This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Smokefoot (talk | contribs) at 15:50, 8 March 2014 (ref and prep and density). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:50, 8 March 2014 by Smokefoot (talk | contribs) (ref and prep and density)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)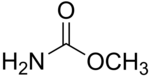
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Methyl carbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.037 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C2H5NO2 |
| Molar mass | 75 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.136 (56 °C) |
| Melting point | 52 °C (126 °F; 325 K) |
| Boiling point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) |
| Solubility in water | good |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Methyl carbamate (also called methylurethane, or urethylane) is an organic compound and the simplest ester of carbamic acid (H2NCO2H). It is a colourless solid.
Methyl carbamate is prepared by the reaction of methanol and urea:
- CO(NH2)2 + CH3OH → CH3OC(O)NH2 + NH3
It also forms in the reaction of ammonia with methyl chloroformate or dimethyl carbonate.
Safety and occurrence
Unlike its close relative ethyl carbamate it is not mutagenic in salmonella (it tested negative in the Ames test), but it is mutagenic in Drosophila. Experimental evidence does show that it is a carcinogen in rat, and not carcinogenic in mice. The compound is "known to the state of California to cause cancer" per Proposition 65.
The compound was detected in wines preserved with dimethyl dicarbonate.
Methyl carbamate is used by the textile industry to manufacture resins to be applied on polyester/cotton blend fabrics as durable-press finishes.
N-Methyl carbamates are widely used as insecticides. They have anticholinesterase activity without a cumulative effect.
See also
- Carbamate
- Ethyl carbamate (urethane)
References
- Peter Jäger, Costin N. Rentzea and Heinz Kieczka "Carbamates and Carbamoyl Chlorides" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_051
- P. Foureman, J.M. Mason, R. Valencia and S. Zimmering, Environ. Mol. Mutagen., 1994, 23 (1), 51 - 63.
- OEHHA
- Inchem.org
- National Toxocology Program
- National Pesticide Information Center at Oregon State University