fabric softener and anti-static compositions – Patent 4118327". Freepatentsonline.com. 1977-03-28. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
- "Contact dermatitis". Medline. Retrieved 2015-10-24.
- "Liquid fabric softener may make clothes more flammable: Quebec coroner". CBC. Retrieved 2015-11-20.
| Laundry | |
|---|---|
| List of laundry topics | |
| Chemicals | |
| Washing | |
| Drying | |
| Folding | |
| Finishing | |
| Concepts | |
| Organizations | |
| Culture | |
| Accessories | |
| Law | |
| Places | |