This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Sodabottle (talk | contribs) at 04:13, 23 February 2012 (+ta wikilink). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 04:13, 23 February 2012 by Sodabottle (talk | contribs) (+ta wikilink)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)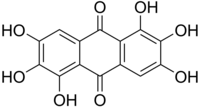
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 1,2,3,5,6,7-Hexahydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione | |
| Other names Rufigallic acid; 1,2,3,5,6,7-Hexahydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone; 1,2,3,5,6,7-Hexahydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C14H8O8 |
| Molar mass | 304.210 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Rufigallol or 1,2,3,5,6,7-hexahydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone is an organic compound with formula C
14O
8H
8, which can be viewed as a derivative of anthraquinone through the replacement of six hydrogen atoms (H) by hydroxyl groups (OH).
The compound is soluble in dioxane, from which it crystallizes as red needles that sublime without melting at 365 °C. It can be obtained by treating gallic acid with concentrated sulfuric acid and then with sodium hydroxide.
Rufigallol is particularly toxic to the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum and has a synergistic effect in combination with the antimalarial drug exifone, which has structural sumilarities to rufigallol.
Rufigallol forms a crimson-colored complex with beryllium, aluminum, thorium, zirconium and hafnium, and this reaction has been used for the spot and spectrophotometric determination of beryllium in low concentrations.
See also
References
- ^ M. A. Azim and A. A. Ayaz (1969), Spectrophotometric determination of beryllium. Microchimica Acta Volume 57, Number 1, pages 153-159 doi:10.1007/BF01216677
- R. W. WINTER, KENNETH A. CORNELL, LINDA L. JOHNSON, MARINA IGNATUSHCHENKO,DAVID J. HINRICHS and MICHAEL K. RISCOE (1996), Potentiation of the Antimalarial Agent Rufigallol. ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Vol. 40, No. 6, pages 1408–1411. Online version accessed on 2010-02-01.