This is an old revision of this page, as edited by BogBot (talk | contribs) at 07:58, 30 August 2011 (populated new fields in {{drugbox}} and reordered per bot approval. Report errors and suggestions to User_talk:BogBot). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 07:58, 30 August 2011 by BogBot (talk | contribs) (populated new fields in {{drugbox}} and reordered per bot approval. Report errors and suggestions to User_talk:BogBot)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound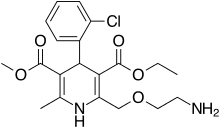 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Amlodipine | Calcium channel blocker |
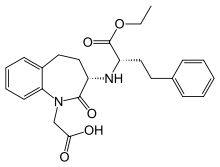
| Benazepril | ACE inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Amlodipine/benazepril, marketed in the U.S. as Lotrel by Novartis and manufactured as a generic drug by Teva and Sandoz, is an antihypertensive medication which combines a calcium channel blocker (amlodipine besilate) with an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (benazepril). This drug, like similar combinations, is prescribed when either agent alone is not sufficient to bring a person's blood pressure down to target range. As a combination agent, Lotrel shares the adverse reaction profile of both of its individual parts.
See also
References
- Lotrel Prescribing Information
- Drugs.com: Lotrel
- RxList.com: Lotrel
External links
| Antihypertensive drugs acting on the renin–angiotensin system (C09) | |
|---|---|
| ACE inhibitors ("-pril") |
|
| AIIRAs ("-sartan") |
|
| Renin inhibitors ("-kiren") | |
| Dual ACE/NEP inhibitors | |
| Neprilysin inhibitors | |
| Other | |
| |
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |