| Revision as of 20:39, 17 April 2018 editAWhiteC (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,749 edits rv to latest version by 2601:402:4400:e7bb:30b2:5ca0:c14:60fb; citation by Medic2410 insufficiently precise← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:28, 23 April 2018 edit undo72.141.131.115 (talk) This section provided no citations and was false in its entirety.Tags: section blanking Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 1,216: | Line 1,216: | ||
| ====Kashmiri==== | ====Kashmiri==== | ||
| ] (کشمیری) is a ] spoken in ], ] and ] provinces of ]. There are over 100,000<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/country/PK/languages|title=Pakistan|work=Ethnologue}}</ref> Kashmiri speakers in Pakistan. | ] (کشمیری) is a ] spoken in ], ] and ] provinces of ]. There are over 100,000<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/country/PK/languages|title=Pakistan|work=Ethnologue}}</ref> Kashmiri speakers in Pakistan. | ||
| ====Arabic==== | |||
| {{main|Arab–Pakistan relations}} | |||
| ] is considered to be the religious language of Pakistan. The ], ], ] and Muslim theology is taught in Arabic with ] translation. The large numbers of Pakistanis living in the ] region and in other Middle Eastern countries has further increased the number of people who can speak Arabic in Pakistan. Arabic is taught as a religious language in Mosques, Schools, Colleges, Universities and ]. Nearly all of Pakistan's Muslim population has had some form of education in the reading, writing and pronunciation of the ]. | |||
| Many ] who took part in ] war have now settled in ] permanently with their families. Millions of Pakistanis that have worked in Middle East also speak ] as a second language. | |||
| ====Other Pakistani languages==== | ====Other Pakistani languages==== | ||
Revision as of 19:28, 23 April 2018
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Demographics of Pakistan" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Demographics of {{{place}}} | |
|---|---|
 Population of Pakistan, 1961–2013 Population of Pakistan, 1961–2013 | |
| Population | 207,774,520 (2017 - excluding AJK, GB) |
| Growth rate | 2.10 (2016) |
| Birth rate | 29.8 births / 1,000 population (2016) |
| Death rate | 7.5 deaths / 1,000 population (2016) |
| Life expectancy | 67.7 years (2016) |
| • male | 65.8 years (2016) |
| • female | 69.8 years (2016) |
| Fertility rate | 2.68 children born / woman (2016) |
| Infant mortality rate | 53.86 deaths / 1,000 live births (2016) |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 35.4% (male 35,475,647 / female 33,586,757) |
| 15–64 years | 60.4% (male 60,766,105 / female 56,886,961) |
| 65 and over | 4.2% (male 3,890,840 / female 4,325,538) (Jan. 2017) |
| Sex ratio | |
| At birth | 1.05 male(s) / female (2016) |
| Under 15 | 1.056 male(s) / female (2016) |
| 15–64 years | 1.068 male(s) / female (2016) |
| 65 and over | 0.9 male(s) / female (2016) |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | noun: Pakistani |
| Major ethnic | See Ethnic groups of Pakistan |
| Language | |
| Official | See Languages of Pakistan |
| Spoken | See List of Pakistani languages by number of native speakers |
Pakistan's latest estimated population is 207,774,520 (excluding autonomous regions Azad Kashmir and Gilgit Baltistan). This makes Pakistan the world's fifth-most-populous country, just behind Indonesia and slightly ahead of Brazil. Including Azad Kashmir, the population would be 211.819 million. Gilgit Baltistan region has an additional estimated population of 1.8 million.
During 1950–2011, Pakistan's urban population expanded over sevenfold, while the total population increased by over fourfold. In the past, the country's population had a relatively high growth rate that has been changed by moderate birth rates. Between 1998-2017, the average population growth rate stood at 2.40%.
Dramatic social changes have led to rapid urbanization and the emergence of megacities. During 1990–2003, Pakistan sustained its historical lead as the second-most urbanized nation in South Asia with city dwellers making up 36% of its population. Furthermore, 50% of Pakistanis now reside in towns of 5,000 people or more.
Pakistan has a multicultural and multi-ethnic society and hosts one of the largest refugee populations in the world as well as a young population.
The Demographic history of Pakistan from the ancient Indus Valley Civilization to modern era includes the arrival and settlement of many cultures and ethnic groups in modern region of Pakistan from Central Asia, Middle East and Europe.
Population
Main article: Census in PakistanGeographic distribution
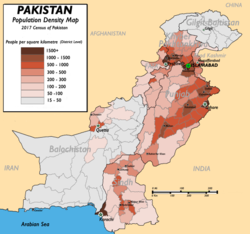
The majority of southern Pakistan's population lives along the Indus River. Karachi is the most populous city in Pakistan. In the northern half, most of the population lives about an arc formed by the cities of Faisalabad, Lahore, Rawalpindi, Sargodha, Islamabad, Multan, Gujranwala, Sialkot, Nowshera, Swabi, Mardan, and Peshawar.
Population size and growth
- Population: 207,774,520 (2017)
- Growth rate: 2.10% (2016)
According to OECD/World Bank, the population in Pakistan increased by 23 million from 1990 to 2008, with a 54% growth in population compared to 34% growth in India and 38% growth in Bangladesh.
Yearly population increase
Pakistan's yearly population from 1950 to 2014, with estimation since last census (1998).
| Year | Population | Absolute increase | Percentage increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 40,381,000 | ||
| 1951 | 41,347,000 | 965,000 | 2.39 |
| 1952 | 42,342,000 | 995,000 | 2.41 |
| 1953 | 43,372,000 | 1,030,000 | 2.43 |
| 1954 | 44,434,000 | 1,062,000 | 2.45 |
| 1955 | 45,536,000 | 1,102,000 | 2.48 |
| 1956 | 46,680,000 | 1,144,000 | 2.51 |
| 1957 | 47,869,000 | 1,189,000 | 2.55 |
| 1958 | 49,104,000 | 1,235,000 | 2.58 |
| 1959 | 50,387,000 | 1,283,000 | 2.61 |
| 1960 | 51,719,000 | 1,332,000 | 2.64 |
| 1961 | 53,101,000 | 1,382,000 | 2.67 |
| 1962 | 54,524,000 | 1,423,000 | 2.68 |
| 1963 | 55,988,000 | 1,464,000 | 2.69 |
| 1964 | 57,495,000 | 1,507,000 | 2.69 |
| 1965 | 59,046,000 | 1,551,000 | 2.70 |
| 1966 | 60,642,000 | 1,596,000 | 2.70 |
| 1967 | 62,282,000 | 1,640,000 | 2.70 |
| 1968 | 63,970,000 | 1,688,000 | 2.71 |
| 1969 | 65,706,000 | 1,736,000 | 2.71 |
| 1970 | 67,491,000 | 1,785,000 | 2.72 |
| 1971 | 69,326,000 | 1,835,000 | 2.72 |
| 1972 | 71,121,000 | 1,795,000 | 2.59 |
| 1973 | 72,912,000 | 1,791,000 | 2.52 |
| 1974 | 74,712,000 | 1,800,000 | 2.47 |
| 1975 | 76,456,000 | 1,744,000 | 2.33 |
| 1976 | 78,153,000 | 1,697,000 | 2.22 |
| 1977 | 80,051,000 | 1,898,000 | 2.43 |
| 1978 | 82,374,000 | 2,323,000 | 2.90 |
| 1979 | 85,219,000 | 2,845,000 | 3.45 |
| 1980 | 88,097,000 | 2,878,000 | 3.38 |
| 1981 | 90,975,000 | 2,878,000 | 3.27 |
| 1982 | 94,096,000 | 3,121,000 | 3.43 |
| 1983 | 96,881,000 | 2,785,000 | 2.96 |
| 1984 | 99,354,000 | 2,473,000 | 2.55 |
| 1985 | 102,079,000 | 2,725,000 | 2.74 |
| 1986 | 105,240,000 | 3,161,000 | 3.10 |
| 1987 | 108,584,000 | 3,344,000 | 3.18 |
| 1988 | 112,021,000 | 3,437,000 | 3.17 |
| 1989 | 115,419,000 | 3,398,000 | 3.03 |
| 1990 | 118,816,000 | 3,397,000 | 2.94 |
| 1991 | 122,248,000 | 3,432,000 | 2.89 |
| 1992 | 124,962,000 | 2,714,000 | 2.22 |
| 1993 | 127,563,000 | 2,601,000 | 2.08 |
| 1994 | 130,746,000 | 3,183,000 | 2.50 |
| 1995 | 134,185,000 | 3,439,000 | 2.63 |
| 1996 | 137,911,000 | 3,726,000 | 2.78 |
| 1997 | 141,445,000 | 3,534,000 | 2.56 |
| 1998 | 144,885,000 | 3,440,000 | 2.43 |
| 1999 | 148,379,000 | 3,494,000 | 2.41 |
| 2000 | 152,429,000 | 4,050,000 | 2.73 |
| 2001 | 156,795,000 | 4,366,000 | 2.86 |
| 2002 | 160,269,000 | 3,474,000 | 2.22 |
| 2003 | 163,166,000 | 2,897,000 | 1.81 |
| 2004 | 166,224,000 | 3,058,000 | 1.87 |
| 2005 | 169,279,000 | 3,055,000 | 1.84 |
| 2006 | 172,382,000 | 3,103,000 | 1.83 |
| 2007 | 175,495,000 | 3,113,000 | 1.81 |
| 2008 | 178,479,000 | 2,984,000 | 1.70 |
| 2009 | 181,457,000 | 2,978,000 | 1.67 |
| 2010 | 184,405,000 | 2,948,000 | 1.62 |
| 2011 | 187,343,000 | 2,938,000 | 1.59 |
| 2012 | 190,284,285 | 2,941,285 | 1.57 |
| 2013 | 193,271,748 | 2,987,463 | 1.55 |
| 2014 | 196,228,805 | 2,957,057 | 1.53 |
UN estimates
| Total population (in thousands) | Population aged 0–14 (%) | Population aged 15–64 (%) | Population aged 65+ (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 37,547 | 40.3 | 54.1 | 5.6 |
| 1955 | 41,109 | 40.3 | 54.8 | 4.9 |
| 1960 | 45,920 | 40.4 | 55.3 | 4.3 |
| 1965 | 51,993 | 41.6 | 54.5 | 3.9 |
| 1970 | 59,383 | 42.6 | 53.6 | 3.8 |
| 1975 | 68,483 | 43.2 | 53.1 | 3.7 |
| 1980 | 80,493 | 43.4 | 52.9 | 3.7 |
| 1985 | 95,470 | 43.4 | 52.9 | 3.8 |
| 1990 | 111,845 | 43.7 | 52.5 | 3.8 |
| 1995 | 127,347 | 43.3 | 52.9 | 3.8 |
| 2000 | 144,522 | 41.4 | 54.7 | 3.9 |
| 2005 | 158,645 | 38.1 | 57.8 | 4.1 |
| 2011 | 173,593 | 35.4 | 60.3 | 4.3 |
Structure of population
The following statistics are for 1 July 2007. They exclude data for Azad Kashmir, the final status of which has not yet been determined. They are based on the results of the Pakistan Demographic Survey (PDS 2007).
The structure of the population by five-year age groups and gender is:
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 76 857 737 | 73 002 651 | 149 860 388 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 9 783 859 | 9 756 608 | 19 540 467 | 13,04 |
| 5–9 | 11 710 324 | 10 844 307 | 22 554 631 | 15,05 |
| 10–14 | 10 636 015 | 9 619 874 | 20 255 889 | 13,52 |
| 15–19 | 9 063 876 | 8 211 804 | 17 275 679 | 11,53 |
| 20–24 | 6 824 723 | 6 733 861 | 13 558 584 | 9,05 |
| 25–29 | 5 268 436 | 5 564 656 | 10 833 092 | 7,23 |
| 30–34 | 3 957 414 | 4 474 911 | 8 432 325 | 5,63 |
| 35–39 | 4 132 910 | 4 219 507 | 8 352 417 | 5,57 |
| 40–44 | 3 496 263 | 3 281 389 | 6 777 652 | 4,52 |
| 45–49 | 3 277 150 | 2 999 342 | 6 276 492 | 4,19 |
| 50–54 | 2 429 295 | 2 156 822 | 4 586 117 | 3,06 |
| 55–59 | 1 864 568 | 1 679 608 | 3 544 175 | 2,36 |
| 60–64 | 1 637 251 | 1 296 418 | 2 933 669 | 1,96 |
| 65–69 | 1 106 476 | 932 030 | 2 038 506 | 1,36 |
| 70–74 | 857 310 | 606 846 | 1 464 156 | 0,98 |
| 75–79 | 358 255 | 295 833 | 654 088 | 0,44 |
| 80–84 | 250 734 | 177 547 | 428 280 | 0,29 |
| 85+ | 202 880 | 151 288 | 354 168 | 0,24 |
The structure of the population by coarse age groups and gender is:
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–14 | 32 130 198 | 30 220 789 | 62 350 987 | 41,61 |
| 15–64 | 41 951 884 | 40 618 318 | 82 570 202 | 55,10 |
| 65+ | 2 775 655 | 2 163 544 | 4 939 199 | 3,30 |
Gender ratios
- Sex ratio at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
- 15–64 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.92 male(s)/female
- total population: 1.07 male(s)/female (2011)
Vital statistics
| Year | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR | CDR | NC | TFR | IMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 1 652 000 | 937 000 | 715 000 | 42.0 | 23.8 | 18.2 | 6.60 | 176.6 |
| 1955–1960 | 1 873 000 | 907 000 | 966 000 | 43.0 | 20.9 | 22.1 | 6.60 | 156.3 |
| 1960–1965 | 2 128 000 | 894 000 | 1 233 000 | 43.5 | 18.3 | 25.2 | 6.60 | 139.5 |
| 1965–1970 | 2 407 000 | 887 000 | 1 520 000 | 43.2 | 15.9 | 27.3 | 6.60 | 125.7 |
| 1970–1975 | 2 738 000 | 890 000 | 1 848 000 | 42.8 | 13.9 | 28.9 | 6.60 | 114.8 |
| 1975–1980 | 3 197 000 | 935 000 | 2 262 000 | 42.9 | 12.6 | 30.3 | 6.60 | 106.6 |
| 1980–1985 | 3 746 000 | 1 019 000 | 2 726 000 | 42.6 | 11.6 | 31.0 | 6.44 | 101.5 |
| 1985–1990 | 4 367 000 | 1 120 000 | 3 247 000 | 42.1 | 10.8 | 31.3 | 6.30 | 96.7 |
| 1990–1995 | 4 566 000 | 1 166 000 | 3 400 000 | 38.2 | 9.7 | 28.5 | 5.67 | 90.1 |
| 1995–2000 | 4 674 000 | 1 201 000 | 3 473 000 | 34.4 | 8.8 | 25.6 | 5.00 | 83.2 |
| 2000–2005 | 4 387 000 | 1 213 000 | 3 175 000 | 28.9 | 8.0 | 20.9 | 4.00 | 76.8 |
| 2005–2010 | 4 666 000 | 1 277 000 | 3 390 000 | 28.1 | 7.7 | 20.4 | 3.65 | 70.9 |
| CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births | ||||||||
Vital statistics
| Year (1st July). | Population (in thousands) | Live births (in thousands) | Deaths (in thousands) | Natural change (in thousands) | Crude birth rate (per 1.000) | Crude death rate (per 1.000) | Natural change (per 1.000) | Fertility rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 173 500 | 4 820 | 1 290 | 3 530 | 27.5 | 7.3 | 20.2 | 3.5 |
| 2010 | 177 100 | 4 820 | 1 290 | 3 530 | 27.5 | 7.3 | 20.2 | 3.5 |
| 2011 | 180 710 | 4 915 | 1 301 | 3 614 | 27.2 | 7.2 | 20.0 | 3.4 |
| 2012 | 184 350 | 4 941 | 1 291 | 3 650 | 26.8 | 7.0 | 19.8 | 3.3 |
| 2013 | 188 020 | 4 964 | 1 297 | 3 667 | 26.4 | 6.9 | 19.5 | 3.2 |
| 2014 | 191 710 | 5 003 | 1 303 | 3 700 | 26.1 | 6.8 | 19.3 | 3.2 |
| 2015 | 195 400 | 5 002 | 1 309 | 3 693 | 25.6 | 6.7 | 18.9 | 3.1 |
| 2016 | 199 710 | 5 033 | 1 318 | 3 715 | 25.2 | 6.6 | 18.6 | 3.0 |
Fertility Rate (The Demographic Health Survey)
Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and CBR (Crude Birth Rate):
| Year | CBR (Total) | TFR (Total) | CBR (Urban) | TFR (Urban) | CBR (Rural) | TFR (Rural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990–1991 | 5,4 (4,7) | 4,9 (3,8) | 5,6 (5,1) | |||
| 2006–2007 | 30,7 | 4,1 (3,1) | 27,6 | 3,3 (2,5) | 32,3 | 4,5 (3,4) |
| 2010–2012 | 3,8 (2,9) | 3,2 (2,4) | 4,2 (3,1) |
Fertility by region 2010–2012 (released in 2012–13)
| Region | Fertility rate |
|---|---|
| Urban | 3.2 |
| Rural | 4.2 |
| Overall | 3.8 |
| ICT Islamabad | 3.0 |
| Punjab | 3.8 |
| Gilgit-Baltistan | 3.8 |
| Sindh | 3.9 |
| Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 3.9 |
| Balochistan | 4.2 |
Contraceptives usage (%) 2010–2012 (released in 2012–13)
| Region | Contraceptives usage (%) |
|---|---|
| Urban | 44.8% |
| Rural | 30.7% |
| Overall | 35.4% |
| ICT Islamabad | 59.4% |
| Punjab | 40.7% |
| Gilgit-Baltistan | 33.6% |
| Sindh | 29.5% |
| Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 28.1% |
| Balochistan | 19.5% |
Mortality and life expectancy
- Maternal mortality ratio: 320 (2009 est.)
- Life expectancy at birth:
- total population: 65.5 years (2007 est.)
- male: 66.5 years (2009 est.)
- female: 67.2 years (2009 est.)
As adultery is a crime punishable by death in Pakistan, just in the main cities 1,210 infants were killed or abandoned to die (2010), 90% of them girls and most less than a week old according to conservative estimates by the Edhi Foundation, a charity working to reverse this increasing trend.
Human development
Human Development Index
Further information: List of Pakistani Districts by Human Development IndexAccording to the 2009 Human Development Report of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), 60.3% of Pakistanis live on less than $2 a day.
| Province | Human Development Index | Comparable country | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medium human development | |||
| Punjab | 0.670 | ||
| Sindh | 0.628 | ||
| Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 0.607 | ||
| Balochistan | 0.556 | ||
Sources: Information on Pakistani regions: Information on other countries: All Estimated at three decimal places.
| Region | Human Development Index | Comparable country | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medium human development | |||
| Urban Sindh | 0.659 | ||
| Urban Punjab | 0.657 | ||
| Urban Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 0.627 | ||
| Urban Balochistan | 0.591 | ||
| Rural Punjab | 0.517 | ||
| Low human development | |||
| Rural Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 0.489 | ||
| Rural Balochistan | 0.486 | ||
| Rural Sindh | 0.456 | ||
| Region | Human Development Index | Comparable country | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medium human development | |||
| Urban Pakistan | 0.656 | ||
| Low human development | |||
| Rural Pakistan | 0.496 | ||
Note: Regarding the above two tables, information on Pakistan has been taken from the PAKISTAN NATIONAL HUMAN DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2003 and for the countries of the world, information has been taken from the Human Development Report 2006 as it best reflects the time when data was taken for Pakistan. Pakistan National Human Development Report gave Pakistan an HDI score of 0.541 whereas the Human Development Report 2006 gave it a score of 0.539.
Sources:
Literacy
definition: aged 10 and over and can read and write as of 2008–09
- Total population: 60%
- Male: 69%
- Female: 45%
Educational institutions by kind
- Primary schools: 156,592
- Middle schools: 320,611
- High schools: 23,964
- College of Arts and Sciences: 3,213
- Degree colleges: 1,202
- Technical and vocational institutions: 3,125
- Universities: 197
Nationality, ethnicity, and language
Ethnic groups

| Ethnic groups in Pakistan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Punjabi | 44.68% | |||
| Pashtun (Pathan) | 15.42% | |||
| Sindhi | 14.10% | |||
| Saraiki | 8.38% | |||
| Muhajir | 7.57% | |||
| Balochi | 3.57% | |||
| Other | 6.28% | |||
Pakistan's diversity is more visible along cultural differences and less along linguistic, religious or genetic lines. Almost all Pakistanis belong to the Indo-Iranian linguistic group of the Indo-European branch. Pakistan's rough estimates vary, but the consensus is that the Punjabis are the largest ethnic group. Pashtuns (Pakhtuns) make up the second largest group and Sindhi are the third-largest ethnic group. Saraikis (a transitional group between Punjabis and Sindhis) make up 10.53% of the total population. The remaining large groups include the Muhajirs and the Baloch people, which make up 7.57% and 3.57% of the total population, respectively. Hindkowans and the Brahui, and the various peoples of the Gilgit–Baltistan, constitute roughly 4.66% of the total population. The Pakhtun and Baloch represent two of the major populations that are linguistically Iranian, while the majority Punjabis, Hindkowans, Sindhis and Saraikis are the major linguistically Indo-Aryan groups.
Descendents of Black Africans that were brought as slaves in the 15th to the 19th century are known as Sheedis. The Sheedis are Muslims and speak Balochi, Sindhi and Urdu.
In 1850, the British started developing Karachi as a major port for trade and commerce, resulting in the arrival of a large number immigrants from Rajasthan, Gujarat and Goa. The Goan Catholics constitute the majority of the Christians in the city.
After the Pakistan–India war in 1971, thousands of Biharis and Bengalis from Bangladesh arrived in the Karachi, followed by Muslim Rohingya refugees from Burma, and Asians from Uganda.
Approximately 1.4 million Afghan citizens reside in Pakistan on a temporary bases. Many of them were born and raised in Pakistan in the last 30 years. The majority of this group are ethnic Pakhtuns from southeastern Afghanistan.
All major ethnic groups in Pakistan, while categorized as separate entities, have thousands of years of shared history and inter-mingling. In addition, inter-marriages between ethnic groups within the country are not uncommon.
Foreign-born population in Pakistan
Main article: Immigration to PakistanAfter the independence of Pakistan in 1947, many Muslims from India migrated to Pakistan and they are the largest group of foreign-born residents. This group is dwindling because of its age. The second-largest group of foreign-born residents consists of Muslim refugees from Afghanistan who are expected to leave Pakistan by the end of 2018. There are also smaller groups of Muslim immigrants from countries such as Burma, Bangladesh, Iraq, Somalia, Iran, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, among others.

| Year | Population | Foreign born | Percentage foreign born |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 46,259,000 | 6,350,296 | 13.73% |
| 1970 | 59,565,000 | 5,105,556 | 8.57% |
| 1980 | 79,297,000 | 5,012,524 | 6.32% |
| 1990 | 111,698,000 | 6,555,782 | 5.87% |
| 2000 | 142,648,000 | 4,242,689 | 2.97% |
| 2005 | 157,935,000 | 3,254,112 | 2.06% |
Source:
Languages
Main article: Languages of Pakistan| Rank | Language | 1998 census | 1981 census | 1961 census | 1951 census |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Punjabi* | 44.15% | 48.17% | 56.39% | 57.08% |
| 2 | Pashto | 15.42% | 13.35% | 8.47% | 8.16% |
| 3 | Sindhi | 14.1% | 12.7% | 12.59% | 12.85% |
| 4 | Saraiki* | 10.53% | 9.54% | ||
| 5 | Urdu | 7.57% | 7.60% | 7.57% | 7.05% |
| 6 | Balochi | 3.57% | 3.02% | 2.49% | 3.04% |
{* Saraiki was included with Punjabi in the 1951 and 1961 censuses.}
Following are the major languages spoken in Pakistan. The percentage of Pakistanis who are native speakers of that language is also given.
| Language | 2008 estimate | 1998 census | Main areas spoken | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Punjabi | 76,369,930 | 44.17% | 58,433,431 | 44.15% | Punjab | |||
| 2 | Pashto | 26,695,760 | 15.44% | 20,408,621 | 15.42% | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | |||
| 3 | Sindhi | 26,540,150 | 15.35% | 18,661,571 | 14.10% | Sindh | |||
| 4 | Saraiki | 18,016,180 | 10.42% | 13,936,594 | 10.53% | South Punjab | |||
| 5 | Urdu | 13,123,110 | 7.59% | 10,019,576 | 7.57% | Karachi, Sindh | |||
| 6 | Balochi | 6,207,110 | 3.59% | 4,724,871 | 3.57% | Balochistan | |||
| 7 | Others | 5,947,760 | 3.44% | 6,167,515 | 4.66% | ||||
| Total | 172,900,000 | 100% | 132,352,279 | 100% | Pakistan | ||||
| Languages of Pakistan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Punjabi | 48% | |||
| Sindhi | 12% | |||
| Saraiki | 10% | |||
| Pashto (Pathan) | 8% | |||
| Urdu | 8% | |||
| Balochi | 3% | |||
| Hindko | 2% | |||
| Brahui | 1% | |||
| Other | 8% | |||
There are around 75 to 80 known Pakistani languages although, in practice, there are primarily six major languages in Pakistan spoken by 95% of the population: Punjabi, Pashto, Sindhi, Saraiki, Urdu, and Balochi. The official language is English and the national language is Urdu, the census indicates that around 8% of the population speak Urdu as their first language. However, due to rapid urbanization and modernization, the use of Urdu as a primary language is increasing, especially amongst the growing urbanized middle class of Pakistan. Most Pakistanis speak or understand at least two to three languages and almost all Pakistanis speak or understand the national language, Urdu.
The most prevalent native languages appear in bold below, with the percentage of the population speaking them as their first language rounded to the nearest percentage point:
Column-generating template families
The templates listed here are not interchangeable. For example, using {{col-float}} with {{col-end}} instead of {{col-float-end}} would leave a <div>...</div> open, potentially harming any subsequent formatting.
| Type | Family | Handles wiki table code? |
Responsive/ mobile suited |
Start template | Column divider | End template |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float | "col-float" | Yes | Yes | {{col-float}} | {{col-float-break}} | {{col-float-end}} |
| "columns-start" | Yes | Yes | {{columns-start}} | {{column}} | {{columns-end}} | |
| Columns | "div col" | Yes | Yes | {{div col}} | – | {{div col end}} |
| "columns-list" | No | Yes | {{columns-list}} (wraps div col) | – | – | |
| Flexbox | "flex columns" | No | Yes | {{flex columns}} | – | – |
| Table | "col" | Yes | No | {{col-begin}}, {{col-begin-fixed}} or {{col-begin-small}} |
{{col-break}} or {{col-2}} .. {{col-5}} |
{{col-end}} |
Can template handle the basic wiki markup {| | || |- |} used to create tables? If not, special templates that produce these elements (such as {{(!}}, {{!}}, {{!!}}, {{!-}}, {{!)}})—or HTML tags (<table>...</table>, <tr>...</tr>, etc.)—need to be used instead.
English
English is the official language, being widely used within the government, by the civil service and the officer ranks of the military. Pakistan's Constitution and laws are written in English. Nearly all schools, colleges and universities use English as the medium of instruction. Amongst the more educated social circles of Pakistan, English is seen as the language of upward mobility and its use is becoming more prevalent in upper social circles, often spoken alongside native Pakistani languages. Among countries that use English as an official language, Pakistan is the third-most populous in the world.
Urdu
Urdu is the national language of Pakistan, the lingua franca chosen to facilitate communication between the country's diverse linguistic populations. Although only about 7.5% of Pakistanis speak it as their first language, it is spoken as a second and often third language by nearly all Pakistanis.
On the annexation of Sindh (1843) and Punjab (1849), the British Raj encouraged its use as the lingua franca and subsequently banned the use of Persian, which had been the lingua franca of the region for many centuries before. Persian had been introduced by Central Asian Turkic invaders who migrated into South Asia, and had been patronised by the Turko-Afghan Delhi Sultanate. This language change was designed to institute a universal language throughout the then British Raj in South Asia as well as minimize the influence that Persia, the Ottoman Empire and Afghanistan had on this transitional region.
Urdu is a relatively new language but has undergone considerable modification and development, with many borrowings from older languages such as Persian, Arabic, Turkish and local South Asian languages. It is a standardized register of Hindustani and in its spoken form. It is widely used, both formally and informally, for personal letters as well as public literature, in the literary sphere and in the popular media. It is a required subject of study in all primary and secondary schools. It is the first language of most Muhajirs – Muslim refugees that arrived from different parts of India after the independence of Pakistan in 1947, and that form nearly 8% of Pakistan's population – and is an acquired language by nearly all of Pakistan's native ethnic groups. It is spoken by almost 92% of the population, making Pakistan a unique country in its choice of national language. Urdu has been promoted as a token of national unity.
In recent years, the Urdu spoken in Pakistan has undergone further evolution and acquired a particularly "Pakistani flavour", often absorbing local native terminology and adopting a strong Punjabi, Sindhi and Pashto leaning in terms of intonations and vocabulary. It is a modern language which is constantly evolving from its original form. It is written in a modified form of the Perso-Arabic script, Nastaliq, and its basic Hindi-based vocabulary has been enriched by words from Persian, Arabic, Turkic languages and English. Urdu has drawn inspiration from Persian literature and has now an enormous stock of words from that language.
The first poetry in Urdu was by the poet Amir Khusro (1253–1325) and the first Urdu book Woh Majlis was written in 1728; the first time the word "Urdu" was used was by Sirajuddin Ali Khan Arzoo in 1741. The Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb Alamgir (1658–1707) spoke Urdu (or Hindustani) fluently as did his descendents while his ancestors mostly spoke Persian and Turkish.
Punjabi
Punjabi is a provincial language spoken mostly in Punjab, as well as by a large number of people in Karachi. Punjabi does not have any official status in Pakistan. The exact number of Punjabi speakers in Pakistan is hard to determine since the boundaries with the closely related Hindko and Saraiki are not always clear-cut. The standard Punjabi variety is from Lahore, Sialkot, Gujranwala and Sheikhupura districts of Pakistani Punjab, and is also nowadays the language of Punjabi literature, film and music, such as Lollywood.
Pashto
Pashto is a provincial language spoken as a first language by about 15% of Pakistanis, mostly in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and in Balochistan as well as by immigrants to the eastern provinces. There are two major dialect patterns within which the various individual dialects may be classified; these are Pakhto, which is the Northern (Peshawar) variety, and the softer Pashto spoken in the southern areas. There are also many Pakistanis from the adjacent regions of Punjab, Sindh and Balochistan who are conversant in Pashto and count it as their second language. They are not included in the overall percentage.
The Pashtuns (Pakhtuns or Pathans), originally from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, FATA and northern Balochistan, are now the city's second largest ethnic group in Karachi after Muhajirs. With as high as 7 million by some estimates, the city of Karachi in Pakistan has the largest concentration of urban Pakhtun population in the world, including 50,000 registered Afghan refugees in the city. Karachi is the biggest Pashto speaking city in the world although the Pashto speakers constitute only about 25% of Karachi's population.
Sindhi
Sindhi is a provincial language spoken as a first language by 15% of Pakistanis, mostly in Sindh. It has a rich literature and is used in schools. It is an Indo-Aryan (Indo-European) language, derived from Sanskrit. The Arabs ruled Sindh for more than 150 years after Muhammad bin Qasim conquered it in 712 AD, remaining there for three years to set up Arab rule. Consequently, the social fabric of Sindh contains elements of Arabic society. Sindhi is spoken by over 36 million people in Pakistan, and is the official language of Sindh province. It is widely spoken in the Lasbela District of Balochistan (where the Lasi tribe speaks a dialect of Sindhi), many areas of the Naseerabad and Jafarabad districts of Balochistan, and by the Sindhi diaspora abroad. Sindhi language has six major dialects: Sireli, Vicholi, Lari, Thari, Lasi and Kachhi. It is written in the Arabic script with several additional letters to accommodate special sounds. The largest Sindhi-speaking cities are Karachi, Hyderabad, Sukkur, Shikarpur, Dadu, Jacobabad, Larkana, Mirpur Khas, Thatta, Badin and Nawabshah. Sindhi literature is also spiritual in nature. Shah Abdul Latif Bhita'i (1689–1752) is one of its greatest poets, and wrote Sassi Punnun and Umar Marvi, folk stories, in his famous book Shah Jo Risalo.
Sindhi dialects:
- Sindhi Saraiki – spoken mainly in Upper Sindh
- Vicholi – in Vicholo, i.e. Central Sindh
- Lari – in Laru, i.e. Lower Sindh
- Lasi – in Lasa B’elo, a part of Kohistan in Baluchistan on the western side of Sindh
- Thari or Thareli – in Tharu, the desert region on the southeast border of Sindh and a part of the Jaisalmer district in Rajasthan
- Kachhi – in the Kutch region and in a part of Kathiawar in Gujarat, on the southern side of Sindh
Vicholi is considered as the standard dialect by all Sindhi speakers.
Saraiki
Saraiki, sometimes spelled Seraiki and Siraiki, is spoken as a first language by about 20 million people, mostly in the southern districts of Punjab: Multan, Lodhran, Bahawalpur, Layyah, Dera Ghazi Khan, Muzaffargarh and Rahim Yar Khan. It is also spoken by the majority of the population of Dera Ismail Khan District in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, Kachi plain of Balochistan, northern parts of Sindh, and cities of Hyderabad and Karachi.
Balochi
Balochi is a provincial language spoken as first language by about 3.5% of Pakistanis, mostly in Balochistan. Sindh and southern Punjab. The name Balochi or Baluchi is not found before the 10th century. It is believed that the language was brought to its present location in a series of migrations Aleppo, Syria. Rakshani is the major dialect group in terms of numbers. Sarhaddi, is a sub dialect of Rakshani. Other sub – dialects are Qalati, Chagai Kharani, and Makrani. The Eastern Hill Balochi or Northern Balochi are distinct dialects.The Kethran language in North East Balochistan is also a variant of Balochi. It is one of the 9 distinguished languages of Pakistan. Since Balochi is a poetic and rich language and have a certain degree of affinity to Urdu, Balochi poets tend to be very good poets in Urdu as well as Ata Shaad, Gul Khan Nasir and Noon Meem Danish are excellent examples of this.
Brahui
Brahui (Template:Lang-ur) is a regional language of uncertain origin despite the fact that the bulk of the language shares lexical similarities to Balochi as well as Sindhi. In colonial times, many British linguists tried to make the claim of a possible Dravidian language origin but this has not been conclusively proven despite ongoing research in the language for a century now. spoken in southern Pakistan, may have evolved from the original languages of Indus valley civilizations at Mehrgarh. However it is heavily influenced by Balochi and Pashto. It is spoken in central and east central Balochistan. The Mengals are a famous Brahvi tribe. Around 1–1.5% of Pakistani population has Brahui as their first language. It is one of the nine distinguished languages of Pakistan.
The Brahui population of Balochistan has been taken by some as the linguistic equivalent of a relict population, perhaps indicating that Dravidian languages were formerly much more widespread and were supplanted by the incoming Indo-Aryan languages. However it has now been demonstrated that the Brahui could only have migrated to Balochistan from central India after 1000 CE. The absence of any Avestan, an older Iranian language, loanwords in Brahui supports this hypothesis. The main Iranian contributor to Brahui vocabulary, Balochi, is a western Iranian language like Kurdish, and moved to the area from the west only around 1000 CE.
Hazaragi
Hazaragi, spoken by the Hazaras in Pakistan, is similar to Dari. It is spoken in parts of the Quetta district of Karachi, Islamabad, and in parts of Ziarat. There are estimated to be 900,000 to 1,000,000 Hazaragi-speakers.
Hindko
Hindko, spoken by the Hindkowans in Pakistan, is similar to the northern dialects of Punjabi. It is spoken in areas of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (including Hazara), Peshawar city, Punjab and Azad Kashmir, by an estimated 2 million people. It shows close affinity to Punjabi and the Lahnda sub-group of Indo-Aryan tongues and can be sub-divided into a northern and southern dialects.
Kashmiri
Kashmiri (کشمیری) is a Dardic language spoken in Azad Kashmir, Gilgit–Baltistan and Punjab provinces of Pakistan. There are over 100,000 Kashmiri speakers in Pakistan.
Other Pakistani languages
Numerous other languages are spoken by relatively small numbers of people, especially in some of the more remote and isolated places in, for example, the Northern Areas of Pakistan. Other Indo-European languages spoken in Pakistan include Pothohari, Shina, Balti, Gujjari, Kutchi, Wakhi, Kashmiri, Marwari, Memoni, Khowar, and Dari Persian. Non-Indo-European languages include Brahui and Burushaski, a language isolate.
There are some languages that are spoken by less than a thousand people, such as Aer.
Classification
Indo-European
Most of Pakistan's languages are Indo-European languages and within the smaller Indo-Iranian sub-branch.
Indo-Aryan languages
Around 80% of Pakistan's population speak one or more of the various Indo-Aryan languages. Usually concentrated in the heavily populated areas east of the Indus river, the Indo-Aryan languages and their cultures form the predominant cultural group in the country. They derive their roots from the Sanskrit language of Aryan invadors and are later heavily influenced by the languages of the later Muslim arrivals (i.e., Turkish, Persian, and Arabic), and are all written in a variant of either the Arabic or Nastaliq script. Urdu, the country's national language, is an Indo-Aryan tongue. Punjabi, Hindko and Seraiki, all mutually intelligible, are classified by linguists as dialects of an Indo-Aryan speech called Lahnda, also spelled as Lehnda. These are also, to a lesser extent, mutually intelligible with Urdu. Added together, speakers of these mutually-intelligible languages make up nearly two-thirds of Pakistan's population. Sindhi is the common language of the people of Sindh in southern Pakistan and has a rich literary history of its own, traced back to the era of the early Arab arrivals. The Dardic languages of Gilgit–Baltistan, Azad Kashmir and the northwestern mountains are sometimes classified by many linguists as belonging to the Indo-Aryan family. Other Indo-Aryan languages include Gujarati, Kutchi, Memoni and others.
Dardic languages
The Dardic languages are spoken in the northern Pakistan. They include Shina (spoken in Gilgit, Chilas and Diamar), Khowar (spoken in Chitral, Ghizer, Swat and the balti language (spoken in including district and district. Majority of population living in the valley of Hunza, Nagar and Yasin speak Mishaski. Kalam Valley of upper Swat), Kalash (spoken by Kalash tribe), Kohistani (spoken in upper Swat and Kohistan) and Kashmiri mostly by Immigrants from Kashmir valley and by a few in the Neelum District.
Kashmiri spoken in north east Azad Kashmir and the adjacent Kashmir valley, (not to be confused with Pahari language spoken in the lower Azad Kashmir) is one of the Dardic languages that has a literary tradition that goes well back into the history whereas other Dardic languages spoken in northern Pakistan, do not have written literature. It is believed to be the result of the northern areas of Pakistan having remained isolated in the mountain valleys from the others for centuries.
Iranian
Pashto, Yidgha and Wakhi are Eastern Iranian languages spoken in Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Balochistan and the Gilgit–Baltistan region of Pakistan. Balochi spoken in Balochistan is classified as a members of the Northwestern Iranian languages. If combined, Iranian peoples who speak Pashto, Balochi, Yidgha and Wakhi comprise about 18% of the population of Pakistan, and are concentrated in the northwest and west of Pakistan.
Brahui
Brahui may or may not be a language isolate and many origins have been hypothesized for it including Iranian and Dravidian. spoken in southern Pakistan, primarily in Kalat in Balochistan. The Brahui population of Balochistan has been taken by some as the linguistic equivalent of a relict population, perhaps indicating that Dravidian languages were formerly much more widespread and were supplanted by the incoming Indo-Aryan languages. However it has now been demonstrated that the Brahui could only have migrated to Balochistan from central India after 1000 CE. The absence of any Avestan, an older Iranian language, loanwords in Brahui supports this hypothesis. The main Iranian contributor to Brahui vocabulary, Balochi, is a western Iranian language like Kurdish, and moved to the area from the west only around 1000 CE.
Burushaski
Burushaski is a language isolate, spoken by Burusho people in Hunza, Nagar, Yasin, and parts of the Gilgit valleys in the Gilgit–Baltistan region of Pakistan.
Religion
Main article: Religion in PakistanReligion in Pakistan (2010)
Islam (96.4%) Other (includes Christian and Hindu) (3.6%)According to the CIA World Factbook, Library of Congress, Oxford University, over 97% of the population of Pakistan is Muslim and the remaining 3% is Christian, Hindu and others. Majority of the Muslims practice Sunni with a significant minority of Shi'as.
Nearly all Pakistani Sunni Muslims belong to the Hanafi school, although there are some Hanbalis and Ahlul Hadeeth. The majority of Shia Muslims belong to the Ithnā‘Ashariyyah branch, while a smaller number practice Ismailism. The Ahmadis make up approximately 2.2% of the Muslim population. There are small non-Muslim religious groups, including Christians, Jews, Hindus, Buddhists, Sikhs, Parsis, Bahá'ís and Zoroastrians (Parsis).
The religious breakdown of the Pakistani population is as follows:
- Muslims: 181,723,000
- Christians: 2,700,000 (approx. 1.8%)
- Hindus: 1,800,000 (approx. 1.6%)
- Ahmadiyya in Pakistan: 4,000,000 (approx 2.2%)
- Buddhists: 106,989
- Sikhs: 30,000
- Zoroastrian/Parsis:
- Jews:
- Animists, Baha'i, Atheists: n/a
Pakistanis around the world
| 1,500,000 | |
| 1,200,000 | |
| 1,200,000 | |
| 600,410 | |
| 350,000 | |
| 100,000 | |
| 85,000 | |
| 61,913 | |
| 52,668 | |
| 52,500 | |
| 50,000 | |
| 35,000 | |
| 21,000 | |
| 9,501 |
See also
References
- ^ "Provisional Summary Results of 6th Population and Housing Census – 2017". Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ "Pakistan population – Demographics of Pakistan 2016". Country Meters. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ "Pakistan, Selected Rankings - 2016". Geoba.se. Retrieved 15 April 2017.
- "The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- Burke, Jason (17 August 2008). "Pakistan looks to life without the general". The Guardian. London.
- CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion Population 1971–2008 (pdf pages 83–85) IEA (OECD/ World Bank) (original population ref OECD/ World Bank, e.g. in IEA Key World Energy Statistics 2010 page 57)
- "International Programs".
- ^ Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision Archived 6 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "Demographic Yearbook". UN Data. United Nations. Retrieved 4 December 2015.
- "- Ministry of Finance - Government of Pakistan -". www.finance.gov.pk. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- "The DHS Program".
- ^ http://measuredhs.com/pubs/pdf/PR35/PR35.pdf
- ^ "United Nations Population Fund". UNFPA. Archived from the original on 25 January 2009. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "World Bank, World Development Indicators – Google Public Data Explorer". Google.com. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- Hasan Mansoor (18 January 2011). "Killings of newborn babies on the rise in Pakistan". AFP. Retrieved 19 January 2011.
- Hosain, Maha (6 April 2010). "How to Warm Ties Among Indians and Pakistanis". Businessweek. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- "Pakistan Census". census.gov.pk. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- "- Human Development Reports" (PDF).
- "NHDRs 2003". Un.org.pk. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- Archived 4 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- "untitled" (PDF). finance.gov.pk. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 October 2011. Retrieved 29 July 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "HEC recognized Universities". Archived from the original on 9 February 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "South Asia ::PAKISTAN". CIA The World Factbook.
- Taus-Bolstad, Stacy (2003). Pakistan in Pictures. Visual geography series (Revised ed.). Minneapolis: Twenty-First Century Books. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-8225-4682-5. Retrieved 11 August 2010.
- Joshua Project. "Sindhi of Afghanistan Ethnic People Profile". Joshuaproject.net. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- Syed Osman Naeem – Development Technology Professionals. "..::-Goans of Pakistan-::."
- "From South to South: Refugees as Migrants: The Rohingya in Pakistan". The Huffington Post.
- "New representative for UNHCR in Pakistan arrives". unhcrpk.org. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ^ "Pakistan to extend stay for Afghans by one more year". 6 December 2017. Retrieved 6 December 2017.
- "UNHCR welcomes new government policy for Afghans in Pakistan". Pakistan: unhcrpk.org. 2016.
- "PAKISTAN: Tolerance wanes as perceptions of Afghan refugees change". Irin. 27 February 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- "Voluntary Repatriation Update" (PDF). Pakistan: UNHCR. November 2016.
- )
- "South Asian Sufis: Devotion, Deviation, and Destiny". Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- "Urdu/Hindi: An Artificial Divide".
- "Bonds of Culture".
- Sharmeen Obaid-Chinoy (17 July 2009). "Karachi's Invisible Enemy". PBS. Retrieved 24 August 2010.
- "In a city of ethnic friction, more tinder". The National. 24 August 2009. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 24 August 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "UN body, police baffled by minister's threat against Afghan refugees". Dawn Media Group. 10 February 2009. Retrieved 24 January 2012.
- , thefridaytimes
- ^ Vogelsang, Wilhelm The Afghans Wiley-Blackwell 2002 ISBN 978-0-631-19841-3 pp.61–62
- ^ (Mallory 1989) harv error: no target: CITEREFMallory1989 (help)
- ^ J. H. Elfenbein, A periplous of the ‘Brahui problem’, Studia Iranica vol. 16 (1987), pp. 215–233.
- "Who are the Hazara?". Tribune. 5 October 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- "Pakistan's regional languages face extinction". The National. Agence France-Presse. 7 January 2017. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- "Pakistan". Ethnologue.
- "Ethnologue report for Pakistan: Languages of Pakistan". ethnologue.com. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- "Browse by Language Family". Ethnologue.
- "Browse by Language Family". Ethnologue.
- ^ "Pakistan, Islam in". Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 29 August 2010.
Approximately 97 percent of Pakistanis are Muslim. The majority are Sunnis following the Hanafi school of Islamic law. Between 10 and 15 percent are Shias, mostly Twelvers.
- "Religions: Muslim 95% (Sunni 75%, Shia 20%), other (includes Christian and Hindu) 5%". Central Intelligence Agency. The World Factbook on Pakistan. 2010. Retrieved 24 August 2010.
- ^ "Country Profile: Pakistan" (PDF). Library of Congress Country Studies on Pakistan. Library of Congress. February 2005. Retrieved 1 September 2010.
Religion: The overwhelming majority of the population (97 percent) is Muslim, of whom approximately 85 percent are Sunni and 15 percent Shi'a.
- "Most Buddhist Nations (2010) – QuickLists – The Association of Religion Data Archives".
- Data Access and Dissemination Systems (DADS). "American FactFinder".
- "Most Pakistanis and Urdu speakers live in this Australian state". sbs.com.au. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
External links
- Pakistan Bureau of Statistics
- infopak.gov.pk – Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Population Reference Bureau
- statpak.gov.pk – Population by mother tongue
- US Census: International Data Base (IDB)