| Revision as of 08:03, 19 September 2019 view sourceMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm →Climate and nature: Task 16: replaced (1×) / removed (0×) deprecated |dead-url= and |deadurl= with |url-status=;Tag: AWB← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:45, 3 October 2019 view source 2001:1a88:191:f700:3ac:cebd:b1b0:e35e (talk) We Anatolians are not Armenians there was never a ancient Armenia , eastern anatolia is not western Armenia , there are only 3 million Armenians and we are over 80 million , your propaganda is shameful , you are ignoring all the native anatolisn muslims in the favor of a handful armenian terrorists , fuck wikipedia everything is a hate campaign against my country , stop calling it armenia , there was never such a country in anchient how ignorant are you kardasian mudshark bastardsTags: Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| The '''Eastern Anatolia Region''' ({{lang-tr|Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi}}) is a ] of ]. | The '''Eastern Anatolia Region''' ({{lang-tr|Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi}}) is a ] of ]. | ||
| The region and the name "Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi" were defined at the ] in 1941. It has the highest average altitude, largest geographical area |
The region and the name "Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi" were defined at the ] in 1941. It has the highest average altitude, largest geographical area.<ref>Lynch, H.F.B, Travels and Studies" London, 1901, vol2 p391. "The natural boundary between ] and ] is the course of the Western Euphrates between the town of Kemah, and its passage through Taurus below Keban-Maden."</ref><ref>Oswald, Felix "A Treatise on the Geology of Armenia", London, 1906.</ref> After the ], the geopolitical term "Eastern Anatolia" was coined to replace what had historically been known as ].<ref name="Sahakyan">{{cite book|last=Sahakyan|first=Lusine|title=Turkification of the Toponyms in the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Turkey|year=2010|publisher=]|location=Montreal|isbn=978-0969987970}}</ref><ref name="Hovannisian3">{{cite book|last1=Hovannisian|first1=Richard|author-link=Richard G. Hovannisian|title=The Armenian Genocide: Cultural and Ethical Legacies|date=2007|publisher=Transaction Publishers|location=New Brunswick, N.J.|isbn=1412835925|page=3|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=K3monyE4CVQC}}</ref><ref name="Cheterian">{{cite book|last1=Cheterian|first1=Vicken|title=Open Wounds: Armenians, Turks and a Century of Genocide|date=2015|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=Oxford and New York City|isbn=1849044589|page=65|quote=As a result of policies such as these, the expression Armenian Plateau, which had been used for centuries to denote the mountainous highlands around Lake Van and Lake Sevan, was eliminated and replaced by the expression 'eastern Anatolia'.}}</ref><ref name="Galichian">{{cite book|last1=Galichian|first1=Rouben|author-link=Rouben Galichian|title=Historic Maps of Armenia: The Cartographic Heritage|date=2004|publisher=I.B. Tauris|location=London and New York City|isbn=1860649793|page=8-9}}</ref><ref name="JSAS">{{cite book|title=Journal of the Society for Armenian Studies|date=2005|location=Los Angeles|volume=14-16|page=55|quote=Most of historical Armenia presently constitutes a part of Turkey (renamed "Eastern Anatolia"), which conducts a policy of minimizing the role of the Armenians in history}}</ref> | ||
| == Substitution with Armenia == | == Substitution with Armenia == | ||
Revision as of 23:45, 3 October 2019
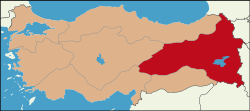
Region of Turkey| Eastern Anatolia Region Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi | |
|---|---|
| Region of Turkey | |
 | |
| Country | Turkey |
| Area | |
| • Total | 165,436 km (63,875 sq mi) |
The Eastern Anatolia Region (Template:Lang-tr) is a geographical region of Turkey.
The region and the name "Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi" were defined at the First Geography Congress in 1941. It has the highest average altitude, largest geographical area. After the Armenian Genocide, the geopolitical term "Eastern Anatolia" was coined to replace what had historically been known as Western Armenia.
Substitution with Armenia
Further information: Geographical name changes in Turkey
Beginning in 1880, the name Armenia was forbidden to be used in official Ottoman documents, in an attempt to censor the history of Armenians in their own homeland. The government of Sultan Abdul Hamid II replaced the name Armenia with such terms as "Kurdistan" or "Anatolia". The Sublime Porte believed there would be no Armenian Question if there was no Armenia. The process of “nationalization” of toponyms was continued by the Kemalists, who were the ideological successors of the Young Turks, and gained momentum during the Republican period. Starting from 1923 the entire territory of Western Armenia was officially renamed “Eastern Anatolia” (literally The Eastern East).

The word Anatolia means “sunrise” or “east” in Greek. This name was given to the Asia Minor peninsula approximately in the 5th or 4th centuries B.C. During the Ottoman era, the term Anadolou included the north-eastern vilayets of Asia Minor with Kyotahia as its center. The numerous European, Ottoman, Armenian, Russian, Persian, Arabic and other primary sources did not confuse the term Armenia with Anatolia. This testifies, inter alia, to the fact that even after the loss of its statehood the Armenian nation still constituted a majority in its homeland, which was recognized by Ottoman occupiers as well.
Historically the Armenian Highlands have been situated to the east of Anatolia, with the border between them located near Sivas (Sebastia) and Kayseri (Caesarea). Therefore, it is incorrect to refer to Armenia as part of "Eastern Anatolia".
In the 17th century, when the Armenian Question was not yet included into the international diplomacy agenda, the terms "Anatolia" or "Eastern Anatolia" were never used to indicate Armenia. Furthermore, the "Islamic World Map" of the 16th century and other Ottoman maps of the 18th and 19th centuries have clearly indicated Armenia (Ermenistan) on a specific territory as well as its cities.
Armenia, together with its boundaries, was unequivocally mentioned in the works of earlier Ottoman historians and chroniclers until the end of the 19th century. Kâtip Çelebi, a famous Ottoman chronicler of the 17th century, had a special chapter titled “About the Country Called Armenia” in his book Jihan Numa. However, when this book was republished in 1957, its modern Turkish editor H. Selen changed this title into “Eastern Anatolia”. Osman Nuri, a historian of the second half of the 19th century, mentions Armenia repeatedly in his three-volume Abdul Hamid and the Period of His Reign.
In the 1960s, the Swiss airline Swissair removed the nomenclature 'plateau arménien' from the maps provided by their planes at the request of the Turkish ambassador in Bern.
Subdivision
- Upper Euphrates Section (Template:Lang-tr)
- Erzurum - Kars Section (Template:Lang-tr)
- Upper Murat - Van Section (Template:Lang-tr)
- Upper Murat Area (Template:Lang-tr)
- Van Area (Template:Lang-tr)
- Hakkari Section (Template:Lang-tr)
Provinces
Provinces that are entirely in the Eastern Anatolia Region:
Provinces that are mostly in the Eastern Anatolia Region:
Location and borders
The Eastern Anatolia Region is located in the easternmost part of Turkey. It is bounded by Turkey's Central Anatolia Region to the west; Turkey's Black Sea Region to the north; Turkey's Southeast Anatolia Region and Iraq to the south; and Iran, Azerbaijan, Armenia and Georgia to the east, where Eastern Anatolia overlaps and converges with the South Caucasus region and Lesser Caucasus mountain plateau.
The area of the region is 146,330 km², which comprises 18.7% of the total area of Turkey.
Population
The total population of the region is 6,100,000 (2000 census) and 5,906,565 (2014 estimate). The region has the second most rural population of Turkey after the Black Sea region. The migration level (to the other regions, especially to Marmara Region) is high and population density (40 person/km²) is lower than the average for Turkey (98 person/km²). The migration toward other Turkey's regions and toward foreign countries is higher than the natural population increase, a fact which is leading to a slight decline of the Region's population.
Geography
The average altitude is 2,200 m. Major geographic features include plains, plateaus and massifs. There is some volcanic activity today.
Massifs and mountains
- There are three massif lines running north-south:
- To the north, the Çimen Dağı, Kop Dağı and Yalnızçam mountains
- In the centre, the Munzur, Karasu Dağı, Aras Dağı mountains
- To the south, Southeast Tauros, Bitlis, Hakkâri, and Buzul mountains.
- The volcanic mountains Nemrut, Süphan, Tendürek and Ararat are in the region.
Plateaus and plains
- The largest plateau in the region is Erzurum-Kars Plato.
- The region includes the Malatya, Elazığ, Bingöl, Muş plains and the Van Lake basin.
Lakes
Rivers
Climate and nature
| Erzurum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Since most of the region is far from the sea, and has high altitude, it has a harsh continental climate with long winters and short summers. During the winter, it is very cold and snowy, during summer the weather is cool in the highlands and warm in the lowlands. The region has the lowest average temperature of all Turkish regions, with -25 °C. Although it can get below -40 °C. The summer average is about 20 °C.
The region's annual temperature difference is the highest in Turkey. Some areas in the region have different microclimates. As an example, Iğdır (near Mount Ararat) has a milder climate.
The region contains 11% percent of the total forested area of Turkey, and it is rich in native plants and animals. Oak and yellow pine trees form the majority of the forests.
The region has high potential for hydroelectric power.
Gallery
-
 View of Mount Ararat from Iğdır
View of Mount Ararat from Iğdır
-
 Cumhuriyet Avenue, Erzurum.
Cumhuriyet Avenue, Erzurum.
-
Çifte Minareli Medrese is an architectural monument of the late Seljuk period in the city of Erzurum
-
Monument of the Nene Hatun in the city of Erzurum
-
Panoramic view of the city of Bingöl
-
Panoramic view of the city of Kars
-
 Akdamar Island and the Armenian Cathedral of the Holy Cross, a 10th-century Armenian church and monastic complex
Akdamar Island and the Armenian Cathedral of the Holy Cross, a 10th-century Armenian church and monastic complex
-
 Kars city centre
Kars city centre
-
Malatya İnönü Stadium
| Geographical regions of Turkey | ||
|---|---|---|
Endnotes
- Lynch, H.F.B, Travels and Studies" London, 1901, vol2 p391. "The natural boundary between Armenia and Asia Minor is the course of the Western Euphrates between the town of Kemah, and its passage through Taurus below Keban-Maden."
- Oswald, Felix "A Treatise on the Geology of Armenia", London, 1906.
- ^ Sahakyan, Lusine (2010). Turkification of the Toponyms in the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Turkey. Montreal: Arod Books. ISBN 978-0969987970.
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard (2007). The Armenian Genocide: Cultural and Ethical Legacies. New Brunswick, N.J.: Transaction Publishers. p. 3. ISBN 1412835925.
- ^ Cheterian, Vicken (2015). Open Wounds: Armenians, Turks and a Century of Genocide. Oxford and New York City: Oxford University Press. p. 65. ISBN 1849044589.
As a result of policies such as these, the expression Armenian Plateau, which had been used for centuries to denote the mountainous highlands around Lake Van and Lake Sevan, was eliminated and replaced by the expression 'eastern Anatolia'.
- ^ Galichian, Rouben (2004). Historic Maps of Armenia: The Cartographic Heritage. London and New York City: I.B. Tauris. p. 8-9. ISBN 1860649793.
- ^ Journal of the Society for Armenian Studies. Vol. 14–16. Los Angeles. 2005. p. 55.
Most of historical Armenia presently constitutes a part of Turkey (renamed "Eastern Anatolia"), which conducts a policy of minimizing the role of the Armenians in history
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-06-20. Retrieved 2011-05-31.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
Categories: