This is an old revision of this page, as edited by That Northern Irish Historian (talk | contribs) at 14:16, 10 June 2024. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:16, 10 June 2024 by That Northern Irish Historian (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) West Central German language| Moselle Franconian | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Germany, France, Luxembourg, Belgium, Romania, Brazil |
| Region | North Rhine-Westphalia, Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland, Lorraine, Liège |
| Language family | Indo-European
|
| Early forms | Proto-Indo-European
|
| Standard forms | |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | |
| Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis)Individual codes: ltz – Luxembourgishhrx – Hunsrik |
| Glottolog | luxe1241 |
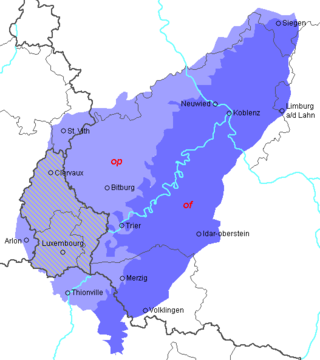 Area where Moselle Franconian / Luxembourgish is spoken with the isogloss between usage of Template:Wiktlb and Template:Wiktlb (Standard German: Template:Wiktde) shown Area where Moselle Franconian / Luxembourgish is spoken with the isogloss between usage of Template:Wiktlb and Template:Wiktlb (Standard German: Template:Wiktde) shown | |
 Moselle Franconian is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger Moselle Franconian is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |

Moselle Franconian (Template:Lang-de, Template:Lang-lb) is a West Central German language, part of the Central Franconian languages area, that includes Luxembourgish. It is spoken in the southern Rhineland and along the course of the Moselle, in the Siegerland of North Rhine-Westphalia, throughout western Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland, Luxembourg, the south of the German-speaking Community of Belgium and in the neighboring French département of Moselle (in Arrondissement of Boulay-Moselle). The Transylvanian Saxon dialect spoken in the Transylvania region of Romania is derived from this dialect as a result of the emigration of numerous "Transylvanian Saxons" between 1100 and 1300, primarily from areas in which the Moselle Franconian dialect was then spoken. Another variety of Moselle Franconian, the Hunsrik, is spoken in some rural areas of southern Brazil, brought by 19th century immigrants from the Hunsrück region in modern Germany.
Varieties
The transition between "dialect" and "separate language" is fluid.

The Linguasphere Register lists five dialects of Moselle Franconian (code 52-ACB-dc) with codes -dca to -dce:
- Trierisch (Rhineland-Palatinate, Luxembourg, northwestern Saarland)
- Eifelisch (Rhineland-Palatinate, East Belgium, Luxembourg, southern North Rhine-Westphalia)
- Untermosellanisch (Rhineland-Palatinate)
- West-Westerwäldisch (Rhineland-Palatinate)
- Siegerländisch (southern North Rhine-Westphalia, northeastern Rhineland-Palatinate)
Also considered part of the Moselle Franconian language are the variants of Lorraine Franconian, Luxembourgish and Transylvanian Saxon dialect.
Some Moselle Franconian dialects have developed into standardized varieties which can be considered separate languages, especially due to the limited intelligibility of some dialects for Standard German speakers:
- Luxembourgish (Lëtzebuergesch)
- Lorraine Franconian
- Transylvanian Saxon dialect
- Hunsrik
Most speakers of Luxembourgish are multilingual, speaking Standard German and French in addition to Luxembourgish.
See also
- Saarland (section Local dialect)
- Rhine Franconian (related neighboring dialect group)
- Meuse-Rhenish
Further reading
- Werner König: dtv-Atlas Deutsche Sprache. dtv-Verlag, München (Munich) 2005; ISBN 3-423-03025-9 (German).
References
- Documentação, Coordenadoria de. "LEI Nº 16.987, DE 3 DE AGOSTO DE 2016". leis.alesc.sc.gov.br. Retrieved 2022-04-11.
- "Texto da Norma". 2019-03-30. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 2022-04-11.
- Ammon, Ulrich - Die Stellung der deutschen Sprache in der Welt Archived 2015-11-09 at the Wayback Machine (de Gruyter Mouton; ISBN 978-3-11-019298-8)
- Linguasphere Register, 1999/2000 edition, p. 430
- http://www.luxembourg.public.lu/catalogue/fr-generalites/ap_histoire/ap_histoire_2008_DE.pdf „Im Alltag sprechen die Luxemburger ihren Dialekt, eine moselfränkische Mundart, die sie selbst noch bis Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts als "Lëtzebuerger Däitsch" ("Luxemburger Deutsch") bezeichneten.“
- "The rise of the national sentiment (19th century)". The Official Portal of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. Retrieved 2019-12-01 – via www.luxembourg.public.lu.
This article about Germanic languages is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |