| Revision as of 17:12, 26 October 2020 edit123456meri (talk | contribs)5 editsmNo edit summaryTags: Reverted Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:44, 28 October 2020 edit undoNinetoyadome (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,186 edits Reverted to revision 985559062 by Materialscientist (talk)Tags: Twinkle UndoNext edit → | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| '''Greater |
'''Greater Armenia''' ({{lang-hy|Մեծ Հայք}}, ''Mets Hayk<nowiki>'</nowiki>'') is the name given to the state of ] that emerged on the ] under the reign of King ] at the turn of the second century BC. The term was used to refer to Armenian kingdoms throughout the ], ], and ] periods by contemporary Armenian and non-Armenian authors alike. | ||
| Though its borders were in a constant state of flux, Greater Armenia roughly encompassed the area stretching from the ] in the west, the region of ] and parts of ] to the east, parts of the modern state of ] to the north, with its southern boundary abutting the northern tip of ]. | Though its borders were in a constant state of flux, Greater Armenia roughly encompassed the area stretching from the ] in the west, the region of ] and parts of ] to the east, parts of the modern state of ] to the north, with its southern boundary abutting the northern tip of ]. | ||
Revision as of 03:44, 28 October 2020
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Greater Armenia" state – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

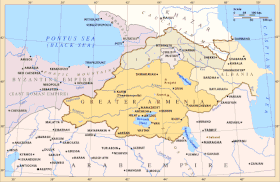


Greater Armenia (Template:Lang-hy, Mets Hayk') is the name given to the state of Armenia that emerged on the Armenian Highlands under the reign of King Artaxias I at the turn of the second century BC. The term was used to refer to Armenian kingdoms throughout the classical, late antique, and medieval periods by contemporary Armenian and non-Armenian authors alike.
Though its borders were in a constant state of flux, Greater Armenia roughly encompassed the area stretching from the Euphrates River in the west, the region of Artsakh and parts of Iranian Azerbaijan to the east, parts of the modern state of Georgia to the north, with its southern boundary abutting the northern tip of Mesopotamia.
To the Romans it was known as Armenia Maior and to the Greek-speaking peoples as Ἀρμενία Μεγάλη (Armenia Megale), to differentiate it with Lesser Armenia (Pok'r Hayk′, in Latin Armenia Minor). It would later be used to distinguish it from the medieval kingdom that was established in Cilicia, which was sometimes referred to as Little Armenia (not to be confused with Lesser Armenia).
References
- (in Armenian) Yeremyan, Suren. «Մեծ Հայք». Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia. Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1981, vol. 7, pp. 434-36.
Further reading
- Adontz, Nicholas (1970). Armenia in the Period of Justinian: The Political Conditions Based on the Naxarar System, trans. Nina Garsoïan. Lisbon: Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation.
- Hewsen, Robert H. (2001). Armenia: A Historical Atlas. Chicago: Chicago University Press.