| Revision as of 22:11, 2 November 2019 editAmbrosiawater (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,096 edits →External links: navbox← Previous edit | Revision as of 01:55, 5 November 2019 edit undo2604:3d09:47f:e4e0:91e8:5041:652e:a6eb (talk) It's fine.Tags: blanking Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| Vaping is far safer than smoking. In 2019 there were 37 deaths due to contaminated vape cartridges with Vitamin E oils which become toxic when breathed in. | |||
| {{pp-pc1|expiry=January 20, 2020}} | |||
| {{pp-pc|small=yes}} | |||
| The '''safety''' '''of''' '''electronic cigarettes''' is uncertain.<ref name=EbbertAgunwamba2015>{{cite journal|last1=Ebbert|first1=Jon O.|last2=Agunwamba|first2=Amenah A.|last3=Rutten|first3=Lila J.|title=Counseling Patients on the Use of Electronic Cigarettes|journal=Mayo Clinic Proceedings|volume=90|issue=1|year=2015|pages=128–134|issn=0025-6196|doi=10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.11.004|pmid=25572196}}</ref><ref name=Siu2015>{{cite journal|last1=Siu|first1=AL|title=Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Interventions for Tobacco Smoking Cessation in Adults, Including Pregnant Women: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.|journal=Annals of Internal Medicine|date=22 September 2015|volume=163|issue=8|pages=622–34|doi=10.7326/M15-2023|pmid=26389730}}</ref><ref name=Harrell2014>{{cite journal|last1=Harrell|first1=PT|last2=Simmons|first2=VN|last3=Correa|first3=JB|last4=Padhya|first4=TA|last5=Brandon|first5=TH|title=Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems ("E-cigarettes"): Review of Safety and Smoking Cessation Efficacy.|journal=Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery|date=4 June 2014|volume=151|issue=3|pages=381–393|doi=10.1177/0194599814536847|pmc=4376316|pmid=24898072}}</ref> There is little data about their safety, and considerable variation among ] and in their ]<ref name=PatnodeHenderson2015>{{cite journal|last1=Patnode|first1=Carrie D.|last2=Henderson|first2=Jillian T.|last3=Thompson|first3=Jamie H.|last4=Senger|first4=Caitlyn A.|last5=Fortmann|first5=Stephen P.|last6=Whitlock|first6=Evelyn P.|title=Behavioral Counseling and Pharmacotherapy Interventions for Tobacco Cessation in Adults, Including Pregnant Women: A Review of Reviews for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force|url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0079361/pdf/PubMedHealth_PMH0079361.pdf|journal=Annals of Internal Medicine|volume=163|issue=8|date=September 2015|pages=608|issn=0003-4819|doi=10.7326/M15-0171|pmid=26491759}}</ref> and thus the contents of the ] delivered to the user.<ref name=Grana2014/> Reviews on the safety of e-cigarettes have reached significantly different conclusions.<ref name=FarsalinosLeHouezec2015/> A 2014 ] (WHO) report cautioned about potential risks of using e-cigarettes.<ref name=WHO2014>{{cite web|url=http://apps.who.int/gb/fctc/PDF/cop6/FCTC_COP6_10-en.pdf|title=Electronic nicotine delivery systems|pages=1–13|publisher=]|date=21 July 2014}}</ref> Regulated US ] (FDA) products such as ] may be safer than e-cigarettes,<ref name=Drummond2014/> but e-cigarettes are generally seen as safer than combusted ]{{#tag:ref|A 2019 review concluded that, "no long term vaping toxicological/safety studies have been done in humans; without these data, saying with certainty that e-cigarettes are safer than combustible cigarettes is impossible."<ref name=GottsJordt2019>{{cite journal|last1=Gotts|first1=Jeffrey E|last2=Jordt|first2=Sven-Eric|last3=McConnell|first3=Rob|last4=Tarran|first4=Robert|title=What are the respiratory effects of e-cigarettes?|journal=BMJ|year=2019|pages=l5275|issn=0959-8138|doi=10.1136/bmj.l5275}}</ref>|group=notes}}<ref name=KnorstBenedetto2014/><ref name=Burstyn2014/> such as cigarettes and cigars.<ref name=KnorstBenedetto2014/> The risk of early death is anticipated to be similar to that of ].<ref name=BradyDeLaRosa2019/> Since vapor does not contain tobacco and does not involve combustion, users may avoid several ],<ref name=FarsalinosPolosa2014>{{cite journal|last1=Farsalinos|first1=K. E.|last2=Polosa|first2=R.|title=Safety evaluation and risk assessment of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: a systematic review|journal=Therapeutic Advances in Drug Safety|volume=5|issue=2|year=2014|pages=67–86|issn=2042-0986|doi=10.1177/2042098614524430|pmc=4110871|pmid=25083263}}</ref> such as ], ], and ].<ref name=SmithBrar2016/> However, e-cigarette use with or without nicotine cannot be considered harmless.<ref name=GloverBreier2016/> Repeated exposure over a long time to e-cigarette vapor poses substantial potential risk.<ref name=TeginMekala2018/> | |||
| The long-term effects of e-cigarette use are unknown.<ref name=Hartmann-BoyceMcRobbie2016>{{cite journal|last1=Hartmann-Boyce|first1=Jamie|last2=McRobbie|first2=Hayden|last3=Bullen|first3=Chris|last4=Begh|first4=Rachna|last5=Stead|first5=Lindsay F|last6=Hajek|first6=Peter|last7=Hartmann-Boyce|first7=Jamie|title=Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation|journal=Cochrane Database Syst Rev|year=2016|volume=9|pages=CD010216|doi=10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub3|pmid=27622384|pmc=6457845}}</ref><ref name=BradyDeLaRosa2019/><ref name=BalsBoyd2019>{{cite journal|last1=Bals|first1=Robert|last2=Boyd|first2=Jeanette|last3=Esposito|first3=Susanna|last4=Foronjy|first4=Robert|last5=Hiemstra|first5=Pieter S.|last6=Jiménez-Ruiz|first6=Carlos A.|last7=Katsaounou|first7=Paraskevi|last8=Lindberg|first8=Anne|last9=Metz|first9=Carlos|last10=Schober|first10=Wolfgang|last11=Spira|first11=Avrum|last12=Blasi|first12=Francesco|title=Electronic cigarettes: a task force report from the European Respiratory Society|journal=European Respiratory Journal|volume=53|issue=2|year=2019|pages=1801151|issn=0903-1936|doi=10.1183/13993003.01151-2018|pmid=30464018}}</ref> The risk from ]s, including death, was reported in 2016 to be low.<ref name=PaleyEchalier2016>{{cite journal|last1=Paley|first1=Grace L.|last2=Echalier|first2=Elizabeth|last3=Eck|first3=Thomas W.|last4=Hong|first4=Augustine R.|last5=Farooq|first5=Asim V.|last6=Gregory|first6=Darren G.|last7=Lubniewski|first7=Anthony J.|title=Corneoscleral Laceration and Ocular Burns Caused by Electronic Cigarette Explosions|journal=Cornea|volume=35|issue=7|year=2016|pages=1015–1018|issn=0277-3740|doi=10.1097/ICO.0000000000000881|pmc=4900417|pmid=27191672}}</ref> Serious adverse events related to e-cigarettes were hypotension, ], chest pain, rapid heartbeat, disorientation, and congestive heart failure but it was unclear the degree to which they were the result of e-cigarettes.<ref name=BrelandSpindle2014/> Less serious ]s include abdominal pain, headache, blurry vision,<ref name=BrelandSpindle2014/> throat and mouth irritation, vomiting, nausea, and coughing.<ref name=Grana2014/> They may produce less adverse effects compared to tobacco products.<ref name=ONF2015>{{cite journal|title=The Potential Adverse Health Consequences of Exposure to Electronic Cigarettes and Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems|journal=Oncology Nursing Forum|volume=42|issue=5|year=2015|pages=445–446|issn=0190-535X|doi=10.1188/15.ONF.445-446|pmid=26302273}}</ref> E-cigarettes reduce lung function, but to a much lower extent than with traditional cigarettes, and they reduce ] function and increase inflammation, but these changes were only substantial with traditional cigarettes.<ref name=Harrell2014/> In 2019, an ].<ref name=CDC2019>{{cite web|url=https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease.html|title=Outbreak of Lung Illness Associated with Using E-cigarette Products|publisher=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention|date=31 October 2019}}{{PD-notice}}</ref> 37 deaths have been confirmed in this outbreak, {{as of|2019|10|29|lc=yes|df=US}}.<ref name=CDC2019/> A 2014 WHO report said, "ENDS use poses serious threats to adolescents and fetuses."<ref name=WHO2014/> Aside from ] exposure in normal use, there are also risks from misuse or accidents<ref name=FarsalinosPolosa2014/> such as ] (especially among small children<ref name=Hajek2014/>),<ref name=Brandon2015/> contact with ],<ref name=Durmowicz2014>{{cite journal|last1=Durmowicz|first1=E. L.|title=The impact of electronic cigarettes on the paediatric population|journal=Tobacco Control|volume=23|issue=Supplement 2|year=2014|pages=ii41–ii46|issn=0964-4563|doi=10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051468|pmid=24732163|pmc=3995262}}</ref> fires caused by vaporizer malfunction,<ref name=Grana2014/> and explosions resulting from extended charging, unsuitable chargers, or design flaws.<ref name=FarsalinosPolosa2014/> Battery explosions are caused by an increase in internal battery temperature and some have resulted in severe skin burns.<ref name=EbbertAgunwamba2015/> There is a small risk of battery explosion in devices modified to increase battery power.<ref name=Rowell2015>{{cite journal|last1=Rowell|first1=Temperance R|last2=Tarran|first2=Robert|title=Will Chronic E-Cigarette Use Cause Lung Disease?|journal=American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology|year=2015|volume=309|issue=12|pages=L1398–L1409|issn=1040-0605|doi=10.1152/ajplung.00272.2015|pmc=4683316|pmid=26408554}}</ref> | |||
| The ] of e-liquids varies,<ref name=Cooke2015/> and contamination with various chemicals have been detected in the liquid.<ref name=Bertholon2013/> Metal parts of e-cigarettes in contact with the e-liquid can contaminate it with metal particles.<ref name=FarsalinosPolosa2014/> Many chemicals including ] such as ] can inadvertently be produced when the ] (]) that touches the e-liquid is heated and chemically reacted with the liquid.<ref name=Bekki2014/> Normal usage of e-cigarettes,{{sfn|Wilder|2016|p=82}} and reduced ] (3.0 V<ref name=Cheng2014/>) devices generate very low levels of formaldehyde.<ref name=Bekki2014/> The later-generation and "tank-style" e-cigarettes with a higher voltage (5.0 V<ref name=Cooke2015/>) may generate equal or higher levels of formaldehyde compared to smoking.<ref name=Orellana-Barrios2015/> A 2015 ] (PHE) report found that high levels of formaldehyde only occurred in overheated "dry-puffing".{{sfn|McNeill|2015|p=77}} Users detect the "dry puff" (also known as a "dry hit"{{sfn|Stratton|2018|p=Characteristics of E-Cigarette Devices, 56}}) and avoid it, and they concluded that "There is no indication that EC users are exposed to dangerous levels of aldehydes."{{sfn|McNeill|2015|p=77-78}} However, e-cigarette users may learn to overcome the unpleasant taste due to elevated ] formation, when the ] craving is high enough.<ref name=Rowell2015/> E-cigarette users who use devices that contain nicotine are exposed to its potentially harmful effects.<ref name=Cheng2014/> Nicotine is associated with ], possible birth defects, and poisoning.<ref name=Jerry2015/> '']'' studies of nicotine have associated it with cancer, but carcinogenicity has not been demonstrated '']''.<ref name=Jerry2015/> There is inadequate research to show that nicotine is associated with cancer in humans.{{sfn|SGUS|2014|p=115}} The risk is probably low from the inhalation of propylene glycol and glycerin.<ref name=Hajek2014/> No information is available on the long-term effects of the inhalation of flavors.<ref name=Bertholon2013/> | |||
| E-cigarettes create vapor that consists of fine and ]s of ], with the majority of particles in the ultrafine range.<ref name=Grana2014/> The vapor have been found to contain ], ], nicotine, ], small amounts of ]s,<ref name=Grana2014/> ]s,<ref name=Hajek2014/> and ], as well as metal ]s, and other substances.<ref name=Grana2014/> Exactly what the ] across and within manufacturers, and depends on the contents of the liquid, the physical and electrical design of the device, and user behavior, among other factors.{{#tag:ref|The engineering designs, including the kind of the battery, heating temperature of the solution, and the style of heating element and storage for the solution, typically affects the nature, number, and size of particles generated.<ref name=Grana2014/>|group=notes}}<ref name=Cheng2014/> E-cigarette vapor potentially contains harmful chemicals not found in tobacco smoke.<ref name=Hildick-SmithPesko2015/> The majority of toxic chemicals found in cigarette smoke are absent in e-cigarette vapor.<ref name=KimKabir2016/> E-cigarette vapor contains lower concentrations of potentially toxic chemicals than with ].<ref name=FernándezBallbè2015>{{cite journal|last1=Fernández|first1=Esteve|last2=Ballbè|first2=Montse|last3=Sureda|first3=Xisca|last4=Fu|first4=Marcela|last5=Saltó|first5=Esteve|last6=Martínez-Sánchez|first6=Jose M.|title=Particulate Matter from Electronic Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes: a Systematic Review and Observational Study|journal=Current Environmental Health Reports|volume=2|issue=4|pages=423–9|year=2015|issn=2196-5412|doi=10.1007/s40572-015-0072-x|pmid=26452675}}</ref> Those which are present, are mostly below 1% of the corresponding levels permissible by ].<ref name=Burstyn2014/> But workplace safety standards do not recognize exposure to certain vulnerable groups such as people with ], children, and infants who may be exposed to second-hand vapor.<ref name=Grana2014/> Concern exists that some of the mainstream vapor exhaled by e-cigarette users may be inhaled by bystanders, particularly indoors.<ref name=Rom2014/> E-cigarette use by a parent might lead to inadvertent health risks to offspring.<ref name=England2015/> A 2014 review recommended that e-cigarettes should be regulated for ].<ref name=Saitta2014/> There is limited information available on the ]s around production, use, and disposal of e-cigarettes that use cartridges.<ref name=Chang2014/> E-cigarettes that are not reusable may contribute to the problem of ].<ref name=Nowak2014/> | |||
| ] | |||
| == Health effects == | == Health effects == | ||
Revision as of 01:55, 5 November 2019
Vaping is far safer than smoking. In 2019 there were 37 deaths due to contaminated vape cartridges with Vitamin E oils which become toxic when breathed in.
Health effects
Concerns

Reviews on the safety of electronic cigarettes, evaluating roughly the same studies, have reached significantly different conclusions. Broad-ranging statements regarding their safety cannot be reached because of the vast differences of devices and e-liquids available. A consensus has not been established for the effects as well as the benefits related to their use. Due to various methodological issues, severe conflicts of interest, and inconsistent research, no definite conclusions can be determined regarding the safety of e-cigarettes. However, e-cigarettes cannot be regarded as a harmless alternative to traditional cigarettes. Guidelines for the design, manufacture or assessment of their safety has not been established.
Repeated exposure over a long time to e-cigarette vapor poses substantial potential risk. Although companies state that e-cigarettes are safe, there is no scientific evidence to support this view. Long-term data showing that vaping is a "healthier alternative" than cigarette smoking does not exist. There is little data about their safety, and considerable variability among vaporizers and in their liquid ingredients and thus the contents of the aerosol delivered to the user. The health community, pharmaceutical industry, and other groups have raised concerns about the emerging phenomenon of e-cigarettes, including the unknown health risks from their long-term use. A 2017 review found "There is a justifiable concern that any broad statement promoting e-cig safety may be unfounded considering the lack of inhalational toxicity data on the vast majority of the constituents in e-cigs. This is particularly true for individuals with existing lung disease such as asthma." A 2014 review has stated, there are "Many unanswered questions about their safety, efficacy for harm reduction and cessation, and total impact on public health." There is concern that e-cigarettes may result in many smokers rejecting historically effective quitting smoking methods. Concern exists that the majority of smokers attempting to quit by vaping may stop smoking but maintain nicotine intake because their long-term effects are not clear.
A policy statement by the American Association for Cancer Research and the American Society of Clinical Oncology has reported that "The benefits and harms must be evaluated with respect to the population as a whole, taking into account the effect on youth, adults, nonsmokers, and smokers." The widespread availability and popularity of flavored e-cigarettes is a key concern regarding the potential public health implications of the products. It is assumed that vaping leads to serious health concerns due to the levels of various toxicants such as nicotine. A 2016 Surgeon General of the United States report stated e-cigarettes typically contain nicotine as well as other chemicals that are known to damage health. For example, users risk exposing their respiratory systems to potentially harmful chemicals in e-cigarettes. E-cigarettes are not safe for youth, young adults, pregnant women, or adults who do not currently use tobacco products. A July 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) report cautioned about the potential risks to children and adolescents, pregnant women, and women of reproductive age regarding e-cigarette use. E-cigarettes are an increasing public health concern due to the rapid rise among adolescents and the uncertainty of potential health consequences. A serious concern regarding vaping is that they could entice children to initiate smoking, either by the argument that nicotine leads to smoking or by making smoking appear more acceptable again. Concerns exist in respect to adolescence vaping due to studies indicating nicotine may potentially have harmful effects on the brain.

It is recommended the precautionary principle be used for e-cigarettes because of the long history of the tobacco crisis, in order to assess their benefits and long-term effects and to avoid another nicotine crisis. A 2015 review suggested that e-cigarettes could be regulated in a similar way as inhalation therapeutic medicine, meaning, they would regulated based on toxicology and safety clinical trials. A 2014 review recommended that e-cigarettes could be adequately regulated for consumer safety with existing regulations on the design of electronic products. Regulation of the production and promotion of e-cigarettes may help lower some of the adverse effects associated with tobacco use. The medical community is concerned that increased availability of e-cigarettes could increase worldwide nicotine dependence, especially among the young as they are enticed by the various flavor options e-cigarettes have to offer. Since vaping does not produce smoke from burning tobacco, the opponents of e-cigarettes fear that traditional smokers will substitute vaping for smoking in settings where smoking is not permitted without any real intention of quitting traditional cigarettes. Furthermore, vaping in public places, coupled with recent e-cigarette commercials on national television, could possibly undermine or weaken current antismoking regulations. Fear exists that wide-scale promotion and use of e-cigarettes, fuelled by an increase in the advertising of these products, may carry substantial public health risks. Public health professionals voiced concerns regarding vaping while using other tobacco products, particularly combustible products. The entrance of large US tobacco manufacturers, which are Altria Group, Reynolds American, and Lorillard, into the e-cigarette sector raises many potential public health issues. Instead of encouraging quitting, the tobacco industry could market e-cigarettes as a way to get around clean indoor air laws, which promotes dual use. It is argued to implement the precautionary principle because dual use could end up being an additional risk. The industry could also lead vapers to tobacco products, which would increase instead of decrease overall addiction. Concerns exist that the emergence of e-cigarettes may benefit Big Tobacco to sustain an industry for tobacco. A 2017 review states that the "Increased concentration of the ENDS market in the hands of the transnational tobacco companies is concerning to the public health community, given the industry's legacy of obfuscating many fundamental truths about their products and misleading the public with false claims, including that low-tar and so-called "light" cigarettes would reduce the harms associated with smoking. Although industry representatives are claiming interest in ENDS because of their harm-reduction potential, many observers believe that profit remains the dominant motivation." E-cigarettes are expanding the tobacco epidemic by bringing lower-risk youth into the market, many of whom then transition to smoking cigarettes.
Unknowns
E-cigarettes have the potential for benefit and harm, the nature and scale of each being uncertain in the absence of much evidence. The health effects related to e-cigarette use is mostly unknown. The health effects on intensive e-cigarette users are unknown. The effect on population health from e-cigarettes is unknown. Smokefree.gov, a website run by the Tobacco Control Research Branch of the National Cancer Institute to provide information to help quit smoking, stated that "Since e-cigs aren't regulated yet, there's no way of knowing how much nicotine is in them or what other chemicals they contain. These two things make the safety of e-cigs unclear." The chemical characteristics of the short-lived free radicals and long-lived free radicals produced from e-cigarettes is unclear. The English National Health Service has stated in 2014, "While e-cigarettes may be safer than conventional cigarettes, we don't yet know the long-term effects of vaping on the body." While quitting smoking may be firmly recommended for smokers who have asthma, it is not clear whether replacing e-cigarettes for cigarettes is a universally safer alternative. The American Diabetes Association states "There is no evidence that e-cigarettes are a healthier alternative to smoking." In August 2014, the Forum of International Respiratory Societies stated that e-cigarettes have not been demonstrated to be safe. Health Canada has stated that, "their safety, quality, and efficacy remain unknown." The National Institute on Drug Abuse stated that "There are currently no accepted measures to confirm their purity or safety, and the long-term health consequence of e-cigarette use remain unknown." There is insufficient data regarding the health benefits of vaping. Vaping requires more forceful sucking than smoking, and this action is still unclear on increased absorption of harmful substances and the user's health. Sucking more forcefully from e-cigarette use may be adverse to human health. The risks from long-term use of nicotine as well as other toxicants that are unique to e-cigarettes are uncertain. The long-term consequences from e-cigarette use on death and disease are unclear. There is limited available research regarding their effects to vulnerable groups such as minors.
Positives

A 2018 Public Health England (PHE) report stated, "The previous estimate that, based on current knowledge, vaping is at least 95% less harmful than smoking remains a good way to communicate the large difference in relative risk unambiguously so that more smokers are encouraged to make the switch from smoking to vaping. It should be noted that this does not mean EC are safe." A 2015 PHE report stated that e-cigarettes are estimated to be 95% less harmful than smoking, but the studies used to support this estimate were viewed as having a weak methodology. It has been extensively disputed in the literature. Many vigorously criticized the validity of the estimate that vaping is 95% less harmful than smoking. It was also criticized by the journal The Lancet for constructing its conclusions on 'flimsy' evidence, which included citing literature with apparent conflicts of interest. It was later discovered that many of the authors who came up with the "95% safer" assertion have ties to the tobacco industry. Some consider that the PHE report's specific number is flawed and confusing, by making opinions at odds with existing knowledge. Despite this, most other health organizations have been more cautious in their public statements on the safety of e-cigarettes. For example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reported that the potential health risks of using e-cigarettes are unclear.

Influential health organizations in England, including Public Health England, the Royal College of Physicians, the Royal Society for Public Health, and the National Health Service, have unequivocally stated that e-cigarettes are 95% safer than traditional cigarettes. This claim originated from a single consensus meeting of 12 people convened by D.J. Nutt in 2014. They reached this conclusion without citing any specific evidence. The Nutt et al. paper did include this caveat: "A limitation of this study is the lack of hard evidence for the harms of most products on most of the criteria", which has generally been ignored by those quoting this report. A 2015 editorial in The Lancet identified financial conflicts of interest associated with Nutt et al., noting that "there was no formal criterion for the recruitment of the experts." The Nutt et al. meeting was funded by Euroswiss Health and Lega Italiana Anti Fumo (LIAF). EuroSwiss Health is one of several companies registered at the same address in a village outside Geneva with the same chief executive, who was reported to have received funding from British American Tobacco (BAT) for writing a book on nicotine as a means of harm reduction and who also endorsed BAT's public health credentials. Another of Nutt's coauthors, Riccardio Polosa, was Chief Scientific Advisor to LIAF, received funding from LIAF, and reported serving as a consultant to Arbi Group Srl, an e-cigarette distributor. He also received funding from Philip Morris International. Later in 2015, The BMJ published an investigative report that raised broader issues surrounding potential conflicts of interest between individuals involved in the Nutt et al. paper. The BMJ provided an infographic illuminating undisclosed connections between key people involved in the paper and the tobacco and e-cigarette industries as well as links between the paper and Public Health England via one of the coauthors. Even so, as of June 2017, the "95% safer" figure remains widely quoted, despite the fact that evidence of the dangers of e-cigarette use has rapidly accumulated since 2014. This new evidence indicates that the true risk of e-cigarette use is much higher than the "95% safer" claim would indicate.
In June 2014, the Royal College of Physicians stated that, "On the basis of available evidence, the RCP believes that e-cigarettes could lead to significant falls in the prevalence of smoking in the UK, prevent many deaths and episodes of serious illness, and help to reduce the social inequalities in health that tobacco smoking currently exacerbates." Since vapor does not contain tobacco and does not involve combustion, users may avoid several harmful constituents usually found in tobacco smoke, such as ash, tar, and carbon monoxide. A 2014 review found that e-cigarette aerosol contains far fewer carcinogens than tobacco smoke, and concluded that e-cigarettes "impart a lower potential disease burden" than traditional cigarettes. The public health community is divided, even polarized, over how the use of these devices will impact the tobacco epidemic. Some tobacco control advocates predict that e-cigarettes will increase rates of cigarette uptake, especially among youth. Others envision that these devices have potential for aiding cessation efforts, or reducing harm among people who continue to smoke. Scientific studies advocate caution before designating e-cigarettes as beneficial but vapers continue to believe they are beneficial. It is estimated their safety risk is similar to that of smokeless tobacco, which has about 1% of the mortality risk of traditional cigarettes. The risk of early death is anticipated to be similar to that of smokeless tobacco.
Negatives

Opinions that e-cigarettes are a safe substitute to traditional cigarettes may compromise tobacco control efforts. The American Cancer Society has stated, "The makers of e-cigarettes say that the ingredients are "safe," but this only means the ingredients have been found to be safe to eat. Inhaling a substance is not the same as swallowing it. There are questions about how safe it is to inhale some substances in the e-cigarette vapor into the lungs." The Canadian Cancer Society has stated that, "A few studies have shown that there may be low levels of harmful substances in some e-cigarettes, even if they don't have nicotine." In the UK a National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guideline did not recommend e-cigarettes as there are questions regarding the safety, efficacy, and quality of these products. The US National Association of County and City Health Officials has stated, "Public health experts have expressed concern that e-cigarettes may increase nicotine addiction and tobacco use in young people." No long-term studies have evaluated future tobacco use as a result of e-cigarette use. E-cigarette vapor potentially contains harmful substances not found in tobacco smoke. There is no benefit for vaping among youth.
Appeal to Young People
E-cigarettes pose potential risks to the population as a whole. E-cigarettes could cause public health harm if they:
- Increase the number of youth and young adults who are exposed to nicotine.
- Lead non-smokers to start smoking conventional cigarettes and other burned tobacco products such as cigars and hookah.
- Sustain nicotine addiction so smokers continue using the most dangerous tobacco products – those that are burned – as well as e-cigarettes, instead of quitting completely.
- Increase the likelihood that former smokers will again become addicted to nicotine by using e-cigarettes, and will start using burned tobacco products again.
Adverse effects
Main article: Adverse effects of electronic cigarettesThe short-term and long-term effects from e-cigarette use remain unclear. The risk from serious adverse events, including death, was reported in 2016 to be low. The long-term health consequences from vaping is probably to be slighter greater than nicotine replacement products. They may produce less adverse effects compared to tobacco products. They may cause long-term and short-term adverse effects, including airway resistance, irritation of the airways, eyes redness, and dry throat. Serious adverse events related to e-cigarettes were hypotension, seizure, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, disorientation, and congestive heart failure but it was unclear the degree to which they were the result of e-cigarettes. Less serious adverse effects include abdominal pain, dizziness, headache, blurry vision, throat and mouth irritation, vomiting, nausea, and coughing. Short-term adverse effects reported most often were mouth and throat irritation, dry cough, and nausea.
Nicotine poisoning related to e-cigarettes include ingestion, inhalation, or absorption via the skin or eyes. Accidental poisoning can result from using undiluted concentrated nicotine when mistakenly used as prepared e-liquid. There is a possibility that inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact can expose people to high levels of nicotine. Concerns with exposure to the e-liquids include leaks or spills and contact with contaminants in the e-liquid. Concern exists from the risk of injury associated with e-cigarette explosions for adults and children. The exact causes of such incidents are not yet clear. Pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and the elderly are more sensitive to nicotine than other individuals. There are safety issues with the nicotine exposure from e-cigarette use, which may cause addiction and other adverse effects.
Aside from toxicity exposure in normal use, there are also risks from misuse or accidents such as nicotine poisoning (especially among small children), contact with liquid nicotine, fires caused by vaporizer malfunction, and explosions resulting from extended charging, unsuitable chargers, or design flaws. Battery explosions are caused by an increase in internal battery temperature and some have resulted in severe skin burns. There is a small risk of battery explosion in devices modified to increase battery power. There is considerable variation among e-cigarettes and in their liquid ingredients. and thus the contents of the aerosol delivered to the user. Repeated exposure over a long time to e-cigarette vapor poses substantial potential risk. The cytotoxicity of e-liquids varies, and contamination with various chemicals have been detected in the liquid. E-cigarette users who use devices that contain nicotine are exposed to its potentially harmful effects. E-cigarette vapor potentially contains harmful chemicals not found in tobacco smoke.
Toxicology
The long-term health impacts of e-cigarette use are unknown. A 2017 review found "The exposure of EC users to potentially toxic chemical emissions is difficult to quantify, given the numerous types of EC devices, different e‑liquids, and disparities in individual use patterns." The long-term health impacts of the main chemicals nicotine and propylene glycol in the aerosol are not fully understood. There is limited peer-reviewed data about the toxicity of e-cigarettes for a complete toxicological evaluation, and their cytotoxicity is unknown. The chemicals and toxicants included in e-cigarettes have not been completely disclosed and their safety is not guaranteed. A 2014 study "indicates that very few commercially marketed e-cigarettes have undergone a thorough toxicology evaluation and standardized testing for evaluating e-cigarette toxicity across brands." They are similar in toxicity to other nicotine replacement products, but e-cigarettes manufacturing standards are variable standards, and many as a result are probably more toxic than nicotine replacement products. The UK National Health Service noted that the toxic chemicals found by the FDA were at levels one-thousandth that of cigarette smoke, and that while there is no certainty that these small traces are harmless, initial test results are reassuring. While there is variability in the ingredients and concentrations of ingredients in e-cigarette liquids, tobacco smoke contains thousands of chemicals, most of which are not understood and many of which are known to be harmful.
Carcinogenicity
Concerns about the carcinogenicity of e-cigarettes arise from both nicotine and from other chemicals that may be in the vapor. As regards nicotine, there is evidence from in vitro and animal research that nicotine may have a role as a tumor promoter, but carcinogenicity has not been demonstrated in vivo. A 2014 Surgeon General of the United States report stated that the single relevant randomized trial "does not indicate a strong role for nicotine in promoting carcinogenesis in humans". They concluded that "There is insufficient data to conclude that nicotine causes or contributes to cancer in humans, but there is evidence showing possible oral, esophageal, or pancreatic cancer risks". Nicotine in the form of nicotine replacement products is less of a cancer risk than with smoking, and they have not been shown to be associated with cancer in the real world. Nicotine promotes metastasis by causing cell cycle progression, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, migration, invasion, angiogenesis, and avoidance of apoptosis in a number of systems. Nicotine does promote the growth of blood vessels that supply tumors and it speeds tumor growth. Whether long-term vaping can raise the chance for malignancy in individuals with a susceptibility for tumor growth is unknown.
Nicotine has been shown to induce DNA damage in the Escherichia colipol A+/pol− test. Low concentrations of nicotine stimulate cell proliferation, while high concentrations are cytotoxic. Nicotine decreases the tumor suppressor Chk2, which is activated by DNA damage. The decrease in Chk2 in cells exposed to nicotine suggests that nicotine may be capable of overriding DNA damage checkpoint activation, disrupting genetic surveillance, and increasing the risk of oncogenesis. There is strong evidence that some substances found in e-cigarette vapors such as formaldehyde and acrolein can induce DNA damage and mutagenesis.
Nicotine promotes endothelial cell migration, proliferation, survival, tube formation, and nitric oxide (NO) production in vitro, mimicking the effect of other angiogenic growth factors. In 2001, it was found that nicotine was a potent angiogenic agent at tissue and plasma concentrations similar to those induced by light to moderate smoking. Effects of nicotine on angiogenesis have been demonstrated for a number of tumor cells, such as breast, colon, and lung. Similar results have also been demonstrated in in vivo mouse models of lung cancer, where nicotine significantly increased the size and number of tumors in the lung, and enhanced metastasis.
A 2014 study suggested that e-cigarette use may be a risk factor for lung cancer. In several in vitro experiments, it has been found that nicotine in concentrations as low as 1 μM decreased the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects exerted by chemotherapeutics on several different malignant cell lines. These effects were partially reverted by exposure to α-bungarotoxin (α-BTX), an inhibitor of α7-nAChR. In the case of radiotherapy (RT), nicotine administration increased survival of H460 and A549 lung cancer cells. This effect was likewise reduced by addition of α-BTX prior to nicotine addition and radiation. On this basis, it is expected that use of nicotine products during cancer treatment may reduce the effects due to reactions following interaction of nicotine with α7-nAChR.

Evidence from experimental in vitro studies on cell cultures, in vivo studies on rodents as well as studies on humans inclusive of epidemiological studies indicate that nicotine may contribute in cancer development by stimulating a number of important processes. Nicotine acts primarily by activation of nicotine acetylcholine receptors and nicotine binds to these receptors with a higher affinity than acetylcholine. Furthermore, the tobacco-specific nitrosamines (TSNAs) NNN (N′-nitrosonornicotine) and NNK (4-(metylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanon) may be formed from nicotine after oral administration. E-cigarettes deliver the potent lung carcinogen NNK. Some evidence indicates that the NNK dose-response curve for cancer is highly nonlinear, with substantial increases in risk at low doses. Known bladder carcinogens have been detected in the urine of e-cigarette users but not in non-users. A 2015 study reported that the urine from users of e-cigarettes had very low levels of NNAL (4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol), which may suggest that endogenous formation of TSNA after nicotine inhalation is negligible. The data does indicate that TSNA may be formed internally after absorption of nicotine through the mucous membranes in the oral cavity and through the skin, while formation after lung absorption may be negligible. Thus, the toxicokinetics of nicotine may depend on the route of administration. The role of nicotine in carcinogenesis is of great importance in the evaluation of potentially harmful effects from non-tobacco related sources of nicotine, such as e-cigarettes.
Nicotine has been shown to induce chromosomal aberration, chromatid exchange, single-strand DNA strand breaks, and micronuclei in vitro. Oxidative stress is probably involved since the effects are reduced in the presence of antioxidants. The finding that the effects decrease after co-incubation with a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist indicates a receptor-dependent pathway for induction of oxidative stress.
The interaction of nicotine with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors activates signaling pathways that result in a number of reactions, such as increased cell proliferation and cell survival. Although nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are the primary receptors, binding of nicotine to β-ARs and EGFRs may also be important. Nicotine induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition, which is one of the vital steps for the acquisition of malignant phenotype. This transition allows the cell to acquire migratory properties, which may facilitate cancer metastases. Moreover, nicotine induces changes that mimic the effects of angiogenic growth factors.
At present, it is not possible to draw a conclusion whether nicotine itself may act as a complete carcinogen. In mice studies with NNK as an initiator, nicotine acts as a promoter after injection or dermal absorption, but not after oral administration. In drinking water experiments, there is considerable first-pass metabolism of nicotine before nicotine enters the systemic circulation. As a result, serum concentration is much lower after ingestion than after intraperitoneal injection administration. Nicotine enhanced tumor growth and progression after injection of malignant cells in mice. Enhancements were found both after exposure of nicotine by intraperitoneal injection, oral, and skin administration. Moreover, cotinine did also enhance tumor growth. Nicotine may inhibit antitumor immune response. It has also been reported that exposure to nicotine adversely affects dendritic cells, a cell type that has an important role in anticancer immunosurveillance. Moreover, in studies on xenograft in mice, nicotine has been found to reduce the effect of radiotherapy and chemoradiotherapy.
There is no long-term research concerning the cancer risk related to the potentially small level of exposure to the identified carcinogens in the e-cigarette vapor. Their long-term effect on risk of developing cancer is not known. Their long-term use is anticipated to raise the risk of developing lung cancer. A 2015 study found carcinogenicity was mainly evident in the lungs, mouth, and throat, which may be associated with nitrosamines, propylene glycol and some flavoring additives. Vaping is associated with a possible risk of developing head and neck cancers. In May 2014, Cancer Research UK stated that there are "very preliminary unpublished results that suggest that e-cigarettes promote tumour growth in human cells." The e-cigarette vapors triggered DNA strand breaks and lowered cell survival in vitro, regardless of nicotine content. A 2013 study found some samples of e-cigarette vapors had cytotoxic effects on cardiac muscle cells, though the effects were less than with cigarette smoke. Studies demonstrate that e-cigarette vapor have adverse effects on primary airway epithelial cells and tumor cell lines, and other epithelial cell lines, that ranged from reducing viability, an increase in production of inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress, to reducing antimicrobial defences and pro-carcinogenic events. In October 2012, the World Medical Association stated, "Manufacturers and marketers of e-cigarettes often claim that use of their products is a safe alternative to smoking, particularly since they do not produce carcinogenic smoke. However, no studies have been conducted to determine that the vapor is not carcinogenic, and there are other potential risks associated with these devices."

Since nicotine-containing e-liquids are made from tobacco they may contain impurities like cotinine, anabasine, anatabine, myosmine and beta-nicotyrine. The health implications of nicotine-related impurities are not known. A 2016 review found "Some studies have demonstrated that impurities and nicotine degradation products such as nicotine-cis-N-oxide, nicotine-trans-N-oxide, myosmine, anabasine, and anatabine, which are very carcinogenic, can be found in e-cigarette refill liquids. The molecules can lead to mutations in genes such as Ras (vital function in signal transduction of cell proliferation), p53 and Retinoblastoma (with roles as tumour suppressors) as these molecules can form adducts with cellular DNA." The majority of e-cigarettes evaluated included carcinogenic TSNAs; heavy metals such as cadmium, nickel, and lead; and the carcinogen toluene. However, in comparison to traditional cigarette smoke, the toxic substance levels identified in e-cigarette vapor were 9- to 450-fold less. E-liquid with tin was cytotoxic. E-cigarettes cannot be considered absolutely safe because there is no safe level for carcinogens.
A 2014 review found higher levels of carcinogens and toxicants than in an FDA regulated nicotine inhaler, suggesting that regulated FDA devices may deliver nicotine more safely. In 2014, the World Lung Foundation (now known as Vital Strategies) stated that "Researchers find that many e-cigarettes contain toxins, contaminants and carcinogens that conflict with the industry's portrayal of its products as purer, healthier alternatives. They also find considerable variations in the amount of nicotine delivered by different brands. None of this information is made available to consumers so they really don't know what they are ingesting, or how much."
A 2014 review found "Various chemical substances and ultrafine particles known to be toxic, carcinogenic and/or to cause respiratory and heart distress have been identified in e-cigarette aerosols, cartridges, refill liquids and environmental emissions." Few of the methods used to analyze the chemistry of e-cigarettes in the studies the review evaluated were validated. Many variables affect the levels of toxicants in the e-cigarette vapor, including the design, the type of liquid, and user behavior. The FDA in 2009 analyzed e-liquid cartridge samples from two brands of e-cigarettes, which were NJOY and Smoking Everywhere. Their analysis of the e-cigarette samples showed that the products contained detectable levels of known carcinogens and toxic chemicals to which users could potentially be exposed. Diethylene glycol was detected in one cartridge at approximately 1%. Diethylene glycol, an ingredient used in antifreeze, is toxic to humans. The source of the diethylene glycol contamination is not clear but could reflect the use of non-pharmaceutical grade propylene glycol. On July 22, 2009, the FDA warned that e-cigarettes may present a health risk.
Propylene glycol and other content

The primary base ingredients of the liquid solution is propylene glycol and glycerin. About 20% to 27% of propylene glycol and glycerin-based liquid particles are inhaled. A 2016 study found that 6% of nicotine, 8% of propylene glycol, and 16% of glycerin was breathed out by e-cigarette users. The long-term effects of inhaled propylene glycol has not been studied, and is unknown. The effects of inhaled glycerin are unknown. Being exposed to propylene glycol may cause irritation to the eyes and respiratory tract. When propylene glycol is heated and aerosolized, it could turn into propylene oxide, which the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) states is possibly carcinogenic to humans. The risk from the inhalation of propylene glycol and glycerin is probably low. Propylene glycol and glycerin have not been shown to be safe. Some research states that propylene glycol emissions may cause respiratory irritation and raise the likelihood to develop asthma. Long-term inhalation of propylene glycol indoors could increase risk to children to develop asthma. To lessen the risks, most e-cigarettes companies began to use water and glycerin as replacement for propylene glycol. The inhaled glycerin could cause lipoid pneumonia. Propylene glycol and glycerin had increased the amount of hydrogen peroxide.
Some e-cigarette products had acrolein identified in the aerosol. It may be generated when glycerin is heated to higher temperatures. Acrolein may induce irritation to the upper respiratory tract, and harm the lining of the lungs. Acrolein induces oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to a disruption in the function of the endothelial cell barrier in the lung. Acrolein may lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Acrolein levels were reduced by 60% in dual users and 80% for those that completely switched to e-cigarettes when compared to traditional cigarettes. A 2017 review stated that "based on the average of 120 puffs/day reported in the literature, our calculated levels of acrolein emitted by e‐cigarette users per day were found to vary between 0.00792 and 8.94 ppm/day." E-cigarettes vapor have been found to create oxidants and reactive oxygen species (OX/ROS). OX/ROS could react with other substances in the e-cigarette vapor because they are highly reactive. Although e-cigarettes have been found to contain OX/ROS at about 100 times less than in cigarette smoke, they probably induce meaningful biological effects. A 2014 study showed that e-liquids from a specific manufacturer contained greater amounts of ethylene glycol than glycerin or propylene glycol, but ethylene glycol has not been permitted for use in products meant for human consumption.
The toxicity of e-cigarettes and e-liquid can vary greatly, as there are differences in construction and materials in the delivery device, kind and origin of ingredients in the e-liquid, and the use or non-use of good manufacturing practices and quality control approaches. If exposure of aerosols to propylene glycol and glycerin rises to levels that one would consider the exposure in association with a workplace setting, it would be sensible to investigate the health of exposed persons. The short-term toxicity of e-cigarette use appears to be low, with the exception for some people with reactive airways.
Flavoring

The essential propylene glycol and/or glycerin mixture may consist of natural or artificial substances to provide it flavor. Health effects of e-cigarette flavorings are not entirely known. There is very limited toxicological data on inhaling flavoring additives. Flavorings can be a significant part of toxicants in the e-cigarette vapor. Each flavor has a different chemical composition, and therefore, probably, a distinct composition of toxicant emissions. The cytotoxicity of e-liquids varies, and contamination with various chemicals have been detected in the liquid. Some liquids were very toxic and others had little or no cytotoxicity. The cytotoxicity is mostly due to the amount and number of flavors added. Since nicotine has a bitter taste, nicotine e-liquids contain chemicals to cover up the nicotine taste. The liquids contain aromatic substances like tobacco, fruit, vanilla, caramel, and coffee. Generally, these additives are imprecisely described, using terms such as "vegetable flavoring". Although they are approved for human consumption there are no studies on the short-term or long-term effects of inhaling them. The safety of inhaling flavors is mostly unknown, and their safety has not been determined by the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association. The majority of flavorings in e-liquids have not been investigated for toxicity by means of inhalation. A 2017 review found "The Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association (FEMA) of the USA, a trade association of flavor ingredient manufacturers which evaluates the safety of food flavorings, has identified 1037 flavoring agents as potential respiratory hazards due to possible volatility and respiratory irritant properties. Common e-cig flavoring agents on this list include, but are not limited to: diacetyl, acetoin, 2,3-pentanedione (buttery flavors), camphor and cyclohexanone (minty flavors), benzaldehyde (cherry or almond flavors), cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon flavor), cresol (leathery or medicinal flavor), butyraldehyde (chocolate flavor), and isoamyl acetate (banana flavor)." A 2017 review stated, "the implication by manufacturers that flavor ingredients used in e-cigarettes and related devices (e.g. hookahs) are safe for inhalation because they have FEMA GRAS™ status for use in food has been stated to be 'false and misleading' by FEMA."
The extensive and unregulated use of flavoring additives may pose health concerns. Many flavors are irritants. The limited data available on their flavoring agents suggest that the majority of flavorings could lead to significant health risks from long-term use, particularly the ones that are sweet. In some cases e-liquids contain very large amounts of flavorings, which may cause irritation and inflammation on respiratory and cardiovascular systems. A 2016 study of 30 e-cigarette products in the US market found that 13 were more than 1% flavor chemicals by weight, some of which were of potential toxicological concern (e.g., cause respiratory irritation). Some flavors are regarded as toxic and a number of them resemble known carcinogens. The cytotoxicity of some flavors such as strawberry seems to be greater than others. A 2016 study of five flavors across six types of e-cigarettes found that flavors significantly affected the in vitro toxicity profile and the strawberry-flavored product was the most toxic. Some artificial flavors are known to be cytotoxic. Unflavored vapor is less cytotoxic than flavored vapor. A 2012 study demonstrated that in embryonic and adult cellular models, some substances of the e-cigarette vapor such as flavoring not found in tobacco smoke were cytotoxic. The caffeine exposures from vaping are approximately at amounts considerably less than in comparison with consuming caffeinated beverages. There is very limited information available regarding the effects of breathing in caffeine. The evidence is unclear that particular flavorings carry health risks, though there are indications that breathing in some may be a source of avoidable risks.
Cinnamaldehyde has been described as a highly cytotoxic material in vitro in cinnamon-flavored refill liquids. Cinnamaldehyde has also been detected in tobacco flavors, sweet flavors (e.g. caramel), and fruit flavors. Cinnamaldehyde have been identified as cytotoxic at the amount of about 400 times less than those allowed for use by the US Environmental Protection Agency. Compared to other flavors, coffee and cinnamon flavor are the most toxic. The four most commonly found flavor additives were vanillin, ethyl maltol, ethyl vanillin and menthol. They are carcinogenic or toxic, which contribute to causing cardiopulmonary diseases and neurodegenerative disorders. An 18-year-old patient reported using a Juul device with mint flavored pods in the days leading to episodes of pneumothorax in January 2019. In sampling multiple e-cigarette delivery systems, a 2019 study found Juul pods were the only product to demonstrate in vitro cytotoxicity from both nicotine and flavor chemical content, in particular ethyl maltol. There is limited information on the effects of inhaling menthol. Many flavoring additives likely cause respiratory effects not typically seen in cigarette smokers. The evidence is sparse to directly associate inhalations of cinnamon with developing or aggravating asthma. Some flavorings could cause lung inflammation. Fruity, sweet, and traditional tobacco flavorings may result in lung toxicity. Flavorings can harm lung cells by producing free radicals and inflammation. Some e-liquids containing cinnamaldehyde stimulate TRPA1, which might induce effects on the lung. In human lung fibroblasts, cinnamon roll flavoring resulted in a noticeable rise in the amount of inflammatory cytokine IL-8. E-liquids contain possibly toxic aldehydes and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Many flavors are known aldehydes, such as anisaldehyde, cinnamaldehyde, and isovaleraldehyde. Saccharides in sweet e-liquid flavors break down and generate furans and aldehydes when vaporized. The consequences of aldehyde-containing flavors on pulmonary surfaces are unknown. A 2012 study found butterscotch flavor was highly toxic with one liquid and two others had a low toxicity. A 2014 in vitro study showed that menthol flavors have a damaging effect on human periodontal ligament fibroblast growth. Methanol had increased the amount of hydrogen peroxide. A 2017 study found a variety of flavoring initiated inflammatory cytokines in lung cell cultures, of which acetoin and maltol were among the most strongest. A 2014 in vitro study demonstrated that e-cigarette use of a "balsamic" flavor with no nicotine can activate the release of proinflammatory cytokine in lung epithelial cells and keratinocytes. Some additives may be added to reduce the irritation on the pharynx. The long-term toxicity is subject to the additives and contaminants in the e-liquid. It is possible that flavors may worsen some of harmful effects in various cell types such as diminished cell viability, escalated rates of apoptosis, escalated DNA strand breaks, alterations in cell morphology and intensified inflammatory mediator production.
Certain flavorings contain diacetyl and acetyl propionyl which give a buttery taste. Some sweet flavors containing diacetyl and acetyl propionyl include butter, chocolate, milk, or toffee. Diacetyl occurs in a variety of e-cigarette flavorings such as caramel, butterscotch, watermelon, pina colada, and strawberry. A 2016 Harvard detected 39 of the 51 flavored e-cigarettes tested contained diacetyl. The American Lung Association recommended in 2016 that the FDA require that diacetyl and other unsafe chemicals be omitted from e-cigarettes. Menthol flavorings could also contain diacetyl. Diacetyl and acetyl propionyl are associated with bronchiolitis obliterans. A 2018 PHE report stated that the e-cigarette flavorings containing diacetyl is not likely to present a considerable risk. A 2015 review recommended for specific regulation of diacetyl and acetyl propionyl in e-liquid, which are safe when ingested but have been associated with respiratory harm when inhaled. Being exposed to diacetyl produces morphological alterations in the liver according to animal studies. Both diacetyl and acetyl-propionyl have been found in concentrations above those recommended by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Diacetyl is normally found at lower levels in e-cigarettes than in traditional cigarettes. 2, 3-pentanedione, is a α-diketone that is chemically and structurally similar to diacetyl. Although it has become a popular replacement for diacetyl, acute inhalation exposure to 2, 3-pentanedione has been shown to cause airway epithelial damage similar to diacetyl. Some liquids use butyric acid instead of diacetyl and acetyl propionyl, but it could have negative health effects. Concerns exist that the flavors and additives in e-cigarettes might lead to diseases, including the popcorn lung. The cardiovascular effects, including a vast range of flavorings and fragrances, is unknown. Compared to other flavors, cherry contains a greater amount of benzaldehyde, a main ingredient for a variety of fruit flavors. Because benzaldehyde can irritate the eyes and mucous membranes of the respiratory tracts with workplace exposure, concerns have been expressed regarding the toxicity of flavored e-cigarette vapor. The irritants butyl acetate, diethyl carbonate, benzoic acid, quinoline, bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, and 2,6-dimethyl phenol were present as undeclared ingredients in the e-liquid. The precise ingredients of e-cigarettes are not known. A 2010 study found rimonabant when examining e-liquids. This weight loss drug has been linked to seizures and suicide. The same study also determined e-liquid can contain amino-tadalafil which is a component of Cialis, used for erectile dysfunction. Users are at risk of encountering negative health outcomes from the small possibility of being exposed to pharmacologic compounds in some e-liquids.
The Centers for Disease Control tested in 2015 36 e-cigarette products for 10 flavor compounds commonly used as additives in tobacco products. Measurable levels of eucalyptol and pulegone were found in the menthol-flavored varieties for all manufacturers. Menthol concentrations ranged from 3,700 to 12,000 μg/g in flavored e-liquids, levels similar to those found in the filler of traditional cigarettes. Interestingly, menthol was found at low concentrations in 40% of the tobacco-flavored nonmenthol products tested. Other flavor compounds found were camphor, methyl, salicylate, pulegone, cinnamaldehyde (CAD), and eugenol. Tierney and colleagues in 2016 analyzed 30 e-cigarette products on the U.S. market and found 13 products contained more than 1% flavor chemicals by weight. Among the chemicals identified were aldehydes (e.g., benzaldehyde and vanillin), which are categorized as primary irritants of the respiratory tract. Tierney and colleagues also found that tobacco-flavored e-liquids were derived from confection-flavored chemicals (e.g., bubble gum and cotton candy flavoring) rather than tobacco extract. Various candy and fruit flavor e-liquids that are enticing to youth exhibit in cell culture cytotoxic or mutagenic effects.
Formaldehyde
The IARC has categorized formaldehyde as a human carcinogen, and acetaldehyde is categorized as a potential carcinogenic to humans. Formaldehyde induced DNA damage and inhibited DNA repair. Acetaldehyde generated crosslinking of DNA-protein which impede with DNA metabolic functions, including replication, repair, recombination, transcription and chromatin remodeling. Aldehydes may cause harmful health effects; though, in the majority of cases, the amounts inhaled are less than with traditional cigarettes. A 2016 study found that e-liquids without flavoring generated no aldehydes, which indicated that the flavors were causing the creation of aldehydes, according to a 2018 PHE report. Many chemical compounds can inadvertently be produced from e-cigarettes, especially carbonyl compounds like formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acrolein, and glyoxal by the chemical reaction of the e-liquid when the nichrome wire (heating element) is heated, to high temperatures. These compounds are frequently identified in e-cigarette aerosols. Potentially hazardous carbonyls have been identified in e-cigarette aerosols produced at temperatures above 200 °C. The propylene glycol-containing liquids produced the most amounts of carbonyls in e-cigarette aerosols. The levels of toxic chemicals in the e-cigarette vapor were found to be 1 to 2 orders of magnitude smaller than with cigarette smoke but greater than from a nicotine inhaler. Nearly all e-cigarettes evaluated, toxic and irritation-causing carbonyls were identified. Reports regarding the levels of toxic chemicals were inconsistent. This includes a study showing that the levels of toxicants in e-cigarettes may be higher than with cigarette smoke.
Battery output voltage influences the level of the carbonyl substances in the e-cigarette vapor. Some newer e-cigarette models let users boost the amount of vapor and nicotine provided by modifying the battery output voltage. E-cigarettes that were modified to boost the vapor production are more dangerous to use. High-voltage e-cigarettes could subject users to large amounts of carbonyls. E-cigarettes with higher voltages (5.0 V) can emit carcinogens including formaldehyde at levels comparable to cigarette smoke, while reduced voltages (3.0 V) generate aerosol with levels of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde roughly 13 and 807-fold less than in cigarette smoke. The average amount of formaldehyde in vapor from high-voltage devices is higher than the average amount of formaldehyde released from cigarettes. "Dripping", where the liquid is dripped directly onto the atomizer, can create carbonyls including formaldehyde.
Controversy exists regarding the specific amount of formaldehyde expected to be breathed in by the user. A 2015 PHE report found that normal e-cigarette use generates very low levels of aldehydes. Normal usage of e-cigarettes generates very low levels of formaldehyde, and at normal settings they generate very low levels of formaldehyde. A 2018 PHE report found that at normal usage temperatures, aldehyde in the e-cigarette vapor is at negligible amounts in comparison with smoking. Later-generation and "hotter" e-cigarettes may generate equal or higher levels of formaldehyde compared to smoking. A 2015 study analyzing 10 puffs found that vaping at a high voltage (5.0 V) generates formaldehyde in e-cigarette vapor; they inferred from the finding that the user vaping at high voltage with 3 mg of e-liquid daily would inhale 14.4±3.3 mg of formaldehyde daily in formaldehyde-emitting chemicals. This was estimated to be a lifetime cancer risk of 5 to 15 times greater than compared with long-term smoking. A 2015 study using a third-generation device, very low levels of formaldehyde were produced on lower power, although, when adjusted to a maximum power setting, levels were greater than with cigarette smoke. Running at a higher power (temperature) not only increases nicotine delivery, but also increases the amount of formaldehyde and other aldehydes that are naturally produced by heating up propylene glycol or glycerin and other toxicants produced in the e-cigarette aerosol. A 2015 PHE report found that by applying maximum power and increasing the time the device is used on a puffing machine, e-liquids can thermally degrade and produce high levels of formaldehyde. Users detect the "dry puff" (also known as a "dry hit") and avoid it, and they concluded that "There is no indication that EC users are exposed to dangerous levels of aldehydes." However, e-cigarette users may learn to overcome the unpleasant taste due to elevated aldehyde formation, when the nicotine craving is high enough.
Nicotine


Pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and the elderly are more sensitive to nicotine than other individuals. There are safety issues with the nicotine exposure from e-cigarettes, which may cause addiction and other adverse effects. Nicotine is regarded as a potentially lethal poison. Concerns exist that vaping can be harmful by exposing users to toxic levels of nicotine. At low amounts, it has a mild analgesic effect. At sufficiently high doses, nicotine may result in nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, salivation, bradyarrhythmia, and possibly seizures and hypoventilation. High doses can induce deleterious effects on the growth of osteoblasts. Higher-doses leads to loss of nicotinic receptor specificity and induces cholinergic toxicity. The highest-doses can lead to coma. However, at the low amount of nicotine provided by e-cigarettes fatal overdose from use is unlikely; in contrast, the potent amount of nicotine in e-cigarettes liquids may be toxic if it is accidentally ingested or absorbed via the skin. The health effects of nicotine in infants and children are unclear.
E-cigarettes provide nicotine to the blood quicker than nicotine inhalers. The levels were above that of nicotine replacement product users. E-cigarettes seem to have a pharmacokinetic nicotine profile closer to nicotine replacement products than with traditional cigarettes. How efficiently different e-cigarettes give nicotine is unclear. Serum cotinine levels are comparable to that of traditional cigarettes, but are inharmonious and rely upon the user and the device. Blood nicotine levels raised more gradually and took more time to get to peak concentration with e-cigarettes than with traditional cigarettes. Vaping was found to have comparable levels of nicotine urinary metabolites to those who were tobacco and smokeless tobacco product users. Though, the oxidative nicotine metabolites were less in those who were vaping. Evidence indicates that some vaping products may deliver the same amount of nicotine as traditional cigarettes. There is fair evidence that chance and degree of dependence are less for e-cigarettes than traditional cigarettes, according to a 2018 National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report. It not clear the level of addictiveness of e-cigarettes, compared with traditional cigarettes, according to a 2018 PHE report. The report also stated "nicotine addictiveness depends on a number of factors including presence of other chemicals, speed of delivery, pH, rate of absorption, the dose, and other aspects of the nicotine delivery system, environment and behaviour." Users vaping without using nicotine exhibited symptoms of dependence, according to a 2015 study. E-cigarette packages and advertisements require health warnings under US law, stating "WARNING: This product contains nicotine. Nicotine is an addictive chemical."
First-generation devices
E-cigarettes resembling cigarettes typically produce much less blood nicotine levels. When compared to traditional cigarettes older devices usually delivered low amounts of nicotine. E-cigarette use can be associated with a substantial dispersion of nicotine, thus generating a plasma nicotine concentration which can be comparable to that of traditional cigarettes. This is due to the minute nicotine particles in the e-cigarette vapor, which permit quick delivery into the bloodstream. The nicotine delivered from e-cigarettes enters the body slower than traditional cigarettes. Studies suggest that inexperienced users obtain moderate amounts of nicotine from e-cigarettes. Concerns were raised over inconsistent amounts of nicotine delivered when drawing on the device.
Later-generation devices
Tank or adjustable e-cigarettes can raise nicotine levels as high as traditional cigarettes. Later-generation e-cigarettes give nicotine more effectively than first-generation e-cigarettes. Later-generation models with concentrated nicotine liquids may deliver nicotine at levels similar to traditional cigarettes. Some e-cigarette tank devices with stronger batteries heat solutions to greater temperatures, which may raise levels of nicotine in the blood similar to those of traditional cigarettes. Research suggests that experienced e-cigarettes users are able to get as much nicotine from e-cigarettes as traditional cigarettes. Later-generation e-cigarettes containing sufficient nicotine elevate heart rate comparable to traditional cigarettes. Later-generation devices delivery 35% to 72% more nicotine than compared with first‐generation devices. Second-generation e-cigarettes raised the heart rate and blood pressure similar to traditional cigarettes. As there are design changes, later-generation devices may provide nicotine similar to traditional cigarettes with a highly concentrated amount potential straight to the brain. Such devices may largely reshape the effects on cardiac safety, misuse, and addiction. There is not much research on fourth-generation devices.
Concerns
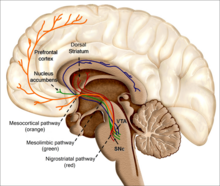
How do e-cigarettes affect the brain? The nicotine in e-liquids readily absorbs into the bloodstream when a person uses an e-cigarette. Upon entering the blood, nicotine stimulates the adrenal glands to release the hormone epinephrine (adrenaline). Epinephrine stimulates the central nervous system and increases blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate. As with most addictive substances, nicotine increases levels of a chemical messenger in the brain called dopamine, which affects parts of the brain that control reward (pleasure from natural behaviors such as eating). These feelings motivate some people to use nicotine again and again, despite possible risks to their health and well-being.
The health effects of long-term nicotine use is unknown. It may be decades before the long-term health effects of nicotine vapor inhalation is known. It is not recommended for non-smokers. Public health authorities do not recommend nicotine use for non-smokers. The pureness of the nicotine differs by grade and producer. The impurities associated with nicotine are not as toxic as nicotine. The health effects of vaping tobacco alkaloids that stem from nicotine impurities in e-liquids is not known. Nicotine affects practically every cell in the body. The complex effects of nicotine are not entirely understood. It poses several health risks. Short-term nicotine use excites the autonomic ganglia nerves and autonomic nerves, but chronic use seems to induce negative effects on endothelial cells. Nicotine may have a profound impact on sleep. The effects on sleep vary after being intoxicated, during withdrawal, and from long-term use. Nicotine may result in arousal and wakefulness, mainly via incitement in the basal forebrain. Nicotine withdrawal, after abstaining from nicotine use in non-smokers, was linked with longer overall length of sleep and REM rebound. A 2016 review states that "Although smokers say they smoke to control stress, studies show a significant increase in cortisol concentrations in daily smokers compared with occasional smokers or nonsmokers. These findings suggest that, despite the subjective effects, smoking may actually worsen the negative emotional states. The effects of nicotine on the sleep-wake cycle through nicotine receptors may have a functional significance. Nicotine receptor stimulation promotes wake time and reduces both total sleep time and rapid eye movement sleep."
Nicotine can weaken antibacterial defenses and modify macrophage activation. Nicotine can cause tremors, high blood pressure, abnormal heart rhythms, and lower coronary blood flow. Nicotine constricts blood vessels. This includes coronary blood vessels and those in the skin. However, blood vessels in the skeletal muscle dilate as a result of nicotine. It can also cause nausea, sweating, and diarrhea. In reaction to nitric oxide, it hinders endothelial-dependent widening of blood vessels. It is associated with stroke, peripheral vascular disease, delayed wound healing, peptic ulcer disease, and esophageal reflux. Vapers that get a higher amount of blood nicotine are probably correlated with increased heart rates. Acute administration of nicotine causes a variety of well-characterized, dose- and route-dependent effects in adults, including cardiovascular effects, such as greater cardiac output, leading to an increase in myocardial oxygen demand. Nicotine is correlated with lung inflammation in adults, which may be as a result of it chemotactic effects. Nicotine may have adverse effects on lipids, cause insulin resistance, and may cause pro-inflammatory effects that could impact beta cell function. Nicotine lowers activity of free radical scavenging enzymes, resulting in more production of hydroxyl free radicals. Nicotine impairs glucose homeostasis, indicating a major role in the development of diabetes mellitus type 2. Osseointegration is a pertinent part of the survival of implants. Nicotine considerably impedes the regenerative capability of mesenchymal stem cells. This includes impeding their proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Nicotine has been correlated with vasoconstriction and a weakened ability to heal at the cellular level. Thus, it apparently compromises implant osseointegration. Nicotine lowers estrogen levels and has been associated with early menopause in women. Nicotine is negatively associated with total sperm motility. Nicotine causes dysfunction of NO synthesis. This may result in inability to get penile erections and erectile dysfunction.
A 2016 review found "Evidence from experimental animal models clearly demonstrate nicotine's ability to enhance existing tissue injury and diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, stroke, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer, renal injury and developmental (e.g. pulmonary, reproductive and central nervous system) abnormalities." The consequence of nicotine use in autoimmunity has been conflicting. Nicotine could have cancer-promoting properties, therefore long-term use may not be harmless. Nicotine may result in neuroplasticity variations in the brain. Nicotine has been demonstrated to alter the amounts of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in humans. Nicotine could make cancer therapies less effective. Based on in vitro and in vivo effects of nicotine, patients should be advised not to use nicotine products during cancer treatment unless it is temporarily needed to stop tobacco smoking. Nicotine can suppress appetite. Nicotine users will probably gain weight after using less nicotine. A long-term risk from vaping a base containing nicotine is nicotine dependence.
Youth
Children are more sensitive to nicotine than adults. The use of products containing nicotine in any form among youth, including in e-cigarettes, is unsafe. Nicotine has more significant and durable damaging effects on adolescent brains compared to adult brains, the former suffering more harmful effects. Animal research offers strong evidence that the limbic system is particularly vulnerable to the long lasting effects of nicotine. In youth, nicotine may result in cognitive impairment as well as the chance of nicotine addiction for life. The adolescent's developing brain is especially sensitive to the harmful effects of nicotine. A short period of regular or occasional nicotine exposure in adolescence exerts long-term neurobehavioral damage. Risks of exposing the developing brain to nicotine include mood disorders and permanent lowering of impulse control. The rise in vaping is of great concern because the parts encompassing in greater cognitive activities including the prefrontal cortex of the brain continues to develop into the 20s Nicotine exposure during brain development may hamper growth of neurons and brain circuits, effecting brain architecture, chemistry, and neurobehavioral activity.
Nicotine changes the way synapses are formed, which can harm the parts of the brain that control attention and learning. Preclinical studies indicate that teens being exposed to nicotine interferes with the structural development of the brain, inducing lasting alterations in the brain's neural circuits. Each e-cigarette brand differs in the exact amount of ingredients and nicotine in each product. Therefore, little is known regarding the health consequences of each brand to the growing brains of youth. In August 2014, the American Heart Association noted that "e-cigarettes could fuel and promote nicotine addiction, especially in children." Whether there are subgroups of adolescents who are at greater risk of developing a nicotine dependence from vaping is not known. A 2014 policy statement by the UK's Faculty of Public Health has stated, "A key concern for everyone in public health is that children and young people are being targeted by mass advertising of e-cigarettes. There is a danger that e-cigarettes will lead to young people and non-smokers becoming addicted to nicotine and smoking. Evidence from the US backs up this concern." Long-term studies on the safety of nicotine-only exposure (e.g., as with using e-cigarettes rather than smoking traditional cigarettes) among youth have not been conducted.
In 2015 the psychological and behavioral effects of e-cigarettes were studied using whole-body exposure to e-cigarette vapor, followed by a series of biochemical and behavioral studies. The results showed that nicotine-containing e-cigarette vapor induces addiction-related neurochemical, physiological and behavioral changes. A 2015 study on the offspring of the pregnant mice, which were exposed to nicotine-containing e-cigarette liquid, showed significant behavioral alterations. This indicated that exposure to e-cigarette components in a susceptible time period of brain development could induce persistent behavioral changes. As indicated in the limited research from animal studies, there is the potential for induced changes in neurocognitive growth among children who have been subjected to e-cigarette vapors consisting of nicotine. The FDA stated in 2019 that some people who use e-cigarettes have experienced seizures, with most reports involving youth or young adult users.

Metals
There is limited evidence on the long-term exposure of metals. Exposure to the levels and kinds of metals found in the aerosol relies upon the material and other manufacturing designs of the heating element. E-cigarettes contain some contamination with small amounts of metals in the emissions but it is not likely that these amounts would cause a serious risk to the health of the user. According to a 2018 PHE report, metals emissions no matter how small, are not needed. They further stated, "EC that generate minimal metal emissions should become an industry standard." The device itself could contribute to the toxicity from the small amounts of silicate and heavy metals found in the liquid and vapor, because they have metal parts that come in contact with the e-liquid. Low levels of possibly harmful chromium, lead, and nickel metals have been found in the emissions. Chromium and nickel nanoparticles have also been found. Copper nanoparticles can induce mitochondrial and DNA injury in lung fibroblasts. DNA repair can be impeded by titanium dioxide nanoparticles from the e-cigarette vapor. This was demonstrated that the titanium dioxide nanoparticles induced single-strand breaks and produced oxidative stress in the DNA of A549 cells. The risk of inhaling nanoparticles is an area of concern. The toxicity of nanoparticles is unknown. Metals including nickel, cadmium, lead and silicate can found in the e-cigarette vapors, and are thought to be carcinogenic, nephrotoxic, neurotoxic, and hemotoxic. Heavy metals are correlated with serious health issues. Inhaling lead can induce serious neurologic injury, notably to the growing brains of children.
Metals may adversely affect the nervous system. Metals found in the e-cigarette vapor may induce cell damage and initiate inflammatory cytokine such as in human lung fibroblasts. A 2017 review found "E-cigarette aerosols and copper nanoparticles induced mitochondrial ROS production, mitochondrial stress (reduced stability of OxPhos electron transport chain (ETC) complex IV subunit) and DNA fragmentation in lung fibroblasts." A 2013 review found metallic and nanoparticles are associated with respiratory distress and disease. A 2014 review found considerable amounts of tin, metals, and silicate particles that came from various components of the e-cigarette were released into the aerosol, which result in exposure that could be higher than with cigarette smoke. A 2013 study found metal particles in the aerosol were at levels 10-50 times less than permitted in inhalation medicines. A 2014 review suggested that there is no evidence of contamination of the aerosol with metals that justifies a health concern. Cadmium that have been found in the e-cigarette vapor is linked to low sperm density.
Comparison of levels of toxicants in e-cigarette aerosol
| Toxicant | Range of content in nicotine inhaler mist (15 puffs∗) | Content in aerosol from 12 e-cigarettes (15 puffs∗) | Content in traditional cigarette micrograms (μg) in smoke from one cigarette |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formaldehyde (μg) | 0.2 | 0.2-5.61 | 1.6-52 |
| Acetaldehyde (μg) | 0.11 | 0.11-1.36 | 52-140 |
| Acrolein (μg) | ND | 0.07-4.19 | 2.4-62 |
| o-Methylbenzaldehyde (μg) | 0.07 | 0.13-0.71 | — |
| Toluene (μg) | ND | ND-0.63 | 8.3-70 |
| p- and m-Xylene (μg) | ND | ND-0.2 | — |
| NNN (ng) | ND | ND-0.00043 | 0.0005-0.19 |
| Cadmium (ng) | 0.003 | ND-0.022 | — |
| Nickel (ng) | 0.019 | 0.011-0.029 | — |
| Lead (ng) | 0.004 | 0.003-0.057 | — |
Abbreviations: μg, microgram; ng, nanogram; ND, not detected.
∗Fifteen puffs were chosen to estimate the nicotine delivery of one traditional cigarette.
Ethical considerations
| Ethical considerations | Supporting arguments | Opposing arguments | Questions to direct future research |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco harm reduction | |||
| Potential for smoking cessation | E-cigarettes may be as effective as the nicotine patch. | Inconclusive evidence of efficacy for smoking cessation. | What is the efficacy of nicotine and non-nicotine e-cigarettes for smoking cessation and reduction? |
| Potential for smoking reduction | Demonstrated in multiple studies. | Unlikely that cigarette reduction results in significant health benefits. | What is the long-term impact of dual use of e-cigarettes and tobacco cigarettes on health outcomes? |
| Product safety | |||
| Potential for long-term adverse effects | Unknown impact of long-term propylene glycol inhalation. | No documented serious adverse events to date. | What are the long-term safety implications of nicotine and non-nicotine e-cigarette use? |
| Propylene glycol inhalation causes short-term respiratory irritation. | |||
| Autonomy to use a product of unknown risk | Ethical imperative given informed consent. | Public health concerns trump individual rights. | How should consumer rights be weighed against public health concerns? |
| Use among non-smokers | |||
| Potential to lead to nicotine addiction | Perceived harmlessness may lead never smokers to initiate e-cigarettes. | No evidence for increased nicotine addiction to cause net public health harms. | What is the long-term health impact of nicotine addiction? |
| Potential gateway effect | Nicotine acts as a priming agent for the brain. | Unclear implications for transitioning to tobacco cigarettes. | How many non-smokers initiating e-cigarettes transition to other tobacco products, including cigarettes? |
| Use among youth | |||
| Potential to lead to nicotine addiction | Minors require protection. | No evidence of increased nicotine addiction causing net public health harms. | How many youth initiating e-cigarettes report continuous long-term product use (1 year or longer)? |
| E-liquid flavorings are attractive to youth. | |||
| Potential gateway effect | Nicotine is a priming agent for the brain. | Unclear implications for transitioning to tobacco cigarettes. | How many youth initiating e-cigarettes transition to other tobacco products, including cigarettes? |
| Nicotine poisoning among children | Increased calls to poison control centers. | None. | To what extent can the risk of nicotine poisoning among children be mitigated? |
| E-liquid flavors are appealing to youth. | |||
| Use in public places | |||
| Potential for passive vaping | Stem cell cytotoxicity. | Limited evidence that passive vaping poses significant health concerns. | What is the long-term impact of passive vaping and second-hand vapor exposure? |
| Aerosolized nicotine emissions. | |||
| Renormalized smoking culture | |||
| Potential to subvert decades of anti-smoking efforts | Increased acceptability of smoke-like vapor and smoking behavior. | No evidence that e-cigarettes would be conflated with tobacco cigarettes. | How are the increased awareness and use of e-cigarettes affecting perceptions of cigarette smoking? |
| Market ownership | |||
| Unethical collaboration with the tobacco industry | Public health endorsement of e-cigarettes increases tobacco company market share. | Possible necessity to collaborate with the tobacco industry to achieve public health gains. | What are the public health implications of tobacco industry ownership of major e-cigarette brands? |
Effects on breathing and lung function
The risks to the lungs are not fully understood, and concern exists regarding the negative effects on lung function. The long-term lung function effects of vaping is unknown. There is limited evidence on the long-term health effects to the lungs. The long-term effect from vaping a base containing nicotine on lung tissue is unknown. Limited evidence suggests that e-cigarettes produce less short-term effects on lung function than with traditional cigarettes. Many ingredients used in e-liquids have not been examined in the lung. The effects of e-cigarette use in respect to asthma and other respiratory diseases are unknown. It is not clear whether long-term inhalation of e-cigarette vapor will make asthma better or worse. A 2015 review found e-cigarettes may induce acute lung disease.
Exposure to inhaled nicotine-containing e-cigarette fluids triggered effects normally associated with the development of a chronic obstructive lung disease-like tissue damage in a nicotine-dependent manner. Preclinical research indicate that vaping escalates the virulence of drug resistant microorganisms and diminishes the capacity of lung cells to eliminate bacteria. E-cigarettes have been correlated with pleural effusions. A 2015 study found that e-cigarette vapors can induce oxidative stress in lung endothelial cells. Constant lung inflammation as a result of the e-cigarette vapor could result in lung pathogenesis and induce serious diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and fibrosis. There is strong evidence that e-cigarette vapors can result in acute endothelial cell injury, but the long-term effects regarding this matter on being exposed over a prolonged period of time to e-cigarette vapor is uncertain. A 2017 review found "Exposure to nicotine that was specifically generated by the use of e-cigarettes, was shown to promote oxidative stress and impairment of autophagy, which in turn serves as a potential mechanism leading to development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease." A 2014 case report observed the correlation between sub-acute bronchiolitis and vaping. After quitting vaping the symptoms improved. Vaping causes bronchospasm. Adolescents who vaped had a higher frequency of chronic bronchitis symptoms.
The long-term effects regarding respiratory flow resistance are unknown. The available evidence indicates that e-cigarettes may result in respiratory effects that are like as well as unlike that of traditional cigarettes. E-cigarettes reduce lung function, but to a much lower extent than with traditional cigarettes. E-cigarettes could harm the respiratory system. Vaping induces irritation of the upper and lower respiratory system. The immediate effects of e-cigarettes after 5 minutes of use on pulmonary function resulted in considerable increases in resistance to lung airflow. A 2013 review found an instant increase in airway resistance after using a single e-cigarette. Higher levels of exhaled nitric oxide were found among test subjects in a 2014 study who vaped with a base of nicotine which was associated with lung inflammation. Any reported harmful effects to cardiovascular and respiratory functions after short-term use of e-cigarettes were appreciably milder in comparison to cigarette smoke. When used in the short-term, an e-cigarette resulted in a rise of respiratory resistance comparatively to traditional cigarettes. E-cigarette use could result in respiratory diseases among youth. Evidence from animal studies indicate that children or adolescents exposed to second-hand vapor containing nicotine may impede their lung development. Adolescents with asthma who vape could have greater odds of having a higher number of respiratory symptoms and aggravations in contrast to their peers who do not vape. Adolescents and children with other respiratory ailments who vape may be at greater chance for aggravating of respiratory symptoms. A 2018 PHE report found "There have been some studies with adolescents suggesting respiratory symptoms among EC experimenters. However, small scale or uncontrolled switching studies from smoking to vaping have demonstrated some respiratory improvements." A 2017 review found "among a population of 11th-grade and 12th-grade students in California, e-cigarette use was associated with twice the risk of respiratory symptoms, and the risk increased with more frequent e-cigarette use."
Comparable to a traditional cigarette, e-cigarette particles are tiny enough to enter the alveoli, enabling nicotine absorption. These particles are also tiny enough to go deep in the lungs and enter into the systemic circulation. Research indicates that e‐cigarette vapor containing particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 μm, just from one puff, enters the systemic circulation via the cardiopulmonary system, leading to a large amount being deposited in the respiratory tract. Local pulmonary toxicity may occur because metal nanoparticles can deposit in the lung's alveolar sacs. E-cigarettes companies state that the particulates produced by an e-cigarette are too tiny to be deposited in the alveoli. Tinier particles deposit more nicotine in the alveoli. Different devices generate different particle sizes and cause different depositions in the respiratory tract, even from the same nicotine liquid. The aerosol production of e-cigarettes during vaping decreases, which requires a more forceful suction to create a similar volume of aerosol. A more forceful suction could affect the deposition of substances into the lungs. Reports in the literature have shown respiratory and cardiovascular effects by these smaller size particles, suggesting a possible health concern. Vaping is potentially harmful, especially to the critically ill, such as people with oncologic, lung, or cardiac diseases.
As with cardiovascular disease, evidence consistently indicates that exposure to e-cigarette aerosol has adverse effects on lungs and pulmonary function. Repeated exposure to acrolein, which is produced by heating the propylene glycol and glycerin in e-liquids, causes chronic pulmonary inflammation, reduction of host defense, neutrophil inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, and protease-mediated lung tissue damage, which are linked to the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. E-cigarette aerosol also exposes users to highly oxidizing free radicals. Animal studies have also shown that e-cigarettes increase pulmonary inflammation and oxidative stress while inhibiting the immune system.
Consistent with these experimental results, people who used e-cigarettes experienced decreased expression of immune-related genes in their nasal cavities, with more genes suppressed than among cigarette smokers, indicating immune suppression in the nasal mucosa. E-cigarette use upregulates expression of platelet-activating factor receptor (PAFR) in users' nasal epithelial cells; PAFR is an important molecule involved in the ability of S.pneumoniae, the leading cause of bacterial pneumonia, to attach to cells it infects (adherence). In light of the immunosuppressive effects observed in nasal mucosa, there is concern that e-cigarette use will predispose users toward more severe respiratory infections, as has been demonstrated in mouse studies.
Given these effects, it is not surprising that e-cigarette use is associated with a doubling of the risk of symptoms of chronic bronchitis among US high school juniors and seniors with higher risk associated with higher use; these risks persisted among former users. Similarly, current e-cigarette use was associated with an increased diagnosis of asthma among Korean high school students among current (e-cigarette users who were never cigarette smokers). E-cigarette users were also more likely to have had days absent from school due to severe asthma symptoms.
Vaping is reportedly tied to a range of lung injuries which include hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH), acute eosinophilic pneumonia (AEP), diffuse alveolar damage, organizing pneumonia (OP), lipoid pneumonia, and giant cell interstitial pneumonia (GIP).
2019 outbreak of lung illness linked to vaping products
Main article: 2019 outbreak of lung illness linked to vaping productsIn 2019, an outbreak of severe vaping-associated lung illness affected users in most states in the US. Cases involved in the outbreak of lung illness were first identified in Illinois and Wisconsin in April 2019. Similar cases of vaping-associated lung illness were reported in the UK and Japan before this outbreak occurred. 1,888 cases have been reported from 49 states, the District of Columbia, and one US territory, as of October 29, 2019. 37 deaths have been confirmed in the US, as of October 29, 2019. Based on reports from several states, symptoms typically develop over a period of days but sometimes can manifest over several weeks.
On September 6, 2019, Dr. Dana Meaney-Delman, serving as the incident manager of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)'s response to this outbreak, said that "Based on the clinical and laboratory evidence to date, we believe that a chemical exposure is likely associated with these illnesses." The CDC stated that the cases have not been linked to one product or substance, saying "Most patients have reported a history of using e-cigarette products containing THC. Many patients have reported using THC and nicotine. Some have reported the use of e-cigarette products containing only nicotine." Many of the samples tested by the states or by the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) as part of the 2019 investigation have been identified as vaping products containing tetrahydrocannabinol (or THC, a psychoactive component of the cannabis plant). Most of those samples with THC tested also contained significant amounts of Vitamin E acetate. On October 17, 2019, the CDC reported that their findings suggest vaping products containing THC are linked to most of the cases and play a major role in the outbreak.
Thickening agents were used to water down and bulk up vape oils. There has been an increase in attention to companies that sell diluent products that are made with Vitamin E acetate. Previously, Vitamin E was used in low concentrations, or lower than 20% of the formula in vape cartridges. As a result of a limited availability of cannabis in California as well as high demand, illicit sellers had used about 50% or higher of diluent thickeners in their formulas to bulk up tiny potency vape cartridges. In September 2019, New York Governor Andrew Cuomo instructed the state health department to issue subpoenas against three sellers of thickening agents used in illicit vaping products.
The e-cigarette industry is placing the blame on illicit vaping liquids for the lung injuries. Juul Labs stated that some news reports state that several cases of lung illness are associated with vaping THC, found in cannabis, "a Schedule 1, controlled substance that we do not sell." The CDC recommends that the public should consider not using vaping products until more is known. They also recommend against vaping any THC products as of October 15, 2019. The US FDA considers it prudent to avoid inhaling Vitamin E acetate. On September 6, 2019, the US FDA stated that because consumers cannot be sure whether any THC vaping products may contain Vitamin E acetate, consumers are urged to avoid buying vaping products on the street, and to refrain from using THC oil or modifying/adding any substances to products purchased in stores.

Effects on cardiovascular system
There is limited available evidence on their long-term cardiovascular effects. No data is available on their effects in individuals with cardiovascular disease, as of 2016. Their cardiovascular effects in individuals who do not have cardiovascular disease is uncertain. Although limited, there is supportive evidence that vaping adversely impacts endothelial function and arterial hardening. Most of the cardiovascular effects of vaping are consistent with those of nicotine. Vaping might bring about some adverse cardiovascular effects to users, especially those who already have cardiovascular disease. However, the risk is believed to be lower than that of cigarette smoking based on research comparing e-cigarette aerosol in contrast to cigarette smoke chemicals. The effects of aldehydes, particulates, and flavorings used in vaping devices on cardiovascular health is not clear. Low amounts of aldehydes can still be a health concern, particularly among individuals with cardiovascular disease. E-cigarettes reduce cardiac muscle function and increase inflammation, but these changes were only substantial with traditional cigarettes. No published research is available on vaping and thrombosis, platelet reactivity, atherosclerosis, or blood vessel function. The small particles generated from e-cigarette use have the ability to get through airways and enter circulation, which pose a potential risk to cardiovascular systems. The minute nicotine particles in the e-cigarette vapor could increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias and hypertension which may put some users, particularly those with atherosclerosis or other cardiovascular risk factors, at significant risk of acute coronary syndrome. There are many compounds in the e-cigarette vapor that have an impact on the onset and advancement of atherosclerosis. Some case reports documented the possible cardiovascular adverse effects from using e-cigarettes, the majority associated was with improper use. Even though e-cigarettes are anticipated to produce fewer harmful substances than traditional cigarettes, limited evidence recognizes they comparatively have a lowered raised cardiovascular risk.
Preliminary studies have shown that using a nicotine containing e-cigarette for just five minutes causes similar lung irritation, inflammation, and effect on blood vessels as smoking a traditional cigarette, which may increase the risk of a heart attack. E-cigarette use leads to sympathomimetic effects because of nicotine intake. It is argued that there could be a risk for harmful effects, including tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy. E-cigarettes containing nicotine may have a lower cardiovascular effect than traditional cigarettes containing nicotine. Research on the consequences of vaping on blood pressure is limited. Short-term physiological effects include increases in blood pressure and heart rate. The increased blood pressure and heart rate among smokers who vaped was lower than with cigarette smoking. A 2016 study found vaping increases aortic stiffness in people who did not have cardiovascular risk factors, an effect that was lower than with cigarette smoking. Habitual vaping was associated with oxidative stress and a shift towards cardiac sympathetic activity, which are both associated with a risk of developing cardiovascular disease. A 2012 case report found a correlation between paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and vaping. Research indicates a relationship between exposure to particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 μm and the chance of developing cardiovascular disease.
E-cigarettes adversely impact the cardiovascular system. Although the specific role of nicotine in cardiovascular disease remains debated, nicotine is not the only biologically active component in e-cigarette aerosol. E-cigarettes work by creating an aerosol of ultrafine particles to carry nicotine deep into the lungs. These particles are as small as—and sometimes smaller than—those in traditional cigarettes. These ultra fine particles are themselves biologically active, trigger inflammatory processes, and are directly implicated in causing cardiovascular disease and acute cardiovascular events. The dose-response effect for exposure to particles is nonlinear, with substantial increases in cardiovascular risk with even low levels of exposure to ultrafine particles. For example, exposure to second-hand cigarette smoke has nearly as large an effect on many risk factors for cardiovascular disease and the risk of acute myocardial infarction as does being an active smoker. Like traditional cigarette smokers, e-cigarette users experience increased oxidative stress and increases in the release of inflammatory mediators. E-cigarette aerosol also induces platelet activation, aggregation, andadhesion. All these changes are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. These physiological changes are manifest in rapid deterioration of vascular function following use of e-cigarettes. E-cigarette and traditional cigarette smoking in healthy individuals with no known cardiovascular disease exhibit similar inhibition of the ability of arteries to dilate in response to the need for more blood flow. This change reflects damage to the lining of the arteries (the vascular endothelium), which increases both the risk of long-term heart disease and an acute event such as a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Using e-cigarettes is also accompanied by a shift in balance of the autonomic (reflex) nervous system toward sympathetic predominance, which is also associated with increased cardiac risk. The biological stresses that e-cigarette use impose on the cardiovascular system are manifest as an increase in risk of acute myocardial infarction. A cross-sectional analysis of data in the US 2014 and 2016 National Health Interview Surveys revealed that daily e-cigarette use was associated with increased odds of having suffered a myocardial infarction, controlling for traditional cigarette smoking, demographic characteristics (age, gender, body mass index, family income) and health characteristics (hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia). Significantly, the effect of using e-cigarettes on the odds of myocardial infarction approached what was found with traditional cigarette smoking.
Effects on oral health
There is little evidence indicating that using e-cigarettes rather than continue to smoke will help periodontal disease. Vaping with or without nicotine or flavoring may help cause periodontal disease. Nicotine as well as their flavoring may be damaging to periodontal ligament, stem cells, and gingival fibroblasts in cultures as a result of creation of aldehydes and/or carbonyls from e-cigarette vapor. It is possible that e-cigarettes could harm the periodontium because of the effects of nicotine on gum tissues and the immune system. Vaping resulted in nicotine stomatitis, hairy tongue, and angular cheilitis. Vaping can cause oral mucosal lesions. No compelling evidence from vaping indicates it directly causes oral cancer.
Other effects
Vaping long-term is anticipated to raise the risk of developing some of the diseases linked to smoking. Concern exists regarding the immunological effects of e-liquid, and analysis on animals demonstrate that nicotine as well as e-liquid vapor, appear to have adverse effects on the immune system. The immunological effects of e-cigarette use is not well understood, and the finding of the limited available research appear to be contradictory. There is a small amount of research available that is related to gastrointestinal and neurological health risks. There were reports of e-cigarettes causing an immune system reaction involving inflammation of the gastrointestinal system. Long-term use could increase the risk of tuberculosis. Some health effects associated with e-cigarette use can include recurring ulcerative colitis, lipoid pneumonia, acute eosinophilic pneumonitis, sub-acute bronchial toxicity, reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, and reversal of chronic idiopathic neutrophilia. Adequate research is not available to ascertain the risk of long-term harm resulting in cerebrovascular disease. Data on the impact of vaping on urologic health is not available. A 2016 study regarding e-liquid exposure in adults rats showed e-cigarettes have an adverse impact on the kidneys. There is limited information on the physiologic effect of vaping with a base of nicotine on surgical outcomes. Although there is no research available on vaping and otologic outcomes, nicotine still induces vasoconstriction while in otologic surgery. It is not known whether there is a benefit for vaping to aid with quitting smoking before surgery. Vaping may have a considerable negative effect on wound healing. Vaping can cause contact dermatitis and thermal injuries.
Not much is known regarding the metabolic effects of vaping. It has not been fully studied in humans as to whether vaping has the same negative effects on metabolic processes as cigarette smoking. Though, animal studies show similar effects of vaping, even without being exposed to nicotine, on weight and metabolic processes, comparing cigarette smoking. This shows other things are responsible for the metabolic effects than just nicotine. Animal studies indicate that vaping has similar negative effects on weight, body fat, glucose and lipid profiles and other cardiovascular potential dangers as traditional cigarettes, but they may be less prominent. A lot of these cardiometabolic effects happen even without nicotine being present.
Aerosol
Composition
Main article: Composition of electronic cigarette aerosolThe composition of the e-cigarette aerosol varies across and within manufacturers. Limited data exists regarding their chemistry. The aerosol of e-cigarettes is generated when the e-liquid reaches a temperature of roughly 100–250 °C within a chamber, which is thought to cause pyrolysis of the e-liquid and could also lead to decomposition of other liquid ingredients. The vapor usually contains propylene glycol, glycerin, nicotine, flavors, aroma transporters, and other substances. The levels of nicotine, TSNAs, aldehydes, metals, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), flavors, and tobacco alkaloids in e-cigarette vapors vary greatly. The yield of chemicals found in the e-cigarette vapor varies depending on, several factors, including the e-liquid contents, puffing rate, and the battery voltage.
First-hand
E-cigarettes consist of fine and ultrafine particles of particulate matter, in the form of an aerosol. The aerosol (mist) produced by an e-cigarette is commonly but inaccurately called vapor. In physics, a vapor is a substance in the gas phase whereas an aerosol is a suspension of tiny particles of liquid, solid or both within a gas. The word "vaping" is not technically accurate when applied to e-cigarettes. The aerosol is made-up of liquid sub-micron particles of condensed vapor; thus, the users of these devices are rather "aerosolizing." This aerosol that is produces looks like cigarette smoke to some extent. After a puff, inhalation of the aerosol travels from the device into the mouth and lungs. The composition of e-liquids varies widely due to the extensive range of nicotine levels and flavoring additives used in these products, which result in a hugely great number of different chemical vapor combinations potentially breathed in by the user.
The particles produced from vaping are comparable in particle-size distribution and number of particles to cigarette smoke, with the majority of them in the ultrafine range. Some e-cigarettes released more particles than cigarette smoke. A 2014 review found that fine particles can be chemically intricate and not uniform, and what a particle is made of, the exact harmful elements, and the importance of the size of the particle is mostly unknown. They found that because these things are uncertain, it is not clear whether the ultrafine particles in e-cigarette vapor have health effects similar to those produced by traditional cigarettes. A 2014 WHO report found e-cigarettes release a lower concentration of particles than traditional cigarettes.
Second-hand
After the aerosol is inhaled, it is exhaled. Emissions from e-cigarettes are not comparable to environmental pollution or cigarette smoke as their nature and chemical composition are completely different. The particles are larger, with the mean size being 600 nm in inhaled aerosol and 300 nm in exhaled aerosol. The exhaled aerosol particle concentration is 5 times lower from an e-cigarette than from a traditional cigarette. The density of particles in the e-cigarette vapor is lower than in cigarette smoke by a factor of between 6 and 880 times lower.
For particulate matter emissions, e-cigarettes slightly exceeded the WHO guidelines, but emissions were 15 times less than traditional cigarette use. In January 2014, the International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease stated "Adverse health effects for exposed third parties (second-hand exposure) cannot be excluded because the use of electronic cigarettes leads to emission of fine and ultrafine inhalable liquid particles, nicotine and cancer-causing substances into indoor air." The dense vapor consists of liquid sub-micron droplets. Substantial levels of particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 μm are exhaled by vapers.
Exposure

Since e-cigarettes have not been widely used long enough for evaluation, the long-term health effects from the second-hand vapor are not known. The short-term health effects from the second-hand vapor is also not known. There is insufficient data to determine the impact on public health from e-cigarettes. The potential harm to bystanders from e-cigarettes is unknown. This is because no long-term data is available. There are limited information on the health effects for children inhaling second-hand vapor. Long-term effects for children inhaling second-hand vapor is not known. Vaping has quickly gained public awareness with greater use among adolescents and adults, resulting in greater inhaled second-hand vapor for adolescents, children, and infants. Second-hand vapor does vary depending on the e-liquid, the device and in the way it is used. There is an array in e-cigarette designs, which has an impact on the amounts of ingredients being exposed to non-users. Heavy advertising and promotion included the assertion that vaping would present little risk to bystanders. E-cigarettes are marketed as "free of primary and second-hand smoke risk" due to no carbon monoxide or tar is expected to be generated during use. However, there is a concern for the health impact of nicotine and other ingredients. Exposure to second-hand vapor may be common. Concerns exist that the increased rates of e-cigarette users who have never smoked could cause harms to public health from the increased nicotine addiction. The growing experimentation with vaping among people under that age of 18 is especially concerning in respect to public health. Ethical concerns arise from possibly vulnerable bystanders being exposed to the not yet known health effects of second-hand vapor. Especially compared to the adverse effects of traditional cigarettes, the overall safety of e-cigarettes is not likely to justify significant public health concerns. Overall, there is a possibility they may greatly harm the public's health. Vaping in areas where smoking is banned indoors could be a move in the wrong direction for public health when considering air quality in addition to being unfavorable for an individual who may have quit nicotine use if they did not vape. Some of the few studies examining the effects on health shown that being exposed to e-cigarette vapor may produce biological effects. Their indiscriminate use is a threat to public health.
Some non-users have reported adverse effects from the second-hand vapor. Second-hand vapor exhaled into the air by e-cigarette users can expose others to potentially harmful chemicals. Vaping exposes non-users to particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 μm, which poses health risks to non-users. E-cigarettes produce propylene glycol aerosols at levels known to cause eye and respiratory irritation to non-users. A 2014 study demonstrated that non-smokers living with vaping device users were exposed to nicotine. A 2015 study concluded that, for indirect exposure, two chemicals—nicotine and propylene glycol—exceeded California Environmental Protection Agency exposure level standards for noncarcinogenic health effects. Between January 2012 and December 2014, the FDA noted 35 adverse effect reports regarding second-hand vaping exposure. A 2016 survey found a sizable percentage of middle and high school students were exposed to second-hand e-cigarette vapors. It is recommended that adolescents stay away from being exposed to second-hand e-cigarette vapor. A 2016 study showed that most participated coughed right away and briefly following a single exposure to e-cigarette vapor, while after 15 minutes it induced a diminished cough reflex sensitivity in healthy never-smokers. Nicotine-free e-cigarette vapor did not have this effect. The health effects of passive exposure to e-cigarettes with no nicotine, as well as the extent of exposure to these products, have just begun to be studied. E-cigarettes that do not contain nicotine generate hazardous vapors and could still present a risk to non-users. Research has not evaluated whether non-users can have allergic reactions from nut potential allergens in e-cigarette aerosol.
Since e-cigarettes do not burn tobacco, no side-stream smoke or any cigarette smoke is produced. Only what is exhaled by e-cigarettes users enters the surrounding air. It is not clear how much of inhaled e-cigarette aerosol is exhaled into the environment where non-users can be exposed. Exhaled vapor consists of nicotine and some other particles, primarily consisting of propylene glycol, glycerin, flavors, and aroma transporters. Bystanders are exposed to these particles from exhaled e-cigarette vapor. Clean air is safer than e-cigarette vapor. A mixture of harmful substances, particularly nicotine, ultrafine particles, and VOCs can be exhaled into the air. The liquid particles condenses into a viewable fog. The e-cigarette vapor is in the air for a short time, with a half-life of about 10 seconds; traditional cigarette smoke is in the air 100 times longer. This is because of fast revaporization at room temperature.
A 2017 review found that the "rapid production of new products has made it hard for the concerned stakeholders such as researchers in the public health field and policy makers to ensure that the products introduced to the public are safe for the users and non-users who are involuntarily exposed to e-cigarette vapors." Little research exists on the exhaled particles, nicotine, and cancer-promoting chemicals into indoor air. Concern exists that some of the mainstream vapor exhaled by e-cigarette users may be inhaled by bystanders, particularly indoors. People living with e‐cigarette users had increased salivary concentrations of cotinine. A small number of e-cigarette studies exist on the effect of indoor air quality done on human test subjects in natural settings. Though, the available studies presented conflicting scientific evidence on the exact exposure from the e-cigarette vapor contents which may be a result of the contrasting methodology used during the research process. Vaping can expose non-users to aldehydes and it reduced indoor air quality due to their released aldehydes. Since e-cigarettes involve an aerosolization process, it is suggested that no meaningful amounts of carbon monoxide are emitted. Thus, cardiocirculatory effects caused by carbon monoxide are not likely. However, in an experimental study, e-cigarettes increased levels of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surrounding air. Passive inhalation of vapor might have significant adverse effects. Though, e-cigarettes exposes non-users to nicotine but not to tobacco-related combustion toxicants. Exposure to e-cigarette vapor can reduce lung function.
E-cigarettes do pollute the air in the form of exhaled mainstream aerosol from people using e-cigarettes. Nicotine, ultrafine particles, and products of heating propylene glycol and glycerin are increased in the air where e-cigarettes are being used, although, as expected, at lower levels than produced by smoking the same number of traditional cigarettes. As with traditional cigarettes, however, when several people are using e-cigarettes indoors at the same time, the air can become polluted. For example, levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in a large hotel event room (4,023m) increased from 2–3 μg/m to as high as 819 μg/m (interquartile range: 761–975 μg/m) when 59–86 people were using e-cigarettes. This level is comparable to a very (conventional tobacco) smoky bar or casino and dramatically exceeds the US Environmental Protection Agency annual time-weighted standard for PM2.5 of 12 μg/m.
Evidence has also shown that bystanders absorb nicotine when people around them use e-cigarettes at levels comparable with exposure to traditional cigarette second-hand smoke. In a study of non-smokers living with nicotine e-cigarette users, those living with traditional cigarette smokers, or those living in homes where no one used either product, cotinine (a metabolite of nicotine) levels in bystanders' urine were significantly elevated in both the people exposed to second-hand e-cigarette aerosol and those exposed to second-hand tobacco smoke compared with people living in aerosol- and smoker-free homes. Interestingly, the levels of elevated urinary cotinine in the two exposed groups were not significantly different (although the passive smokers had higher point estimates), despite the fact that the increase in air pollution in the smokers' homes was much higher than in the e-cigarette users' homes (geometric mean air nicotine concentrations of 0.13 μg/m in e-cigarette users' homes, 0.74 μg/m in smokers' homes, and 0.02 μg/m in the control homes).
On the basis of emerging evidence, in 2014 the American Industrial Hygiene Association concluded that "e-cigarettes are not emission-free and that their pollutants could be of health concern for users and those who are exposed secondhand....heir use in the indoor environment should be restricted, consistent with current smoking bans, until and unless research documents that they will not significantly increase the risk of adverse health effects to room occupants." Similarly, in 2016 the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) updated its standard for "Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality" to incorporate emissions from e-cigarettes into the definition of "environmental tobacco smoke," which is incompatible with acceptable indoor air quality. As of April 2017, 12 US states and 615 localities had prohibited the use of e-cigarettes in venues in which traditional cigarette smoking was prohibited.
There are benefits to banning vaping indoors in public and working areas, since there is a potential harm of renormalizing tobacco use in smoke-free areas, in addition to, vaping may result in spread of nicotine and other chemicals indoors. E-cigarettes used in indoor environments can put at risk non-smokers to elevated levels of nicotine and aerosol emissions. Non-smokers exposed to e-cigarette aerosol produced by a machine and pumped into a room were found to have detectable levels of the nicotine metabolite cotinine in their blood. The same study stated that 80% of nicotine is normally absorbed by the user, so these results may be higher than in actual second-hand exposure. A 2015 PHE report concluded that e-cigarettes "release negligible levels of nicotine into ambient air with no identified health risks to bystanders". The e-cigarette vapor creates personal exposures that would warrant supervision.

The available evidence demonstrates that the e-cigarette vapor emitted from e-cigarettes is not just "harmless water vapor" as is repeatedly stated in the advertising of e-cigarettes, and they can cause indoor air pollution. A 2014 practice guideline by NPS MedicineWise states, "Although data on health effects of passive vapour are currently lacking, the risks are argued to be small, but claims that e-cigarettes emit only water vapour are nevertheless incorrect. Serum cotinine levels (a metabolite of nicotine) have been found to be similar in bystanders exposed to either e-cigarette vapour or cigarette smoke." A 2015 California Department of Public Health has reported that "Mainstream and secondhand e-cigarette aerosol has been found to contain at least ten chemicals that are on California's Proposition 65 list of chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm."
A white paper published in 2014 by the American Industrial Hygiene Association concluded e-cigarettes emit airborne contaminants that may be inhaled by the user and those nearby. Due to this possible risk, they urged restriction of their use indoors, similar to smoking bans, until research has shown the aerosol does not significantly harm others in the area. A 2014 review suggested that the levels of inhaled contaminants from the e-cigarette vapor are not of significant health concern for human exposures by the standards used in workplaces to ensure safety. The compounds that are present, are mostly below 1% of the corresponding levels permissible by workplace safety standards. But workplace safety standards do not recognize exposure to certain vulnerable groups such as people with medical ailments, children, and infants who may be exposed to second-hand vapor. Some chemicals from e-cigarette exposures could surpass workplace safety standards. E-cigarette convention studies indicate that second-hand e-cigarette vapor may be significant for workers in conventions where there are people using e-cigarettes, particularly those who encounter the vapor in more than one of these events. Exposure studies suggest that e-cigarette use in indoor areas is higher than the smoke-free level put forth by the US Surgeon General and the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. The use of e-cigarettes in a smoke-free area could expose non-users to toxicants. The effect on users and bystanders is probably much less harmful than traditional cigarettes.
Second-hand vapor exposes bystanders to numerous pollutants at amounts higher than background air. A 2016 WHO report stated that "While some argue that exposure to SHA is unlikely to cause significant health risks, they concede that SHA can be deleterious to bystanders with some respiratory pre-conditions. It is nevertheless reasonable to assume that the increased concentration of toxicants from SHA over background levels poses an increased risk for the health of all bystanders." A 2014 WHO report stated passive exposure was as a concern, indicating that current evidence is insufficient to determine whether the levels of exhaled vapor are safe to involuntarily exposed bystanders. The report stated that "it is unknown if the increased exposure to toxicants and particles in exhaled aerosol will lead to an increased risk of disease and death among bystanders." The British Medical Association (BMA) reported in 2013 that there are "concerns that the use of e-cigarettes could threaten the norm of not smoking in public places and workplaces." Several medical organizations advocate that vaping be banned in public places and workplaces. A 2014 review found it is safe to infer that their effects on bystanders are minimal in comparison to traditional cigarettes. E-cigarette vapor has notably fewer toxicants than cigarette smoke.

Third-hand
E‐cigarettes can be unsafe to non-users via third-hand exposure, including children, pregnant women, casino employees, housekeeping employees, and vulnerable groups. E-cigarette use by a parent might lead to inadvertent health risks to offspring. E-cigarettes pose many safety concerns to children. For example, indoor surfaces can accumulate nicotine where e-cigarettes were used, which may be inhaled by children, particularly youngsters, long after they were used. A policy statement by the American Association for Cancer Research and the American Society of Clinical Oncology has reported that "Third-hand exposure occurs when nicotine and other chemicals from second-hand aerosol deposit on surfaces, exposing people through touch, ingestion, and inhalation". A 2015 PHE report stated the amount of nicotine deposited was low and that an infant would have to lick 30 square meters to be exposed to 1 mg of nicotine. There are no published studies of third-hand exposure from e-cigarettes, however initial data suggests that nicotine from e-cigarettes may stick to surfaces and would be hard to remove. The extent of third-hand contamination indoors from e-cigarettes in real-world settings has not been established but would be of particular concern for children living in homes of e-cigarette users, as they spend more time indoors, are in proximity to and engage in greater activity in areas where dust collects and may be resuspended (e.g., carpets on the floor), and insert nonfood items in their mouths more frequently.
Effects during pregnancy
Concerns exist regarding pregnant women exposure to e-cigarette vapor through direct use or via exhaled vapor. Vaping during pregnancy is not recommended. It is recommended that pregnant women stay away from being exposed to second-hand e-cigarette vapor. No evidence have shown that e-cigarettes are safe to use for pregnant women. No amount of nicotine is safe for pregnant women. As of 2014, there are no conclusions on the possible hazards of pregnant women using e-cigarettes, and there is an increasing amount of research on the negative effects of nicotine on prenatal brain development. E-cigarette use during pregnancy can be harmful to the fetus. Nicotine accumulates in the fetus because it goes through the placenta. Nicotine has been found in placental tissue as early as seven weeks of embryonic gestation, and nicotine concentrations are higher in fetal fluids than in maternal fluids. It also attaches to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the fetus brain. When the brain is being developed, activating nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by nicotine can result in long-term developmental turmoil. Nicotine can induce a genotoxic effect in fetal cells. Nicotine is harmful to the growing fetus. It seems to be more harmful to the growing fetus during the latter stage of pregnancy.
As of 2015, the long-term issues of e-cigarettes on both mother and unborn baby are unknown. Being exposed over a long period of time to e-cigarette vapors may raise the possibility of unfavorable reproductive outcomes. The rate of e-cigarette use among pregnant adolescents is unknown, but the effects of nicotine and the potential for harm by other e-cigarette toxicants indicate that the use of e-cigarettes is a fetal risk factor among pregnant adolescent girls. Prenatal nicotine exposure is associated with adverse effects on the growing fetus, including effects to normal growth of the endocrine, reproductive, respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurologic systems. Prenatal nicotine exposure has been associated with dysregulation of catecholaminergic, serotonergic, and other neurotransmitter systems. Prenatal nicotine exposure is associated with lower birth weights compared to other infants, preterm birth, stillbirth, sudden infant death syndrome, and alterations to normal brain development. When birth weight is normal there still can be damage. Nicotine may result in premature birth, miscarriage, fetal neurotoxicity, and fetal lung development issues. Nicotine delivered by e-cigarettes during pregnancy can result in multiple adverse consequences, including sudden infant death syndrome, and could result in altered corpus callosum and deficits in auditory processing. Prenatal nicotine exposure is associated with asthma and wheezing which may continue into adulthood. Gestational age nicotine exposure is associated with many neurological deficits. Prenatal exposure has been associated with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure in minors. Prenatal nicotine exposure in females may lead toward early menarche. An infant was born with necrotizing enterocolitis due to e-cigarette use during pregnancy. Evidence from animal studies indicate that being exposed to second-hand vapor containing nicotine during pregnancy may impede fetal lung development. Vaping during pregnancy resulted in a reduction in lung volume. Low amounts of aldehydes can still be a health concern among pregnant women.
In what way the e-liquid ingredients could affect a fetus is unknown. Several ingredients used in e-liquid has not been studied for safety during pregnancy. Studies examining the cytotoxicity of e-liquid flavorings found toxicity to be greater in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells relative to human pulmonary fibroblasts, raising potential concerns about exposure risks for pregnant women. There are concerns about the health impacts of pediatric exposure to second-hand and third-hand e-cigarette vapor. A 2014 Surgeon General report found "that nicotine adversely affects maternal and fetal health during pregnancy, and that exposure to nicotine during fetal development has lasting adverse consequences for brain development." The belief that e-cigarettes are safer than traditional cigarettes could increase their use in pregnant women. The toxic effects identified with e-cigarette refill liquids on stem cells may be interpreted as embryonic death or birth defects. Since e-cigarettes are not substantiated as cessation tools, may contain nicotine at inconsistent levels and added ingredients that are possibly harmful, to bear with e-cigarettes to be used among pregnant women to decrease smoking puts this group at considerable risk.
It is discouraged for pregnant and breastfeeding females to substitute cigarettes with e-cigarettes. It is recommended that females who smoke during pregnancy to quit using cigarettes. There is concern for breastfeeding females using e-cigarettes, due to the lack of data on propylene glycol transferring to breastmilk. It is discouraged to use e-cigarettes while breastfeeding infants or young children. The consequences of vaping on infants feeding on breast milk is uncertain.
Environmental impact
There is limited information available on any environmental issues connected to the production, usage, and disposal of e-cigarette models that use cartridges. As of 2014, no formal studies have been done to evaluate the environmental effects of making or disposing of any part of e-cigarettes including the batteries or nicotine production. As of 2014, it is uncertain if the nicotine in e-liquid is United States Pharmacopeia-grade nicotine, a tobacco extract, or synthetic nicotine when questioning the environmental impact of how it is made. It is not clear which manufacturing methods are used to make the nicotine used in e-cigarettes. The emissions from making nicotine could be considerable from manufacturing if not appropriately controlled. Some e-cigarette brands that use cartridges state their products are 'eco-friendly' or 'green', despite the absence of any supporting studies. Some writers contend that such marketing may raise sales and increase e-cigarette interest, particularly among minors.
It is unclear how many traditional cigarettes are comparable to using one e-cigarette that uses a cartridge for the average user. Information is limited on energy and materials used for production of e-cigarettes versus traditional cigarettes, for comparable use. E-cigarettes can be made manually put together in small factories, or they can be made in automated lines on a much bigger scale. Larger plants will produce greater emissions to the surrounding environment, and thus will have a greater environmental impact. Although some brands have begun recycling services for their e-cigarette cartridges and batteries, the prevalence of recycling is unknown, as is the prevalence of information provided by manufacturers on how to recycle disposable parts. E-cigarettes that are not reusable may contribute to the problem of electronic waste. A 2016 review found "Heavy metals may be released, if disposable ECs are disposed into the environment." E-cigarettes that are thrown away are ending up in landfills is a rising public health concern. E-cigarettes batteries contaminate the land and water and may release lead into the environment. E-liquids that are not entirely used up could contain nicotine and heavy metals. This is another risk for the environment. Since the majority of e-cigarettes are reusable they are possibly more environmentally friendly than using single-use devices. Compared to traditional cigarettes, e-cigarettes do not create litter in the form of discarded cigarette butts. Traditional cigarettes tend to end up in the ocean where they cause pollution.
Public perceptions
Marketing and advertisement play a significant role in the public's perception of e-cigarettes. Some tobacco users think vaping is safer than tobacco or other smoking cessation aids. It is generally considered by users that e-cigarettes are safer than tobacco. Emerging research indicates that vaping is not as safe as previously thought. Many users think that e-cigarettes are healthier than traditional cigarettes for personal use or for other people. Many youth believe vaping is a safe substitute to traditional cigarettes. A 2016 review suggests "that the perceived health risks, specific product characteristics (such as taste, price and inconspicuous use), and higher levels of acceptance among peers and others potentially make e-cigarettes initially more attractive to adolescents than tobacco cigarettes. Youths who have lower harm perceptions may be particularly susceptible to e-cigarette and polytobacco use, conversely those who perceive e-cigarettes as more harmful would be less likely to use them. Usually, only a small proportion of users are concerned about the potential adverse health effects or toxicity of e-cigarettes. A nation-wide US survey among adults found 11.1% thought vaping during pregnancy was not as harmful as smoking, 51.0% thought it was as harmful, 11.6% thought it would be an increased harm, and 26.2% were unsure. A 2015 study showed that 60% of all adolescence stated vaping were safe or a minor health risk and that 53.4% considered vaping safer than cigarette smoking. A 2017 review found, based on literature from January 2006 to October 2016, examining perceptions regarding vaping during pregnancy, that the majority of respondents perceived vaping can carry health risks to mother and child, but also thought they may be less harmful than traditional cigarettes. Many adolescent asthmatics have a favorable view of vaping. A 2016 survey of people 14 years of age and up in Germany reported that 20.7% of participants consider e-cigarettes to be not as harmful as cigarettes, 46.3% just as harmful, and 16.1% thought they were more harmful, and 17.0% gave no answer. In terms of harm perception, a 2016 study found that flavored e-cigarette use reduced the prevalence of perception of the dangers of tobacco use among youth. Another 2016 study found more nuanced results, demonstrating that tobacco flavor increased harm perception while fruit and sweet flavors decreased harm perception among UK adolescents. Similarly, a 2016 study in the US found that, for US adolescents, fruit-flavored e-cigarettes were perceived to be less harmful than tobacco flavored ones. There is indication that an individual's perception of a substance's potential harms and benefits and their behavior of use is influenced by the availability of information discussing the health effects of that substance. A 2015 analysis reports that 34.20% (8433/24,658) of American youth sampled believe that e-cigarettes are less harmful than cigarettes, and 45% (11,096/24,658) are not sure.
As of 2018, under 50% of adults in the UK believe vaping is less harmful than smoking. Action on Smoking and Health (ASH) in the UK found that in 2015, compared to the year before, "there has been a growing false belief that electronic cigarettes could be as harmful as smoking". Among smokers who had heard of e-cigarettes but never tried them, this "perception of harm has nearly doubled from 12% in 2014 to 22% in 2015." ASH expressed concern that "The growth of this false perception risks discouraging many smokers from using electronic cigarettes to quit and keep them smoking instead which would be bad for their health and the health of those around them." A 2015 PHE report noted that in the US belief among respondents to a survey that vaping was safer than smoking cigarettes fell from 82% in 2010 to 51% in 2014. The report blamed "misinterpreted research findings", attracting negative media coverage, for the growth in the "inaccurate" belief that e-cigarettes were as harmful as smoking. A 2017 review noted that there is a public misconception that vaping is safer than cigarette smoking. A 2016 review noted that the increasing use of e-cigarettes may be due in part to "the misperception that e-cigarettes are a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes." A 2014 review noted that "users do not appear to fully understand their health risks." Beliefs on vaping may be surpassing our scientific knowledge of these products. Proponents of vaping have stated that nicotine is 'as safe as caffeine'. E-cigarettes are believed to be considerably safer compared with smoking and nicotine is thought to be comparatively harmless. As a consequence, it is believed to be without risk to use them indoors or near babies.
A 2014 worldwide survey found that 88% of respondents stated that vaping were less harmful than cigarette smoke and 11% believed that vaping were absolutely harmless. A 2013 four-country survey found higher than 75% of current and former smokers think e-cigarettes are safer than traditional cigarettes. A 2017 report found that among high income countries, Republic of Korea in 2016 was 66%, the US in 2016 was 37%, Netherlands in 2015 was 32%, Canada in 2016 was 30%, the UK in 2016 was 24%, Australia in 2016 was 22%, Uruguay in 2014 was 19%, and among low income countries, Malaysia in 2013 was 70%, Zambia in 2014 was 57%, Thailand in 2012 was 54%, Mexico from 2014-15 was 38%, Bangladesh from 2014-15 was 37%, Brazil from 2012-13 was 22%, and China from 2013-15 was 15%, for the percentage of respondents of adult smokers believing e-cigarette use is just as risky or more risky to health than cigarettes.
A 2016 review found that "The vaping communities' apparent lack of acknowledgment of the potential negative impacts of e-cigarettes appears to have discredited them in the eyes of many public health officials. Continuing down this path may generate beliefs that the vaping community cares little for public health, are primarily interested in selling their fast-growing companies to the highest tobacco company bidder, and will oppose any meaningful regulations of their product, however reasonable and necessary they may be—essentially aligning the vaping community's practices to tobacco companies' well-established playbook." A 2017 review found that "Although it was originally argued that e‐cigarettes are 'harm free,' the present prevailing belief is that they are 'reduced harm' alternatives to conventional cigarettes. This latter notion is still debatable and not supported by conclusive evidence, especially considering the wide variation between e‐cigarette products." E-cigarette advertisements with warnings could strengthen e-cigarette harm perceptions, and lower the likelihood of buying e-cigarettes.
Gallery
- E-cigarette related media
- NIDA Live - The Science of Vaping.
- Why Teens are Attracted to Vaping.
-
 In 2019, an outbreak of lung injury was linked to vaping.
In 2019, an outbreak of lung injury was linked to vaping.
- Dr. Nora Volkow on Addiction - A Disease of Free Will.
- Julius Dein Performs A Magic Trick on a Vape.
See also
- Health effects of tobacco
- Regulation of electronic cigarettes
- Positions of medical organizations on electronic cigarettes
Notes
- All patients have reported using vaping products. The outbreak has raised concern among public health officials, and revived the debate regarding the effects of vaping. This is the first time that vaping products has been linked to an outbreak of lung illness. Except for one confirmed case in Canada, it seems to be occurring only in the US.
Bibliography
- McNeill, A; Brose, LS; Calder, R; Bauld, L; Robson, D (February 2018). "Evidence review of e-cigarettes and heated tobacco products 2018" (PDF). UK: Public Health England. pp. 1–243.
- Stratton, Kathleen; Kwan, Leslie Y.; Eaton, David L. (January 2018). Public Health Consequences of E-Cigarettes (PDF). National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. pp. 1–774. doi:10.17226/24952. ISBN 978-0-309-46834-3. PMID 29894118.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|agency=ignored (help) - "Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems and Electronic Non-Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/ENNDS)" (PDF). World Health Organization WHO. August 2016. pp. 1–11.
- Wilder, Natalie; Daley, Claire; Sugarman, Jane; Partridge, James (April 2016). "Nicotine without smoke: Tobacco harm reduction". UK: Royal College of Physicians. pp. 1–191.
- McNeill, A; Brose, LS; Calder, R; Hitchman, SC; Hajek, P; McRobbie, H (August 2015). "E-cigarettes: an evidence update" (PDF). UK: Public Health England. pp. 1–113.
- "State Health Officer's Report on E-Cigarettes: A Community Health Threat" (PDF). California Tobacco Control Program. California Department of Public Health. January 2015. pp. 1–21.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention Health Promotion (US) Office on Smoking Health (2014). The Health Consequences of Smoking—50 Years of Progress: A Report of the Surgeon General. Surgeon General of the United States. pp. 1–943. PMID 24455788.
References
- Chapman 2015, p. 15.
- ^ Farsalinos, Konstantinos; LeHouezec, Jacques (2015). "Regulation in the face of uncertainty: the evidence on electronic nicotine delivery systems (e-cigarettes)". Risk Management and Healthcare Policy. 8: 157–67. doi:10.2147/RMHP.S62116. ISSN 1179-1594. PMC 4598199. PMID 26457058.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Baraona, L. Kim; Lovelace, Dawn; Daniels, Julie L.; McDaniel, Linda (2017). "Tobacco Harms, Nicotine Pharmacology, and Pharmacologic Tobacco Cessation Interventions for Women". Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health. 62 (3): 253–269. doi:10.1111/jmwh.12616. ISSN 1526-9523. PMID 28556464.
- Eltorai, Adam EM; Choi, Ariel R; Eltorai, Ashley Szabo (2018). "Impact of Electronic Cigarettes on Various Organ Systems". Respiratory Care. 64 (3): 328–336. doi:10.4187/respcare.06300. ISSN 0020-1324. PMID 30401756.
- ^ Pisinger, Charlotta; Døssing, Martin (December 2014). "A systematic review of health effects of electronic cigarettes". Preventive Medicine. 69: 248–260. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.10.009. PMID 25456810.
- ^ Serror, K.; Chaouat, M.; Legrand, Matthieu M.; Depret, F.; Haddad, J.; Malca, N.; Mimoun, M.; Boccara, D. (2018). "Burns caused by electronic vaping devices (e-cigarettes): A new classification proposal based on mechanisms". Burns. 44 (3): 544–548. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2017.09.005. ISSN 0305-4179. PMID 29056367.
- ^ Tegin, Gulay; Mekala, Hema Madhuri; Sarai, Simrat Kaur; Lippmann, Steven (2018). "E-Cigarette Toxicity?". Southern Medical Journal. 111 (1): 35–38. doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000749. ISSN 1541-8243. PMID 29298367.
- ^ H. Vogel, MSN, FNP, AOCNP, Wendy (2016). "E-Cigarettes: Are They as Safe as the Public Thinks?". Journal of the Advanced Practitioner in Oncology. 7 (2): 235–240. doi:10.6004/jadpro.2016.7.2.9. ISSN 2150-0878. PMC 5226315. PMID 28090372.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Drummond, MB; Upson, D (February 2014). "Electronic cigarettes. Potential harms and benefits". Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 11 (2): 236–42. doi:10.1513/annalsats.201311-391fr. PMC 5469426. PMID 24575993.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
PatnodeHenderson2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Grana, R; Benowitz, N; Glantz, SA (13 May 2014). "E-cigarettes: a scientific review". Circulation. 129 (19): 1972–86. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.114.007667. PMC 4018182. PMID 24821826.
- ^ Saitta, D; Ferro, GA; Polosa, R (Mar 2014). "Achieving appropriate regulations for electronic cigarettes". Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 5 (2): 50–61. doi:10.1177/2040622314521271. PMC 3926346. PMID 24587890.
- ^ Clapp, Phillip W.; Jaspers, Ilona (2017). "Electronic Cigarettes: Their Constituents and Potential Links to Asthma". Current Allergy and Asthma Reports. 17 (11): 79. doi:10.1007/s11882-017-0747-5. ISSN 1529-7322. PMC 5995565. PMID 28983782.
- ^ Oh, Anne Y.; Kacker, Ashutosh (December 2014). "Do electronic cigarettes impart a lower potential disease burden than conventional tobacco cigarettes?: Review on e-cigarette vapor versus tobacco smoke". The Laryngoscope. 124 (12): 2702–2706. doi:10.1002/lary.24750. PMID 25302452.
- ^ "Electronic Cigarettes – An Overview" (PDF). German Cancer Research Center. 2013.
- "E-cigarettes: An Emerging Public Health Challenge". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 20 October 2015.
- ^ Brandon, T. H.; Goniewicz, M. L.; Hanna, N. H.; Hatsukami, D. K.; Herbst, R. S.; Hobin, J. A.; Ostroff, J. S.; Shields, P. G.; Toll, B. A.; Tyne, C. A.; Viswanath, K.; Warren, G. W. (2015). "Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems: A Policy Statement from the American Association for Cancer Research and the American Society of Clinical Oncology". Clinical Cancer Research. 21 (3): 514–525. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2544. ISSN 1078-0432. PMID 25573384.
- ^ "E-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults: A Report of the Surgeon General" (PDF). Surgeon General of the United States. 2016. pp. 1–298.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Greenberg, Jordan M.; Carballosa, Carlos M.; Cheung, Herman S. (2017). "Concise Review: The Deleterious Effects of Cigarette Smoking and Nicotine Usage and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Function and Implications for Cell-Based Therapies". STEM CELLS Translational Medicine. 6 (9): 1815–1821. doi:10.1002/sctm.17-0060. ISSN 2157-6564. PMC 5689746. PMID 28696009.
- ^ "THE FACTS on e-cigarette use among youth and young adults". Surgeon General of the United States. 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "Electronic Cigarettes". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 September 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
WHO2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Barraza, Leila F.; Weidenaar, Kim E.; Cook, Livia T.; Logue, Andrea R.; Halpern, Michael T. (2017). "Regulations and policies regarding e-cigarettes". Cancer. 123 (16): 3007–3014. doi:10.1002/cncr.30725. ISSN 0008-543X. PMID 28440949.
- Smith, Nikki (20 January 2016). "Headlines about e-cigarettes don't mean they're 'not safer than tobacco'". Cancer Research UK.
- ^ Greenhill, Richard; Dawkins, Lynne; Notley, Caitlin; Finn, Mark D.; Turner, John J.D. (2016). "Adolescent Awareness and Use of Electronic Cigarettes: A Review of Emerging Trends and Findings". Journal of Adolescent Health. 59 (6): 612–619. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.08.005. ISSN 1054-139X. PMID 27693128.
- "Electronic Cigarettes – What's the bottom line?" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 22 February 2018.
- Bush, Ashley M.; Holsinger, James W.; Prybil, Lawrence D. (2016). "Employing the Precautionary Principle to Evaluate the Use of E-Cigarettes". Frontiers in Public Health. 4: 5. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2016.00005. ISSN 2296-2565. PMC 4740382. PMID 26870723.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rowell2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Rom, Oren; Pecorelli, Alessandra; Valacchi, Giuseppe; Reznick, Abraham Z. (2014). "Are E-cigarettes a safe and good alternative to cigarette smoking?". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1340 (1): 65–74. doi:10.1111/nyas.12609. ISSN 0077-8923. PMID 25557889.
- ^ Palazzolo, Dominic L. (November 2013). "Electronic cigarettes and vaping: a new challenge in clinical medicine and public health. A literature review". Frontiers in Public Health. 1 (56): 56. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2013.00056. PMC 3859972. PMID 24350225.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Dominic L. Palazzolo available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Dominic L. Palazzolo available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
- ^ Nansseu, Jobert Richie N.; Bigna, Jean Joel R. (2016). "Electronic Cigarettes for Curbing the Tobacco-Induced Burden of Noncommunicable Diseases: Evidence Revisited with Emphasis on Challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa". Pulmonary Medicine. 2016: 1–9. doi:10.1155/2016/4894352. ISSN 2090-1836. PMC 5220510. PMID 28116156.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Jobert Richie N. Nansseu and Jean Joel R. Bigna available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Jobert Richie N. Nansseu and Jean Joel R. Bigna available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Drope, Jeffrey; Cahn, Zachary; Kennedy, Rosemary; Liber, Alex C.; Stoklosa, Michal; Henson, Rosemarie; Douglas, Clifford E.; Drope, Jacqui (2017). "Key issues surrounding the health impacts of electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) and other sources of nicotine". CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 67 (6): 449–471. doi:10.3322/caac.21413. ISSN 0007-9235. PMID 28961314.
- ^ Bhatnagar, A.; Whitsel, L. P.; Ribisl, K. M.; Bullen, C.; Chaloupka, F.; Piano, M. R.; Robertson, R. M.; McAuley, T.; Goff, D.; Benowitz, N. (24 August 2014). "Electronic Cigarettes: A Policy Statement From the American Heart Association". Circulation. 130 (16): 1418–1436. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000107. PMID 25156991.
- Bullen, Chris; Knight-West, Oliver (2016). "E-cigarettes for the management of nicotine addiction". Substance Abuse and Rehabilitation. 7: 111–118. doi:10.2147/SAR.S94264. ISSN 1179-8467. PMC 4993405. PMID 27574480.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Glantz, Stanton A.; Bareham, David W. (January 2018). "E-Cigarettes: Use, Effects on Smoking, Risks, and Policy Implications". Annual Review of Public Health. 39 (1): 215–235. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040617-013757. ISSN 0163-7525. PMC 6251310. PMID 29323609.
 This article incorporates text by Stanton A. Glantz and David W. Bareham available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Stanton A. Glantz and David W. Bareham available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- Vasiljevic, Milica; St John Wallis, Amelia; Codling, Saphsa; Couturier, Dominique-Laurent; Sutton, Stephen; Marteau, Theresa M (2018). "E-cigarette adverts and children's perceptions of tobacco smoking harms: an experimental study and meta-analysis". BMJ Open. 8 (7): e020247. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020247. ISSN 2044-6055. PMC 6082488. PMID 30012646.
 This article incorporates text by Milica Vasiljevic, Amelia St John Wallis, Saphsa Codlin, Dominique-Laurent Couturier, Stephen Sutton, and Theresa M Marteau available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Milica Vasiljevic, Amelia St John Wallis, Saphsa Codlin, Dominique-Laurent Couturier, Stephen Sutton, and Theresa M Marteau available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Hua, My; Talbot, Prue (2016). "Potential health effects of electronic cigarettes: A systematic review of case reports". Preventive Medicine Reports. 4: 169–178. doi:10.1016/j.pmedr.2016.06.002. ISSN 2211-3355. PMC 4929082. PMID 27413679.
 This article incorporates text by My Hua and Prue Talbot available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by My Hua and Prue Talbot available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Orellana-Barrios, Menfil A.; Payne, Drew; Mulkey, Zachary; Nugent, Kenneth (2015). "Electronic cigarettes-a narrative review for clinicians". The American Journal of Medicine. 128 (7): 674–81. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.01.033. ISSN 0002-9343. PMID 25731134.
- "E-Cigarettes". Tobacco Control Research Branch of the National Cancer Institute.
- ^ Benowitz, Neal L.; Fraiman, Joseph B. (2017). "Cardiovascular effects of electronic cigarettes". Nature Reviews Cardiology. 14 (8): 447–456. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2017.36. ISSN 1759-5002. PMC 5519136. PMID 28332500.
- "Stop smoking treatments". UK National Health Service. 25 July 2014.
- "Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes--2015: Summary of Revisions". Diabetes Care. 54 (38): S25. 2015. doi:10.2337/dc15-S003. PMID 25537706.
- "E-Cigarettes". Oncology Times. 36 (15): 49–50. August 2014. doi:10.1097/01.COT.0000453432.31465.77.
- "Nicotine addiction". Health Canada. 7 March 2013.
- "DrugFacts: Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products". National Institute on Drug Abuse. May 2016.
- ^ Gorlova, Olga Y; Xu, Ying; Guo, Yanfang; Liu, Kaiqian; Liu, Zheng; Wang, Xiaobo (2016). "E-Cigarette Awareness, Use, and Harm Perception among Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies". PLOS ONE. 11 (11): e0165938. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1165938X. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0165938. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5115669. PMID 27861501.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Cervellin, Gianfranco; Borghi, Loris; Mattiuzzi, Camilla; Meschi, Tiziana; Favaloro, Emmanuel; Lippi, Giuseppe (2013). "E-Cigarettes and Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Science and Mysticism". Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 40 (1): 060–065. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1363468. ISSN 0094-6176. PMID 24343348.
- ^ Rinkoo, ArvindVashishta; Kaur, Jagdish (2017). "Getting real with the upcoming challenge of electronic nicotine delivery systems: The way forward for the South-East Asia region". Indian Journal of Public Health. 61 (5): S7–S11. doi:10.4103/ijph.IJPH_240_17. ISSN 0019-557X. PMID 28928312.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Wilder 2016, p. 127.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, 9.
- ^ Kaur, Gagandeep; Pinkston, Rakeysha; Mclemore, Benathel; Dorsey, Waneene C.; Batra, Sanjay (2018). "Immunological and toxicological risk assessment of e-cigarettes". European Respiratory Review. 27 (147): 170119. doi:10.1183/16000617.0119-2017. ISSN 0905-9180. PMID 29491036.
- Detailed reference list is located at a separate image page.
- McNeill 2018, p. 175.
- McNeill 2015, p. 76.
- ^ Couch, Elizabeth T.; Chaffee, Benjamin W.; Gansky, Stuart A.; Walsh, Margaret M. (2016). "The changing tobacco landscape". The Journal of the American Dental Association. 147 (7): 561–569. doi:10.1016/j.adaj.2016.01.008. ISSN 0002-8177. PMC 4925234. PMID 26988178.
- Camenga, Deepa R.; Tindle, Hilary A. (2018). "Weighing the Risks and Benefits of Electronic Cigarette Use in High-Risk Populations". Medical Clinics of North America. 102 (4): 765–779. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2018.03.002. ISSN 0025-7125. PMID 29933828.
- ^ Chaffee, Benjamin W.; Couch, Elizabeth T.; Ryder, Mark I. (2016). "The tobacco-using periodontal patient: role of the dental practitioner in tobacco cessation and periodontal disease management". Periodontology 2000. 71 (1): 52–64. doi:10.1111/prd.12120. ISSN 0906-6713. PMC 4842013. PMID 27045430.
- ^ Bhatnagar, Aruni (2016). "Cardiovascular Perspective of the Promises and Perils of E-Cigarettes". Circulation Research. 118 (12): 1872–1875. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308723. ISSN 0009-7330. PMC 5505630. PMID 27283531.
- ^ Chen, Jinsong; Bullen, Chris; Dirks, Kim (2017). "A Comparative Health Risk Assessment of Electronic Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 14 (4): 382. doi:10.3390/ijerph14040382. ISSN 1660-4601. PMC 5409583. PMID 28379177.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Jinsong Chen, Chris Bullen, and Kim Dirks available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Jinsong Chen, Chris Bullen, and Kim Dirks available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- Detailed reference list is located at a separate image page.
- "RCP statement on e-cigarettes". Royal College of Physicians. 25 June 2014.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
FarsalinosPolosa2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Smith, L; Brar, K; Srinivasan, K; Enja, M; Lippmann, S (June 2016). "E-cigarettes: How "safe" are they?". J Fam Pract. 65 (6): 380–5. PMID 27474819.
- ^ MacDonald, Marjorie; O'Leary, Renee; Stockwell, Tim; Reist, Dan (2016). "Clearing the air: protocol for a systematic meta-narrative review on the harms and benefits of e-cigarettes and vapour devices". Systematic Reviews. 5 (1): 85. doi:10.1186/s13643-016-0264-y. ISSN 2046-4053. PMC 4875675. PMID 27209032.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Marjorie MacDonald, Renee O'Leary, Tim Stockwell, and Dan Reist available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Marjorie MacDonald, Renee O'Leary, Tim Stockwell, and Dan Reist available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Dagaonkar RS, R.S.; Udwadi, Z.F. (2014). "Water pipes and E-cigarettes: new faces of an ancient enemy" (PDF). Journal of the Association of Physicians of India. 62 (4): 324–328. PMID 25327035.
- ^ Caponnetto, P.; Russo, C.; Bruno, C.M.; Alamo, A.; Amaradio, M.D.; Polosa, R. (March 2013). "Electronic cigarette: a possible substitute for cigarette dependence". Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease. 79 (1): 12–19. doi:10.4081/monaldi.2013.104. ISSN 1122-0643. PMID 23741941.
- Brady, Benjamin R.; De La Rosa, Jennifer S.; Nair, Uma S.; Leischow, Scott J. (2019). "Electronic Cigarette Policy Recommendations: A Scoping Review". American Journal of Health Behavior. 43 (1): 88–104. doi:10.5993/AJHB.43.1.8. ISSN 1087-3244. PMID 30522569.
- "Electronic Cigarettes – Are e-cigarettes less harmful than regular cigarettes?" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 22 February 2018.
- McCausland, Kahlia; Maycock, Bruce; Jancey, Jonine (2017). "The messages presented in online electronic cigarette promotions and discussions: a scoping review protocol". BMJ Open. 7 (11): e018633. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018633. ISSN 2044-6055. PMC 5695349. PMID 29122804.
- "What about electronic cigarettes? Aren't they safe?". American Cancer Society.
- "Ways to quit". Canadian Cancer Society. 2016.
- "Nicotine products can help people to cut down before quitting smoking". National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. June 2013.
- "Regulation of Electronic Cigarettes ("E-Cigarettes")" (PDF). National Association of County and City Health Officials. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 November 2014.
- ^ Pepper, J. K.; Brewer, N. T. (2013). "Electronic nicotine delivery system (electronic cigarette) awareness, use, reactions and beliefs: a systematic review". Tobacco Control. 23 (5): 375–384. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051122. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 4520227. PMID 24259045.
- ^ Hildick-Smith, Gordon J.; Pesko, Michael F.; Shearer, Lee; Hughes, Jenna M.; Chang, Jane; Loughlin, Gerald M.; Ipp, Lisa S. (2015). "A Practitioner's Guide to Electronic Cigarettes in the Adolescent Population". Journal of Adolescent Health. 57 (6): 574–9. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2015.07.020. ISSN 1054-139X. PMID 26422289.
- Livingston, Catherine J.; Freeman, Randall J.; Costales, Victoria C.; Westhoff, John L.; Caplan, Lee S.; Sherin, Kevin M.; Niebuhr, David W. (2019). "Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems or E-cigarettes: American College of Preventive Medicine's Practice Statement". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 56 (1): 167–178. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.09.010. ISSN 0749-3797. PMID 30573147.
- "Did You Know? – Public Health Impact". Surgeon General of the United States. 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Cite error: The named reference
PaleyEchalier2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Cite error: The named reference
ONF2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Singh, Jasjot; Luquet, Emilie; Smith, DavidP.T.; Potgieter, HermanJ.; Ragazzon, Patricia (2016). "Toxicological and analytical assessment of e-cigarette refill components on airway epithelia" (PDF). Science Progress. 99 (4): 351–398. doi:10.3184/003685016X14773090197706. ISSN 0036-8504. PMID 28742478.
- ^ Breland, Alison B.; Spindle, Tory; Weaver, Michael; Eissenberg, Thomas (2014). "Science and Electronic Cigarettes". Journal of Addiction Medicine. 8 (4): 223–233. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000049. ISSN 1932-0620. PMC 4122311. PMID 25089952.
- ^ Gualano, Maria Rosaria; Passi, Stefano; Bert, Fabrizio; La Torre, Giuseppe; Scaioli, Giacomo; Siliquini, Roberta (2015). "Electronic cigarettes: assessing the efficacy and the adverse effects through a systematic review of published studies". Journal of Public Health. 37 (3): 488–497. doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdu055. ISSN 1741-3842. PMID 25108741.
- ^ Kaisar, Mohammad Abul; Prasad, Shikha; Liles, Tylor; Cucullo, Luca (2016). "A Decade of e-Cigarettes: Limited Research & Unresolved Safety Concerns". Toxicology. 365: 67–75. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2016.07.020. ISSN 0300-483X. PMC 4993660. PMID 27477296.
- Yang, L.; Rudy, S. F.; Cheng, J. M.; Durmowicz, E. L. (2014). "Electronic cigarettes: incorporating human factors engineering into risk assessments". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii47–ii53. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051479. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995290. PMID 24732164.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Durmowicz2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - "Tips to Help Avoid "Vape" Battery Explosions". United States Food and Drug Administration. 20 December 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Electronic Cigarettes: Vulnerability of Youth". Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol. 28 (1): 2–6. 2015. doi:10.1089/ped.2015.0490. PMC 4359356. PMID 25830075.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Cheng, T. (2014). "Chemical evaluation of electronic cigarettes". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii11–ii17. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051482. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995255. PMID 24732157.
- ^ Hajek, P; Etter, JF; Benowitz, N; Eissenberg, T; McRobbie, H (31 July 2014). "Electronic cigarettes: review of use, content, safety, effects on smokers and potential for harm and benefit". Addiction. 109 (11): 1801–10. doi:10.1111/add.12659. PMC 4487785. PMID 25078252.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
EbbertAgunwamba2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cooke, Andrew; Fergeson, Jennifer; Bulkhi, Adeeb; Casale, Thomas B. (2015). "The Electronic Cigarette: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice. 3 (4): 498–505. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.05.022. ISSN 2213-2198. PMID 26164573.
- ^ Bertholon, J.F.; Becquemin, M.H.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Dautzenberg, B. (2013). "Electronic Cigarettes: A Short Review". Respiration. 86 (5): 433–8. doi:10.1159/000353253. ISSN 1423-0356. PMID 24080743.
- Simon Robb (24 December 2016). "Man's e-cigarette blew up in his pocket as he sat on a bus". Metro (British newspaper). DMG Media.
- ^ "Cancer Research UK Briefing: Electronic Cigarettes" (PDF). Cancer Research UK. May 2014.
- ^ Orr, M. S. (2014). "Electronic cigarettes in the USA: a summary of available toxicology data and suggestions for the future". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii18–ii22. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051474. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995288. PMID 24732158.
- Rahman MA, Hann N, Wilson A, Worrall-Carter L (2014). "Electronic cigarettes: patterns of use, health effects, use in smoking cessation and regulatory issues". Tob Induc Dis. 12 (1): 21. doi:10.1186/1617-9625-12-21. PMC 4350653. PMID 25745382.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Wilder 2016, p. 87.
- "E-cigarettes to be regulated as medicines". National Health Service. 12 June 2013.
- ^ Jerry JM, Collins GB, Streem D (2015). "E-cigarettes: Safe to recommend to patients?". Cleve Clin J Med. 82 (8): 521–6. doi:10.3949/ccjm.82a.14054. PMID 26270431.
- ^ SGUS 2014, p. 116.
- SGUS 2014, p. 115.
- Schaal, C.; Chellappan, S. P. (2014). "Nicotine-Mediated Cell Proliferation and Tumor Progression in Smoking-Related Cancers". Molecular Cancer Research. 12 (1): 14–23. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0541. ISSN 1541-7786. PMC 3915512. PMID 24398389.
- ^ Collaco, Joseph M. (2015). "Electronic Use and Exposure in the Pediatric Population". JAMA Pediatrics. 169 (2): 177–182. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.2898. PMC 5557497. PMID 25546699.
- ^ Sanner, Tore; Grimsrud, Tom K. (2015). "Nicotine: Carcinogenicity and Effects on Response to Cancer Treatment – A Review". Frontiers in Oncology. 5: 196. doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00196. ISSN 2234-943X. PMC 4553893. PMID 26380225.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Tore Sanner, and Tom K. Grimsrud available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Tore Sanner, and Tom K. Grimsrud available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, Conclusion 10-4.; 8.
- ^ WHO 2016, p. 3.
- ^ Qasim, Hanan; Karim, Zubair A.; Rivera, Jose O.; Khasawneh, Fadi T.; Alshbool, Fatima Z. (2017). "Impact of Electronic Cigarettes on the Cardiovascular System". Journal of the American Heart Association. 6 (9): e006353. doi:10.1161/JAHA.117.006353. ISSN 2047-9980. PMC 5634286. PMID 28855171.
- Flach, Susanne; Maniam, Pavithran; Manickavasagam, Jaiganesh (2019). "E‐cigarettes and head and neck cancers: A systematic review of the current literature". Clinical Otolaryngology. 44 (5): 749–756. doi:10.1111/coa.13384. ISSN 1749-4478. PMID 31148389.
- ^ Kim, Ki-Hyun; Kabir, Ehsanul; Jahan, Shamin Ara (2016). "Review of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: their potential human health impact". Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part C. 34 (4): 262–275. doi:10.1080/10590501.2016.1236604. ISSN 1059-0501. PMID 27635466.
- Knorst, Marli Maria; Benedetto, Igor Gorski; Hoffmeister, Mariana Costa; Gazzana, Marcelo Basso (2014). "The electronic cigarette: the new cigarette of the 21st century?". Jornal Brasileiro de Pneumologia. 40 (5): 564–572. doi:10.1590/S1806-37132014000500013. ISSN 1806-3713. PMC 4263338. PMID 25410845.
- ^ Hiemstra, Pieter S.; Bals, Robert (2016). "Basic science of electronic cigarettes: assessment in cell culture and in vivo models". Respiratory Research. 17 (1): 127. doi:10.1186/s12931-016-0447-z. ISSN 1465-993X. PMC 5055681. PMID 27717371.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Pieter S. Hiemstra and Robert Bals available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Pieter S. Hiemstra and Robert Bals available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- "WMA Statement on Electronic Cigarettes and Other Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems". World Medical Association. October 2012.
- Arnold, Carrie (2014). "Vaping and Health: What Do We Know about E-Cigarettes?". Environmental Health Perspectives. 122 (9): A244–A249. doi:10.1289/ehp.122-A244. ISSN 0091-6765. PMC 4154203. PMID 25181730.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Cahn, Z.; Siegel, M. (February 2011). "Electronic cigarettes as a harm reduction strategy for tobacco control: a step forward or a repeat of past mistakes?". Journal of Public Health Policy. 32 (1): 16–31. doi:10.1057/jphp.2010.41. PMID 21150942.
- ^ "WHO Right to Call for E-Cigarette Regulation". World Lung Federation. 26 August 2014.
- ^ Breland, Alison; Soule, Eric; Lopez, Alexa; Ramôa, Carolina; El-Hellani, Ahmad; Eissenberg, Thomas (2017). "Electronic cigarettes: what are they and what do they do?". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1394 (1): 5–30. Bibcode:2017NYASA1394....5B. doi:10.1111/nyas.12977. ISSN 0077-8923. PMC 4947026. PMID 26774031.
- ^ "FDA Warns of Health Risks Posed by E-Cigarettes". United States Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2017. Archived from the original on 1 November 2017.
- ^ "Summary of Results: Laboratory Analysis of Electronic Cigarettes Conducted By FDA". United States Food and Drug Administration. 22 April 2014. Archived from the original on 29 June 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Alawsi, F.; Nour, R.; Prabhu, S. (2015). "Are e-cigarettes a gateway to smoking or a pathway to quitting?". BDJ. 219 (3): 111–115. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.2015.591. ISSN 0007-0610. PMID 26271862.
- ^ McNeill 2018, p. 162.
- ^ Franck, Caroline; Filion, Kristian B.; Kimmelman, Jonathan; Grad, Roland; Eisenberg, Mark J. (2016). "Ethical considerations of e-cigarette use for tobacco harm reduction". Respiratory Research. 17 (1): 53. doi:10.1186/s12931-016-0370-3. ISSN 1465-993X. PMC 4869264. PMID 27184265.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Caroline Franck, Kristian B. Filion, Jonathan Kimmelman, Roland Grad and Mark J. Eisenberg available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Caroline Franck, Kristian B. Filion, Jonathan Kimmelman, Roland Grad and Mark J. Eisenberg available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Jimenez Ruiz, CA; Solano Reina, S; de Granda Orive, JI; Signes-Costa Minaya, J; de Higes Martinez, E; Riesco Miranda, JA; Altet Gómez, N; Lorza Blasco, JJ; Barrueco Ferrero, M; de Lucas Ramos, P (August 2014). "The electronic cigarette. Official statement of the Spanish Society of Pneumology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR) on the efficacy, safety and regulation of electronic cigarettes". Archivos de Bronconeumologia. 50 (8): 362–7. doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2014.02.006. PMID 24684764.
- ^ Cai, Hua; Wang, Chen (2017). "Graphical review: The redox dark side of e-cigarettes; exposure to oxidants and public health concerns". Redox Biology. 13: 402–406. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.05.013. ISSN 2213-2317. PMC 5493817. PMID 28667909.
- ^ Bekki, Kanae; Uchiyama, Shigehisa; Ohta, Kazushi; Inaba, Yohei; Nakagome, Hideki; Kunugita, Naoki (2014). "Carbonyl Compounds Generated from Electronic Cigarettes". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 11 (11): 11192–11200. doi:10.3390/ijerph111111192. ISSN 1660-4601. PMC 4245608. PMID 25353061.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Dinakar, Chitra; Longo, Dan L.; O'Connor, George T. (2016). "The Health Effects of Electronic Cigarettes". New England Journal of Medicine. 375 (14): 1372–1381. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1502466. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 27705269.
- ^ Burstyn, Igor (9 January 2014). "Peering through the mist: systematic review of what the chemistry of contaminants in electronic cigarettes tells us about health risks". BMC Public Health. 14 (1): 18. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-14-18. ISSN 1471-2458. PMC 3937158. PMID 24406205.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Schick, Suzaynn F.; Blount, Benjamin C; Jacob, Peyton; Saliba, Najat A; Bernert, John T; El Hellani, Ahmad; Jatlow, Peter; Pappas, R Steve; Wang, Lanqing; Foulds, Jonathan; Ghosh, Arunava; Hecht, Stephen S; Gomez, John C; Martin, Jessica R; Mesaros, Clementina; Srivastava, Sanjay; St. Helen, Gideon; Tarran, Robert; Lorkiewicz, Pawel K; Blair, Ian A; Kimmel, Heather L; Doerschuk, Claire M.; Benowitz, Neal L; Bhatnagar, Aruni (2017). "Biomarkers of Exposure to New and Emerging Tobacco and Nicotine Delivery Products". American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 313 (3): L425–L452. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00343.2016. ISSN 1040-0605. PMC 5626373. PMID 28522563.
- ^ Ramôa, C. P.; Eissenberg, T.; Sahingur, S. E. (2017). "Increasing popularity of waterpipe tobacco smoking and electronic cigarette use: Implications for oral healthcare". Journal of Periodontal Research. 52 (5): 813–823. doi:10.1111/jre.12458. ISSN 0022-3484. PMC 5585021. PMID 28393367.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, 4.
- ^ Wolff, Mary S.; Buckley, Jessie P.; Engel, Stephanie M.; McConnell, Rob S.; Barr, Dana B. (2017). "Emerging exposures of developmental toxicants". Current Opinion in Pediatrics. 29 (2): 218–224. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000455. ISSN 1040-8703. PMC 5473289. PMID 28059904.
- ^ Cormet-Boyaka, Estelle; Zare, Samane; Nemati, Mehdi; Zheng, Yuqing (2018). "A systematic review of consumer preference for e-cigarette attributes: Flavor, nicotine strength, and type". PLOS ONE. 13 (3): e0194145. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1394145Z. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0194145. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5854347. PMID 29543907.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Samane Zare, Mehdi Nemati, and Yuqing Zheng available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Samane Zare, Mehdi Nemati, and Yuqing Zheng available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Bourke, Liam; Bauld, Linda; Bullen, Christopher; Cumberbatch, Marcus; Giovannucci, Edward; Islami, Farhad; McRobbie, Hayden; Silverman, Debra T.; Catto, James W.F. (2017). "E-cigarettes and Urologic Health: A Collaborative Review of Toxicology, Epidemiology, and Potential Risks" (PDF). European Urology. 71 (6): 915–923. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.12.022. hdl:1893/24937. ISSN 0302-2838. PMID 28073600.
- ^ Wilder 2016, p. 82.
- Naik, Pooja; Cucullo, Luca (2015). "Pathobiology of tobacco smoking and neurovascular disorders: untied strings and alternative products". Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. 12 (1): 25. doi:10.1186/s12987-015-0022-x. ISSN 2045-8118. PMC 4628383. PMID 26520792.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Stratton 2018, p. Other Toxicants, Caffeine; 197.
- ^ McNeill 2018, p. 19.
- Stratton 2018, p. Exposure to Flavorings, 175.
- ^ Jankowski, Mateusz; Brożek, Grzegorz; Lawson, Joshua; Skoczyński, Szymon; Zejda, Jan (2017). "E-smoking: Emerging public health problem?". International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health. 30 (3): 329–344. doi:10.13075/ijomeh.1896.01046. ISSN 1232-1087. PMID 28481369.
- ^ Bonilla, Alex; Blair, Alexander J.; Alamro, Suliman M.; Ward, Rebecca A.; Feldman, Michael B.; Dutko, Richard A.; Karagounis, Theodora K.; Johnson, Adam L.; Folch, Erik E.; Vyas, Jatin M. (2019). "Recurrent spontaneous pneumothoraces and vaping in an 18-year-old man: a case report and review of the literature". Journal of Medical Case Reports. 13 (1). doi:10.1186/s13256-019-2215-4. ISSN 1752-1947. PMC 6732835. PMID 31495337.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Alex Bonilla, Alexander J. Blair, Suliman M. Alamro, Rebecca A. Ward, Michael B. Feldman, Richard A. Dutko, Theodora K. Karagounis, Adam L. Johnson, Erik E. Folch, and Jatin M. Vyas available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Alex Bonilla, Alexander J. Blair, Suliman M. Alamro, Rebecca A. Ward, Michael B. Feldman, Richard A. Dutko, Theodora K. Karagounis, Adam L. Johnson, Erik E. Folch, and Jatin M. Vyas available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Shields, Peter G.; Berman, Micah; Brasky, Theodore M.; Freudenheim, Jo L.; Mathe, Ewy A; McElroy, Joseph; Song, Min-Ae; Wewers, Mark D. (2017). "A Review of Pulmonary Toxicity of Electronic Cigarettes In The Context of Smoking: A Focus On Inflammation". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 26 (8): 1175–1191. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0358. ISSN 1055-9965. PMC 5614602. PMID 28642230.
- Stratton 2018, p. FLAVORINGS, 172.
- ^ Editorial Staff (7 July 2016). "Popcorn Lung: A Dangerous Risk of Flavored E-Cigarettes". American Lung Association.
- McNeill 2018, p. 159.
- Konstantinos E. Farsalinos; I. Gene Gillman; Stephen S. Hecht; Riccardo Polosa; Jonathan Thornburg (16 November 2016). Analytical Assessment of e-Cigarettes: From Contents to Chemical and Particle Exposure Profiles. Elsevier Science. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-12-811242-7.
- ^ Benowitz, Neal L.; Burbank, Andrea D. (2016). "Cardiovascular toxicity of nicotine: Implications for electronic cigarette use". Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 26 (6): 515–23. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2016.03.001. ISSN 1050-1738. PMC 4958544. PMID 27079891.
- Dhand, Rajiv (2017). "Inhaled Drug Therapy 2016: The Year in Review". Respiratory Care. 62 (7): 978–996. doi:10.4187/respcare.05624. ISSN 0020-1324. PMID 28559466.
- Sanford Z, Goebel L (2014). "E-cigarettes: an up to date review and discussion of the controversy". W V Med J. 110 (4): 10–5. PMID 25322582.
- ^ Schraufnagel, Dean E.; Blasi, Francesco; Drummond, M. Bradley; Lam, David C. L.; Latif, Ehsan; Rosen, Mark J.; Sansores, Raul; Van Zyl-Smit, Richard (2014). "Electronic Cigarettes. A Position Statement of the Forum of International Respiratory Societies". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 190 (6): 611–618. doi:10.1164/rccm.201407-1198PP. ISSN 1073-449X. PMID 25006874.
- ^ Stratton 2018, p. Other Toxicants, Pharmaceutical Drugs; 197.
- ^ Collaco, Joseph M.; McGrath-Morrow, Sharon A. (2017). "Electronic Cigarettes: Exposure and Use Among Pediatric Populations". Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery. 31 (2): 71–77. doi:10.1089/jamp.2017.1418. ISSN 1941-2711. PMC 5915214. PMID 29068754.
- ^ Huang, Shu-Jie; Xu, Yan-Ming; Lau, Andy T. Y. (2017). "Electronic cigarette: A recent update of its toxic effects on humans". Journal of Cellular Physiology. 233 (6): 4466–4478. doi:10.1002/jcp.26352. ISSN 0021-9541. PMID 29215738.
- McNeill 2018, p. 160.
- ^ Zborovskaya, Y (2017). "E-Cigarettes and Smoking Cessation: A Primer for Oncology Clinicians". Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing. 21 (1): 54–63. doi:10.1188/17.CJON.54-63. PMID 28107337.
- ^ Born, H.; Persky, M.; Kraus, D. H.; Peng, R.; Amin, M. R.; Branski, R. C. (2015). "Electronic Cigarettes: A Primer for Clinicians". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 153 (1): 5–14. doi:10.1177/0194599815585752. ISSN 0194-5998. PMID 26002957.
- ^ McNeill 2015, p. 77.
- McNeill 2018, p. 158.
- Stratton 2018, p. Characteristics of E-Cigarette Devices, 56.
- McNeill 2015, p. 77-78.
- Detailed reference list is located at a separate image page.
- ^ Lachenmeier, Dirk W.; Rehm, Jürgen (2015). "Comparative risk assessment of alcohol, tobacco, cannabis and other illicit drugs using the margin of exposure approach". Scientific Reports. 5: 8126. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E8126L. doi:10.1038/srep08126. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4311234. PMID 25634572.
- ^ England, Lucinda J.; Bunnell, Rebecca E.; Pechacek, Terry F.; Tong, Van T.; McAfee, Tim A. (2015). "Nicotine and the Developing Human". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 49 (2): 286–93. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2015.01.015. ISSN 0749-3797. PMC 4594223. PMID 25794473.
- Kim, Jason H.; Patel, Sandeep (2017). "Is It Worth Discriminating Against Patients Who Smoke? A Systematic Literature Review on the Effects of Tobacco Use in Foot and Ankle Surgery". The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery. 56 (3): 594–599. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2017.02.006. ISSN 1067-2516. PMID 28476393.
- ^ Biyani, Sneh; Derkay, Craig S. (2017). "E-cigarettes: An update on considerations for the otolaryngologist". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 94: 14–16. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.12.027. ISSN 0165-5876. PMID 28167004.
- ^ Schivo, Michael; Avdalovic, Mark V.; Murin, Susan (February 2014). "Non-Cigarette Tobacco and the Lung". Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology. 46 (1): 34–53. doi:10.1007/s12016-013-8372-0. ISSN 1080-0549. PMID 23673789.
- ^ Callahan-Lyon, P. (2014). "Electronic cigarettes: human health effects". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii36–ii40. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051470. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995250. PMID 24732161.
- Marsot, A.; Simon, N. (March 2016). "Nicotine and Cotinine Levels With Electronic Cigarette: A Review". International Journal of Toxicology. 35 (2): 179–185. doi:10.1177/1091581815618935. ISSN 1091-5818. PMID 26681385.
- ^ England, Lucinda J.; Aagaard, Kjersti; Bloch, Michele; Conway, Kevin; Cosgrove, Kelly; Grana, Rachel; Gould, Thomas J.; Hatsukami, Dorothy; Jensen, Frances; Kandel, Denise; Lanphear, Bruce; Leslie, Frances; Pauly, James R.; Neiderhiser, Jenae; Rubinstein, Mark; Slotkin, Theodore A.; Spindel, Eliot; Stroud, Laura; Wakschlag, Lauren (2017). "Developmental toxicity of nicotine: A transdisciplinary synthesis and implications for emerging tobacco products". Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 72: 176–189. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.11.013. ISSN 0149-7634. PMC 5965681. PMID 27890689.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, Conclusion 8-2.; 7.
- McNeill 2018, p. 55.
- McNeill 2018, p. 57.
- Bold, Krysten W.; Sussman, Steve; O'Malley, Stephanie S.; Grana, Rachel; Foulds, Jonathan; Fishbein, Howard; Krishnan-Sarin, Suchitra (2018). "Measuring E-cigarette dependence: Initial guidance". Addictive Behaviors. 79: 213–218. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.11.015. ISSN 0306-4603. PMC 5807200. PMID 29174664.
- ^ Nowak D, Jörres RA, Rüther T (2014). "E-cigarettes--prevention, pulmonary health, and addiction". Dtsch Arztebl Int. 111 (20): 349–55. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2014.0349. PMC 4047602. PMID 24882626.
- Schroeder, M. J.; Hoffman, A. C. (2014). "Electronic cigarettes and nicotine clinical pharmacology". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii30–ii35. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051469. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995273. PMID 24732160.
- FDA (4 May 2009). "FDA 2009 Study Data: Evaluation of e-cigarettes" (PDF). Food and Drug Administration (US) -center for drug evaluation and research.
- Jeong, Won Tae; Cho, Hyun Ki; Lee, Hyung Ryeol; Song, Ki Hoon; Lim, Heung Bin (2019). "Comparison of the content of tobacco alkaloids and tobacco-specific nitrosamines in 'heat-not-burn' tobacco products before and after aerosol generation". Inhalation Toxicology. 30 (13–14): 527–533. doi:10.1080/08958378.2019.1572840. ISSN 0895-8378. PMID 30741569.
- Di Matteo, Vincenzo; Pierucci, Massimo; Di Giovanni, Giuseppe; Benigno, Arcangelo; Esposito, Ennio (2007). "The Neurobiological Bases for the Pharmacotherapy of Nicotine Addiction". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 13 (12): 1269–1284. doi:10.2174/138161207780618920. ISSN 1381-6128. PMID 17504235.
- ^ "Electronic Cigarettes (E-cigarettes)". National Institute on Drug Abuse. March 2018.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Golub, Justin S.; Samy, Ravi N. (2015). "Preventing or reducing smoking-related complications in otologic and neurotologic surgery". Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery. 23 (5): 334–340. doi:10.1097/MOO.0000000000000184. ISSN 1068-9508. PMID 26339963.
- McNeill 2018, p. 58.
- ^ Stratton 2018, p. Minor Tobacco Alkaloids, 193.
- ^ Chaturvedi, Pankaj; Mishra, Aseem; Datta, Sourav; Sinukumar, Snita; Joshi, Poonam; Garg, Apurva (2015). "Harmful effects of nicotine". Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. 36 (1): 24–31. doi:10.4103/0971-5851.151771. ISSN 0971-5851. PMC 4363846. PMID 25810571.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Toda, Noboru; Toda, Hiroshi (2010). "Nitric oxide-mediated blood flow regulation as affected by smoking and nicotine". European Journal of Pharmacology. 649 (1–3): 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.09.042. ISSN 0014-2999. PMID 20868673.
- ^ Garcia, Alexandra N.; Salloum, Ihsan M. (2015). "Polysomnographic sleep disturbances in nicotine, caffeine, alcohol, cocaine, opioid, and cannabis use: A focused review". The American Journal on Addictions. 24 (7): 590–598. doi:10.1111/ajad.12291. ISSN 1055-0496. PMID 26346395.
- Irish, Leah A.; Kline, Christopher E.; Gunn, Heather E.; Buysse, Daniel J.; Hall, Martica H. (2015). "The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: A review of empirical evidence". Sleep Medicine Reviews. 22: 23–36. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.001. ISSN 1087-0792. PMC 4400203. PMID 25454674.
- Siqueira, Lorena M. (2016). "Nicotine and Tobacco as Substances of Abuse in Children and Adolescents". Pediatrics. 139 (1): e20163436. doi:10.1542/peds.2016-3436. ISSN 0031-4005. PMID 27994114.
- ^ Stratton 2018, p. Other Effects of Nicotine, Cardiovascular Effects; 111.
- Morris, Pamela B.; Ference, Brian A.; Jahangir, Eiman; Feldman, Dmitriy N.; Ryan, John J.; Bahrami, Hossein; El-Chami, Mikhael F.; Bhakta, Shyam; Winchester, David E.; Al-Mallah, Mouaz H.; Sanchez Shields, Monica; Deedwania, Prakash; Mehta, Laxmi S.; Phan, Binh An P.; Benowitz, Neal L. (2015). "Cardiovascular Effects of Exposure to Cigarette Smoke and Electronic Cigarettes". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 66 (12): 1378–1391. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.07.037. ISSN 0735-1097. PMID 26383726.
- ^ Maddatu, Judith; Anderson-Baucum, Emily; Evans-Molina, Carmella (2017). "Smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes". Translational Research. 184: 101–107. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2017.02.004. ISSN 1931-5244. PMC 5429867. PMID 28336465.
- ^ Ghanem, A.; Abduljabbar, T.; Akram, Z.; Vohra, F.; Kellesarian, S.V.; Javed, F. (2017). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of pre-clinical studies assessing the effect of nicotine on osseointegration". International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 46 (4): 496–502. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2016.12.003. ISSN 0901-5027. PMID 28189374.
- Lee, Peter N.; Fariss, Marc W. (2016). "A systematic review of possible serious adverse health effects of nicotine replacement therapy". Archives of Toxicology. 91 (4): 1565–1594. doi:10.1007/s00204-016-1856-y. ISSN 0340-5761. PMC 5364244. PMID 27699443.
- Gomes, João Pedro; Watad, Abdulla; Shoenfeld, Yehuda (2017). "Nicotine and Autoimmunity: the Lotus' Flower in Tobacco". Pharmacological Research. 128: 101–109. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2017.10.005. ISSN 1043-6618. PMID 29051105.
- Weaver, Michael; Breland, Alison; Spindle, Tory; Eissenberg, Thomas (2014). "Electronic Cigarettes". Journal of Addiction Medicine. 8 (4): 234–240. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000043. ISSN 1932-0620. PMC 4123220. PMID 25089953.
- SA, Meo; SA, Al Asiri (2014). "Effects of electronic cigarette smoking on human health" (PDF). Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18 (21): 3315–9. PMID 25487945.
- Machaalani, Rita; Chen, Hui (2018). "Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), its tyrosine kinase receptor B (TrkB) and nicotine". NeuroToxicology. 65: 186–195. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2018.02.014. ISSN 0161-813X. PMID 29499216.
- Glover, Marewa; Breier, Bernhard H.; Bauld, Linda (2016). "Could Vaping be a New Weapon in the Battle of the Bulge?". Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 19 (12): 1536–1540. doi:10.1093/ntr/ntw278. hdl:1893/26149. ISSN 1462-2203. PMID 27798086.
- Smith, Tracy T.; Rupprecht, Laura E.; Denlinger-Apte, Rachel L.; Weeks, Jillian J.; Panas, Rachel S.; Donny, Eric C.; Sved, Alan F. (2017). "Animal research on nicotine reduction: Current evidence and research gaps". Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 19 (9): 1005–1015. doi:10.1093/ntr/ntx077. ISSN 1462-2203. PMC 5896531. PMID 28379511.
- ^ Yuan, Menglu; Cross, Sarah J.; Loughlin, Sandra E.; Leslie, Frances M. (2015). "Nicotine and the adolescent brain". The Journal of Physiology. 593 (16): 3397–3412. doi:10.1113/JP270492. ISSN 0022-3751. PMC 4560573. PMID 26018031.
- ^ Chapman 2015, p. 6.
- ^ "Know the Risks". Surgeon General of the United States. 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "FDA's Plan for Tobacco and Nicotine Regulation". United States Food and Drug Administration. 15 March 2018.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Modesto-Lowe, Vania; Alvarado, Camille (2017). "E-cigs . . . Are They Cool? Talking to Teens About E-Cigarettes". Clinical Pediatrics. 56 (10): 947–952. doi:10.1177/0009922817705188. ISSN 0009-9228. PMID 28443340.
- "People who want to quit smoking should consult their GP". Faculty of Public Health. July 2014. Archived from the original on 2016-06-15.
- Collaco, Joseph M.; McGrath-Morrow, Sharon A. (2018). "Electronic Cigarettes: Exposure and Use Among Pediatric Populations". Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery. 31 (2): 71–77. doi:10.1089/jamp.2017.1418. ISSN 1941-2711. PMC 5915214. PMID 29068754.
- "Some E-cigarette Users Are Having Seizures, Most Reports Involving Youth and Young Adults". United States Food and Drug Administration. 3 April 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "Why Is Nicotine Unsafe for Kids, Teens, and Young Adults?". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 3 December 2018.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Wyman, Anne E.; Hines, Stella E. (2018). "Update on metal-induced occupational lung disease". Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 18 (2): 73–79. doi:10.1097/ACI.0000000000000420. ISSN 1528-4050. PMID 29337701.
- Brown, C. J.; Cheng, J. M. (2014). "Electronic cigarettes: product characterisation and design considerations". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii4–ii10. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051476. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995271. PMID 24732162.
- V.Courtney Broaddus; Robert C Mason; Joel D Ernst; Talmadge E King Jr.; Stephen C Lazarus; John F. Murray; Jay A. Nadel; Arthur Slutsky; Michael Gotway (17 March 2015). Murray & Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 820. ISBN 978-0-323-26193-7.
- Crowley, Ryan A. (2015). "Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems: Executive Summary of a Policy Position Paper From the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine. 162 (8): 583–4. doi:10.7326/M14-2481. ISSN 0003-4819. PMID 25894027.
- ^ Kleinstreuer, Clement; Feng, Yu (2013). "Lung Deposition Analyses of Inhaled Toxic Aerosols in Conventional and Less Harmful Cigarette Smoke: A Review". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 10 (9): 4454–4485. doi:10.3390/ijerph10094454. ISSN 1660-4601. PMC 3799535. PMID 24065038.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Franck, Caroline; Filion, Kristian B.; Kimmelman, Jonathan; Grad, Roland; Eisenberg, Mark J. (2016). "Table 1: Ethical considerations surrounding the availability and use of e-cigarettes". Respiratory Research. 17 (1): 53. doi:10.1186/s12931-016-0370-3. PMC 4869264. PMID 27184265.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Caroline Franck, Kristian B. Filion, Jonathan Kimmelman, Roland Grad and Mark J. Eisenberg available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Caroline Franck, Kristian B. Filion, Jonathan Kimmelman, Roland Grad and Mark J. Eisenberg available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- Eissenberg, Thomas (October 2013). "NIDA TV Spotlight on Electronic Cigarettes". National Institute on Drug Abuse.
- "Position Statement on Electronic Cigarettes [ECs] or Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems [ENDS]" (PDF). The International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. October 2013. p. 8.
- McNeill 2018, p. 12.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, 7.
- ^ "Vape Epidemic". United States Department of Health and Human Services. 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Harrell2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Zainol Abidin, Najihah; Zainal Abidin, Emilia; Zulkifli, Aziemah; Karuppiah, Karmegam; Syed Ismail, Sharifah Norkhadijah; Amer Nordin, Amer Siddiq (2017). "Electronic cigarettes and indoor air quality: a review of studies using human volunteers". Reviews on Environmental Health. 0 (3): 235–244. doi:10.1515/reveh-2016-0059. ISSN 2191-0308. PMID 28107173.
- "Position Statement Electronic Cigarettes". Cancer Council Australia, Heart Foundation of Australia.
- ^ Chun, Lauren F; Moazed, Farzad; Calfee, Carolyn S; Matthay, Michael A.; Gotts, Jeffrey Earl (2017). "Pulmonary Toxicity of E-cigarettes". American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 313 (2): L193–L206. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00071.2017. ISSN 1040-0605. PMC 5582932. PMID 28522559.
- Stratton 2018, p. Vulnerable/Susceptible Populations, Asthma and Other Respiratory Diseases of Childhood; 448.
- Stratton 2018, p. Vulnerable/Susceptible Populations, Cystic Fibrosis; 448.
- McNeill 2018, p. 174.
- ^ Evans, S. E.; Hoffman, A. C. (2014). "Electronic cigarettes: abuse liability, topography and subjective effects". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii23–ii29. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051489. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995256. PMID 24732159.
- ^ "White Paper: Electronic Cigarettes in the Indoor Environment" (PDF). American Industrial Hygiene Association. 19 October 2014.
- Henry, Travis S.; Kligerman, Seth J.; Raptis, Constantine A.; Mann, Howard; Sechrist, Jacob W.; Kanne, Jeffrey P. (2019). "Imaging Findings of Vaping-Associated Lung Injury". American Journal of Roentgenology: 1–8. doi:10.2214/AJR.19.22251. ISSN 0361-803X. PMID 31593518.
- ^ "Severe Pulmonary Disease Associated with Using E-Cigarette Products". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 30 August 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Hammond, David (2019). "Outbreak of pulmonary diseases linked to vaping". BMJ: l5445. doi:10.1136/bmj.l5445. ISSN 0959-8138. PMID 31506254.
- "Quebec resident confirmed as first Canadian case of vaping-related illness". CBC.ca. 27 September 2019.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
CDC2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Layden, Jennifer E.; Ghinai, Isaac; Pray, Ian; Kimball, Anne; Layer, Mark; Tenforde, Mark; Navon, Livia; Hoots, Brooke; Salvatore, Phillip P.; Elderbrook, Megan; Haupt, Thomas; Kanne, Jeffrey; Patel, Megan T.; Saathoff-Huber, Lori; King, Brian A.; Schier, Josh G.; Mikosz, Christina A.; Meiman, Jonathan (2019). "Pulmonary Illness Related to E-Cigarette Use in Illinois and Wisconsin — Preliminary Report". New England Journal of Medicine. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1911614. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 31491072.
- Cite error: The named reference
GottsJordt2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - "Transcript of September 6, 2019, Telebriefing: Investigation of Pulmonary Disease Among People Who Use E-cigarettes". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 6 September 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Vaping Illnesses: Consumers can Help Protect Themselves by Avoiding Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-Containing Vaping Products". United States Food and Drug Administration. 6 September 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Dickson, EJ (10 September 2019). "Three Companies Subpoenaed in Weed Vape Illness Investigation". Rolling Stone.
- Goldman, Henry (9 September 2019). "Cuomo Signals N.Y. Crackdown on Vaping Products After Illnesses". Bloomberg News.
- Vergano, Dan (30 August 2019). "The Vaping Lung Illness Outbreak Has Now Spread To 25 States". BuzzFeed News.
- April Joyner (18 August 2019). "CDC probes lung illnesses linked to e-cigarette use". Reuters.
- "New York State Department of Health Announces Update on Investigation into Vaping-Associated Pulmonary Illnesses". New York State Department of Health. 5 September 2019.
- ^ Skotsimara, Georgia; Antonopoulos, Alexios S; Oikonomou, Evangelos; Siasos, Gerasimos; Ioakeimidis, Nikolaos; Tsalamandris, Sotirios; Charalambous, Georgios; Galiatsatos, Nikos; Vlachopoulos, Charalambos; Tousoulis, Dimitris (2019). "Cardiovascular effects of electronic cigarettes: A systematic review and meta-analysis". European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. 26 (11): 1219–1228. doi:10.1177/2047487319832975. ISSN 2047-4873. PMID 30823865.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, 3.
- Milosz Knura, Jonasz Dragon, Krzysztof Labuzek, Boguslaw Okopien (January 2018). "[The impact of electronic cigarettes usage on the endothelial function and the progression of atherosclerosis]". Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski : Organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego. 44 (259): 26–30. PMID 29374420.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Chapman 2015, p. 5.
- ^ Nelluri, Bhargava; Murphy, Katie; Mookadam, Farouk; Mookadam, Martina (2016). "The current literature regarding the cardiovascular effects of electronic cigarettes". Future Cardiology. 12 (2): 167–179. doi:10.2217/fca.15.83. ISSN 1479-6678. PMID 26916427.
- Oakes, Joshua M.; Fuchs, Robert M.; Gardner, Jason D.; Lazartigues, Eric; Yue, Xinping (2018). "Nicotine and the renin-angiotensin system". American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 315 (5): R895–R906. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00099.2018. ISSN 0363-6119. PMC 6295500. PMID 30088946.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, Conclusion 12-1.; 9.
- ^ Javed, Fawad; Kellesarian, Sergio V.; Sundar, Isaac K.; Romanos, Georgios E.; Rahman, Irfan (2017). "Recent Updates on Electronic Cigarette Aerosol and Inhaled Nicotine Effects on Periodontal and Pulmonary Tissues". Oral Diseases. 23 (8): 1052–1057. doi:10.1111/odi.12652. ISSN 1354-523X. PMC 5545167. PMID 28168771.
- ^ Sultan, Ahmed S.; Jessri, Maryam; Farah, Camile S. (2018). "Electronic nicotine delivery systems: Oral health implications and oral cancer risk". Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine. doi:10.1111/jop.12810. ISSN 0904-2512. PMID 30507043.
- ^ Visconti, Michael J.; Ashack, Kurt A. (2019). "Dermatologic manifestations associated with electronic cigarette use". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 81 (4): 1001–1007. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.03.088. ISSN 0190-9622. PMID 30965061.
- Guzik, Amy; Bushnell, Cheryl (2017). "Stroke Epidemiology and Risk Factor Management". CONTINUUM: Lifelong Learning in Neurology. 23 (1, Cerebrovascular Disease): 15–39. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000416. ISSN 1080-2371. PMID 28157742.
- ^ Fracol, Megan; Dorfman, Robert; Janes, Lindsay; Kulkarni, Swati; Bethke, Kevin; Hansen, Nora; Kim, John (2017). "The Surgical Impact of E-Cigarettes: A Case Report and Review of the Current Literature". Archives of Plastic Surgery. 44 (6): 477–481. doi:10.5999/aps.2017.00087. ISSN 2234-6163. PMC 5801784. PMID 29069879.
- ^ Verhaegen, A.; Van Gaal, L. (2017). "Do E-cigarettes induce weight changes and increase cardiometabolic risk? A signal for the future". Obesity Reviews. 18 (10): 1136–1146. doi:10.1111/obr.12568. ISSN 1467-7881. PMID 28660671.
- ^ Offermann, Francis (June 2014). "The Hazards of E-Cigarettes". ASHRAE Journal. 56 (6).
- Peterson, Lisa A.; Hecht, Stephen S. (2017). "Tobacco, e-cigarettes, and child health". Current Opinion in Pediatrics. 29 (2): 225–230. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000456. ISSN 1040-8703. PMC 5598780. PMID 28059903.
- Biyani, S; Derkay, CS (28 April 2015). "E-cigarettes: Considerations for the otolaryngologist". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 79 (8): 1180–3. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.04.032. PMID 25998217.
- Bam, T. S.; Bellew, W.; Berezhnova, I.; Jackson-Morris, A.; Jones, A.; Latif, E.; Molinari, M. A.; Quan, G.; Singh, R. J.; Wisotzky, M. (1 January 2014). "Position statement on electronic cigarettes or electronic nicotine delivery systems ". The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 18 (1): 5–7. doi:10.5588/ijtld.13.0815. PMID 24365545.
- ^ "Surgeon General Reports Youth and Young Adult E-Cigarette Use Poses a Public Health Threat". United States Department of Health and Human Services. 8 December 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Cite error: The named reference
FernándezBallbè2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - "American Lung Association Statement on E-Cigarettes". American Lung Association. 25 August 2014.
- Wilder 2016, p. 84.
- Heydari, Gholamreza; Ahmady, ArezooEbn; Chamyani, Fahimeh; Masjedi, Mohammadreza; Fadaizadeh, Lida (2017). "Electronic cigarette, effective or harmful for quitting smoking and respiratory health: A quantitative review papers". Lung India. 34 (1): 25–28. doi:10.4103/0970-2113.197119. ISSN 0970-2113. PMC 5234193. PMID 28144056.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Glasser, Allison M.; Collins, Lauren; Pearson, Jennifer L.; Abudayyeh, Haneen; Niaura, Raymond S.; Abrams, David B.; Villanti, Andrea C. (2016). "Overview of Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems: A Systematic Review". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 52 (2): e33–e66. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2016.10.036. ISSN 0749-3797. PMC 5253272. PMID 27914771.
- ^ Dicpinigaitis, Peter V. (2017). "Effect of tobacco and electronic cigarette use on cough reflex sensitivity". Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 47: 45–48. doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2017.01.013. ISSN 1094-5539. PMID 28185897.
- Neuberger, Manfred (2015). "The electronic cigarette: a wolf in sheep's clothing". Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift. 127 (9–10): 385–387. doi:10.1007/s00508-015-0753-3. ISSN 0043-5325. PMID 26230008.
- ^ Hess, Isabel; Lachireddy, Kishen; Capon, Adam (2016). "A systematic review of the health risks from passive exposure to electronic cigarette vapour". Public Health Research & Practice. 26 (2). doi:10.17061/phrp2621617. ISSN 2204-2091. PMID 27734060.
- Marynak K; Holmes CB; King BA; Promoff G; Bunnell R; McAfee T (12 December 2014). "State laws prohibiting sales to minors and indoor use of electronic nicotine delivery systems--United States, November 2014". MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 63 (49): 1145–1050. PMC 4584536. PMID 25503916.
- Khan, Mohammad Saud; Khateeb, Faisal; Akhtar, Jamal; Khan, Zubair; Lal, Amos; Kholodovych, Veronika; Hammersley, Jeffrey (2018). "Organizing pneumonia related to electronic cigarette use: A case report and review of literature". The Clinical Respiratory Journal. 12 (3): 1295–1299. doi:10.1111/crj.12775. ISSN 1752-6981.
- Dautzenberg, B.; Adler, M.; Garelik, D.; Loubrieu, J.F.; Mathern, G.; Peiffer, G.; Perriot, J.; Rouquet, R.M.; Schmitt, A.; Underner, M.; Urban, T. (2017). "Practical guidelines on e-cigarettes for practitioners and others health professionals. A French 2016 expert's statement". Revue des Maladies Respiratoires. 34 (2): 155–164. doi:10.1016/j.rmr.2017.01.001. ISSN 0761-8425. PMID 28189437.
- ^ McNeill 2015, p. 65.
- "e-Cigarettes: a safe way to quit?". NPS MedicineWise. 11 June 2014. Archived from the original on 19 March 2017.
- Chapman 2015, p. 1.
- ^ Stratton 2018, p. Secondhand Exposure to E-Cigarette Aerosol, Synthesis; 84.
- Grana RA, Ling PM (2014). ""Smoking revolution": a content analysis of electronic cigarette retail websites". Am J Prev Med. 46 (4): 395–403. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2013.12.010. PMC 3989286. PMID 24650842.
- WHO 2016, p. 4.
- "E-cigarettes not proven quitting aid, says BMA". British Medical Association. 30 January 2013. Archived from the original on 26 February 2013.
- "Know The Risks: E-Cigarettes & Young People – Aerosol and Other Risks". Surgeon General of the United States. 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Holbrook, Bradley D. (2016). "The effects of nicotine on human fetal development". Birth Defects Research Part C: Embryo Today: Reviews. 108 (2): 181–192. doi:10.1002/bdrc.21128. ISSN 1542-975X. PMID 27297020.
- "Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS), including E-cigarettes". New Zealand Ministry of Health. 2014. Archived from the original on 2015-05-11.
- Kaur, J.; Rinkoo, A. V. (2014). "A call for an urgent ban on E-cigarettes in India--a race against time". Global Health Promotion. 22 (2): 71–74. doi:10.1177/1757975914537322. ISSN 1757-9759. PMID 24938513.
- Suter, Melissa A.; Mastrobattista, Joan; Sachs, Maike; Aagaard, Kjersti (2015). "Is There Evidence for Potential Harm of Electronic Cigarette Use in Pregnancy?". Birth Defects Research Part A: Clinical and Molecular Teratology. 103 (3): 186–195. doi:10.1002/bdra.23333. ISSN 1542-0752. PMC 4830434. PMID 25366492.
- Stratton 2018, p. Summary, 18–19.
- Cite error: The named reference
Siu2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Chang, H. (2014). "Research gaps related to the environmental impacts of electronic cigarettes". Tobacco Control. 23 (Supplement 2): ii54–ii58. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2013-051480. ISSN 0964-4563. PMC 3995274. PMID 24732165.
- ^ Brian Clark Howard (11 April 2012). "Cigarettes vs. e-Cigarettes: Which Is Less Environmentally Harmful?". National Geographic.
- Carroll Chapman, SL; Wu, LT (18 Mar 2014). "E-cigarette prevalence and correlates of use among adolescents versus adults: A review and comparison". Journal of Psychiatric Research. 54: 43–54. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.03.005. PMC 4055566. PMID 24680203.
- Chen, I‐Ling; Todd, Ian; Fairclough, Lucy C. (2019). "Immunological and pathological effects of electronic cigarettes". Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. 125 (3): 237–252. doi:10.1111/bcpt.13225. ISSN 1742-7835. PMID 30861614.
- Schneider, Sven; Diehl, Katharina (2016). "Vaping as a Catalyst for Smoking? An Initial Model on the Initiation of Electronic Cigarette Use and the Transition to Tobacco Smoking Among Adolescents". Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 18 (5): 647–653. doi:10.1093/ntr/ntv193. ISSN 1462-2203. PMID 26386472.
- Perikleous, Evanthia P.; Steiropoulos, Paschalis; Paraskakis, Emmanouil; Constantinidis, Theodoros C.; Nena, Evangelia (2018). "E-Cigarette Use Among Adolescents: An Overview of the Literature and Future Perspectives". Frontiers in Public Health. 6: 86. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2018.00086. ISSN 2296-2565. PMC 5879739. PMID 29632856.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Evanthia P. Perikleous, Paschalis Steiropoulos, Emmanouil Paraskakis, Theodoros C. Constantinidis, and Evangelia Nena available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Evanthia P. Perikleous, Paschalis Steiropoulos, Emmanouil Paraskakis, Theodoros C. Constantinidis, and Evangelia Nena available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- McNeill 2018, p. 190.
- McCubbin, Andrea; Fallin-Bennett, Amanda; Barnett, Janine; Ashford, Kristin (2017). "Perceptions and use of electronic cigarettes in pregnancy". Health Education Research. 32 (1): 22–32. doi:10.1093/her/cyw059. ISSN 0268-1153. PMC 5914445. PMID 28158490.
- McNeill 2018, p. 189.
- ^ McCausland, Kahlia; Maycock, Bruce; Leaver, Tama; Jancey, Jonine (2019). "The Messages Presented in Electronic Cigarette–Related Social Media Promotions and Discussion: Scoping Review". Journal of Medical Internet Research. 21 (2): e11953. doi:10.2196/11953. ISSN 1438-8871. PMC 6379814. PMID 30720440.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) This article incorporates text by Kahlia McCausland, Bruce Maycock, Tama Leaver, and Jonine Jancey available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Kahlia McCausland, Bruce Maycock, Tama Leaver, and Jonine Jancey available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- McNeill 2018, p. 20.
- ^ "Electronic cigarette use among smokers slows as perceptions of harm increase". ASH UK. 22 May 2015.
- McNeill 2015, p. 79.
- McNeill 2015, p. 6, 11, 79-80.
- Camenga, Deepa R.; Klein, Jonathan D. (2016). "Tobacco Use Disorders". Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 25 (3): 445–460. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2016.02.003. ISSN 1056-4993. PMC 4920978. PMID 27338966.
- Correa, John B.; Ariel, Idan; Menzie, Nicole S.; Brandon, Thomas H. (2017). "Documenting the emergence of electronic nicotine delivery systems as a disruptive technology in nicotine and tobacco science". Addictive Behaviors. 65: 179–184. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.10.021. ISSN 0306-4603. PMC 5140675. PMID 27816664.
- McKee, M. (2014). "Electronic cigarettes: peering through the smokescreen". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 90 (1069): 607–609. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2014-133029. ISSN 0032-5473. PMID 25294933.
- ^ de Andrade, M.; Angus, K.; Hastings, G. (2015). "Teenage perceptions of electronic cigarettes in Scottish tobacco-education school interventions: co-production and innovative engagement through a pop-up radio project". Perspectives in Public Health. 136 (5): 288–293. doi:10.1177/1757913915612109. ISSN 1757-9139. PMID 26543156.
- Tomashefski, Amy (2016). "The perceived effects of electronic cigarettes on health by adult users: A state of the science systematic literature review". Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners. 28 (9): 510–515. doi:10.1002/2327-6924.12358. ISSN 2327-6886. PMID 26997487.
- McNeill 2018, p. 188.
- Wagener, Theodore L.; Meier, Ellen; Tackett, Alayna P.; Matheny, James D.; Pechacek, Terry F. (2016). "A Proposed Collaboration Against Big Tobacco: Common Ground Between the Vaping and Public Health Community in the United States". Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 18 (5): 730–736. doi:10.1093/ntr/ntv241. ISSN 1462-2203. PMID 26508399.
- Collins, Lauren; Glasser, Allison M; Abudayyeh, Haneen; Pearson, Jennifer L; Villanti, Andrea C (2018). "E-Cigarette Marketing and Communication: How E-Cigarette Companies Market E-Cigarettes and the Public Engages with E-cigarette Information". Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 21 (1): 14–24. doi:10.1093/ntr/ntx284. ISSN 1462-2203. PMC 6610165. PMID 29315420.
- "Lung Injury Associated with E-cigarette or Vaping Products". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019.
External links
 Media related to Electronic cigarettes at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Electronic cigarettes at Wikimedia Commons
| Electronic cigarettes | |
|---|---|
| General topics | |
| Brands and companies | |
| Controversy | |
| See also | |