This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 205.188.116.136 (talk) at 01:21, 25 September 2006 (So many...). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:21, 25 September 2006 by 205.188.116.136 (talk) (So many...)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) For other uses, see Dinosaur (disambiguation).
| Dinosaurs Temporal range: Triassic – Cretaceous | |
|---|---|

| |
| Replica of Tyrannosaurus rex at the Senckenberg Museum. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Sauropsida |
| Subclass: | Diapsida |
| Infraclass: | Archosauromorpha Template:Taxobox norank entry |
| Superorder: | Dinosauria * Owen, 1842 |
| Orders & Suborders | |
Dinosaurs were vertebrate animals that dominated terrestrial ecosystems for over 160 million years, first appearing approximately 230 million years ago. At the end of the Cretaceous Period, 65 million years ago, dinosaurs became extinct. Many taxonomists consider modern birds to be the direct descendants of theropod dinosaurs.
Since the first dinosaur was recognized in the 19th century, mounted, fossilized dinosaur skeletons have become major attractions at museums around the world. Dinosaurs have become a part of world culture and remain consistently popular, especially among children. They have been featured in best-selling books and films such as Jurassic Park, and new discoveries are regularly covered by the media.
The term dinosaur is sometimes used informally to describe other prehistoric reptiles, such as the pelycosaur Dimetrodon, the winged pterosaurs and the aquatic ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, although technically none of these were dinosaurs.
What is a dinosaur?
Definition

The taxon Dinosauria was formally named by the English palaeontologist Richard Owen in 1842 as "a distinct tribe or suborder of Saurian reptiles". The term is derived from the Greek words δεινός (deinos meaning "terrible", "fearsome" or "formidable") and σαύρα (saura meaning "lizard" or "reptile"). Owen chose it to express his awe at the size and majesty of the extinct animals, not out of fear or trepidation at their size and often-formidable arsenal of teeth and claws.
Dinosaurs were an extremely varied group of animals; according to a 2006 study, 527 dinosaur genera have been identified with certainty so far, and 1,844 genera are believed to have existed. Some were herbivorous, others carnivorous. Some dinosaurs were bipeds, some were quadrupeds and others, such as Ammosaurus and Iguanodon, could walk just as easily on two or four legs. Regardless of body type, nearly all known dinosaurs were well-adapted for a predominantly terrestrial, rather than aquatic or aerial, habitat.
Dinosaur synapomorphies
All dinosaurs so far discovered share certain modifications to the ancestral archosaurian skeleton. Although some later groups of dinosaurs featured further modified versions of these traits, they are considered typical across Dinosauria; the earliest dinosaurs had them and passed them on to all their descendants. Such common structures across a taxonomic group are called synapomorphies.
Dinosaur synapomorphies include: reduced fourth and fifth digits on the manus (hand), reduced number of digits on the pes (foot) to three main toes, a sacrum (the region of the vertebral column to which the pelvis attaches, composed of three or more fused vertebrae) and an open or perforate acetabulum (hip socket with a hole its centre). Dinosaurs are unique among all tetrapods in having this perforate acetabulum.
Other shared anatomical features
Scientists generally agree that a variety of other anatomical features were shared by most dinosaurs. These include forelimbs shorter and lighter than hind limbs, an unusual secondary palate that permitted dinosaurs to eat and breathe simultaneously, a relatively straight femur with medially-directed femoral head, two pairs of holes in the temporal region of the skull (i.e. a diapsid skull), rearward-pointing elbows in the front limbs and forward-pointing knees in the hind limbs.
The hip joint arrangement described above allowed an erect stance, in which hind limbs were situated directly beneath the body or 'underslung'. This stance is like that of most mammals today but unlike that of other reptiles, which have a less erect posture and limbs splayed out to either side. The vertical action of the limbs in dinosaurs allowed for more efficient and faster locomotion, compared to the clumsier and slower movement of other 'sprawled' reptiles. It also allowed many types of dinosaurs to become bipedal.

Taxonomic definition
Under phylogenetic taxonomy, dinosaurs are defined as all descendants of the most recent common ancestor of Triceratops. They are divided into Ornithischia (bird-hipped) and Saurischia (lizard-hipped), depending upon pelvic structure. Ornithischian dinosaurs had a four-pronged pelvic configuration, incorporating a caudally-directed (rear-pointing) pubis bone with (most commonly) a forward-pointing process. By contrast, the pelvic structure of saurischian dinosaurs was three-pronged, and featured a pubis bone directed cranially, or forwards, only. Ornithischia includes all taxa sharing a more recent common ancestor with Triceratops than with Saurischia. It has also been suggested that Dinosauria be defined as all the descendants of the most recent common ancestor of Megalosaurus and Iguanodon.
Size
While the evidence is incomplete, it is clear that, as a group, dinosaurs were large. Even by dinosaur standards, the sauropods were gigantic. For much of the dinosaur era, the smallest sauropods were larger than anything else in their habitat, and the largest were an order of magnitude more massive than anything else that has since walked the Earth. Giant prehistoric mammals such as the Indricotherium and the Columbian mammoth were dwarfed by the giant sauropods, and only a handful of modern aquatic animals approach them in size — most notably the blue whale, which reaches up to 190,000 kg (209 tons) and 33.5 m (110 ft) in length.
Most dinosaurs, however, were much smaller than the giant sauropods. Current evidence suggests that dinosaur average size varied through the Triassic, early Jurassic, late Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. According to paleontologist Bill Erickson, estimates of median dinosaur weight range from 500 kg to 5 tonnes; a recent study of 63 dinosaur genera yielded an average weight in excess of 850 kg — comparable to the weight of a grizzly bear — and a median weight of nearly 2 tons, or about as much as a giraffe. This contrasts sharply with the size of modern mammals; on average, mammals weigh only 863 grams, or about as much as a large rodent. The smallest dinosaur was bigger than two-thirds of all current mammals; the majority of dinosaurs were bigger than all but 2% of living mammals.
Largest and smallest dinosaurs
Only a tiny percentage of animals ever fossilize, and most of these remain buried in the earth. Few of the specimens that are recovered are complete skeletons, and impressions of skin and other soft tissues are rare. Rebuilding a complete skeleton by comparing the size and morphology of bones to those of similar, better-known species is an inexact art, and reconstructing the muscles and other organs of the living animal is, at best, a process of educated guesswork. As a result, scientists will probably never be certain of the largest and smallest dinosaurs.

The tallest and heaviest dinosaur known from a complete skeleton is the Brachiosaurus specimen that was discovered in Tanzania between 1907–12. It is now mounted and on display at the Humboldt Museum of Berlin and is 12 m (38 ft) tall and probably weighed between 30,000–60,000 kg (33–66 short tons). The longest complete dinosaur is the 27 m (89 ft) long Diplodocus, which was discovered in Wyoming in the United States and displayed in Pittsburgh's Carnegie Natural History Museum in 1907.
There were larger dinosaurs, but knowledge of them is based entirely on a small number of incomplete fossil samples. The largest herbivorous specimens on record were all discovered in the 1970s or later, and include the massive Argentinosaurus, which may have weighed 80,000–100,000 kg (88–121 tons); the longest, the 40 m (130 ft) long Supersaurus; and the tallest, the 18 m (60 ft) Sauroposeidon, which could have reached a sixth-floor window. The largest known carnivorous dinosaur was Spinosaurus, reaching a length of 16-18 meters (53-60 ft), and weighing in at 9 tons. Other large meat-eaters included Giganotosaurus, Mapusaurus, Tyrannosaurus rex and Carcharodontosaurus.
The smallest dinosaurs known were about the size of a crow or a chicken. The theropods Microraptor, Parvicursor, and Saltopus were all under 60 cm (2 ft) in length.
Behavior
Interpretations of dinosaur behavior are generally based on the pose of body fossils and their habitat, computer simulations of their biomechanics, and comparisons with modern animals in similar ecological niches. As such, the current understanding of dinosaur behavior relies on speculation, and will likely remain controversial for the foreseeable future. However, there is general agreement that some behaviors which are common in crocodiles, dinosaurs' closest living relatives, were also common among dinosaurs.
The first perceived direct evidence of herding behavior was the 1878 discovery of 31 Iguanodon dinosaurs which were thought to have perished together in Bernissart, Belgium, after they fell into a deep, flooded sinkhole and drowned. Despite the deposition of those skeletons being now regarded as more gradual, other, well supported, mass death sites were subsequently discovered. Those, along with multiple trackways, suggest that herd or pack behavior was common in many dinosaur species. Trackways of hundreds or even thousands of herbivores indicate that duck-bills (hadrosaurids) may have moved in great herds, like the American Bison or the African Springbok. Sauropod tracks document that these animals traveled in groups composed of several different species, at least in Oxford, England, and others kept their young in the middle of the herd for defense according to trackways at Davenport Ranch, Texas. Dinosaurs may have congregated in herds for defense, for migratory purposes, or to provide protection for their young.
Jack Horner's 1978 discovery of a Maiasaura ("good mother dinosaur") nesting ground in Montana demonstrated that parental care continued long after birth among the ornithopods. There is also evidence that other Cretaceous-era dinosaurs, like the Patagonian sauropod Saltasaurus (1997 discovery), had similar nesting behaviors, and that the animals congregated in huge nesting colonies like those of penguins. The Mongolian maniraptoran Oviraptor was discovered in a chicken-like brooding position in 1993, which may mean it was covered with an insulating layer of feathers that kept the eggs warm. Trackways have also confirmed parental behavior among sauropods and ornithopods from the Isle of Skye in northwestern Scotland. Nests and eggs have been found for most major groups of dinosaurs, and it appears likely that dinosaurs communicated with their young, in a manner similar to modern birds and crocodiles.
The crests and frills of some dinosaurs, like the marginocephalians, theropods and lambeosaurines, may have been too fragile to be used for active defense, so they were likely used for sexual or aggressive displays, though little is known about dinosaur mating and territorialism. The nature of dinosaur communication also remains enigmatic, and is an active area of research. For example, recent evidence suggests that the hollow crests of the lambeosaurines may have functioned as resonance chambers used for a wide range of vocalizations.
From a behavioral standpoint, one of the most valuable dinosaur fossils was discovered in the Gobi Desert in 1971. It included a Velociraptor attacking a Protoceratops, proving that dinosaurs did indeed attack and eat each other. While cannibalistic behavior among theropods is no surprise, this too was confirmed by tooth marks from Madagascar in 2003.
There seem to have been no burrowing species of dinosaur and few climbing species. This is somewhat surprising when compared to the later mammalian radiation in the Cenozoic, which included many species of these types. As to how the animals moved, biomechanics has provided significant insight. For example, studies of the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on dinosaurs' skeletal structure have demonstrated how fast dinosaurs could run, whether diplodocids could create sonic booms via whip-like tail snapping, whether giant theropods had to slow down when rushing for food to avoid fatal injuries, and if sauropods could float.
Evolution of dinosaurs

Dinosaurs diverged from their archosaur ancestors approximately 230 million years ago during the Middle to Late Triassic period, roughly 20 million years after the Permian-Triassic extinction event wiped out an estimated 95% of all life on Earth. Radiometric dating of fossils from the early dinosaur genus Eoraptor establishes its presence in the fossil record at this time. Paleontologists believe Eoraptor resembles the common ancestor of all dinosaurs; if this is true, its traits suggest that the first dinosaurs were small, bipedal predators. Such a notion is corroborated by the more primitive dinosaur-like ornithodirans hailing from Middle Triassic strata of Argentina such as Marasuchus and Lagerpeton, which were also small bipedal, perhaps leaping, predators.
The first few lines of primitive dinosaurs diversified rapidly through the rest of the Triassic period; dinosaur species quickly evolved the specialized features and range of sizes needed to exploit nearly every terrestrial ecological niche. During the period of dinosaur predominance, which encompassed the ensuing Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, nearly every known land animal larger than 1 meter in length was a dinosaur.
Study of dinosaurs
Knowledge about dinosaurs is derived from a variety of fossil and non-fossil records, including fossilized bones, feces, trackways, gastroliths, feathers, impressions of skin, internal organs and soft tissues. Many fields of study contribute to our understanding of dinosaurs, including physics, chemistry, biology, and the earth sciences (of which paleontology is a sub-discipline).
Dinosaur remains have been found on every continent on Earth, including Antarctica. Numerous fossils of the same dinosaur species have been found on completely different continents, corroborating the generally-accepted theory that all land masses were at one time connected in a super-continent called Pangaea. Pangaea began to break apart during the Triassic period roughly 230 million years ago.
The current "dinosaur renaissance"
The field of dinosaur research has enjoyed a surge in activity that began in the 1970s and is ongoing. This was triggered, in part, by John Ostrom's discovery of Deinonychus, an active, vicious predator that may have been warm-blooded, in marked contrast to the prevailing image of dinosaurs as sluggish and cold-blooded. Vertebrate paleontology, arguably the primary scientific discipline involved in dinosaur research, has become a global science. Major new dinosaur discoveries have been made by paleontologists working in previously unexploited regions, including India, South America, Madagascar, Antarctica, and in China. The widespread application of cladistics, which rigorously analyzes the relationships between biological organisms, has also proved useful in classifying dinosaurs. Cladistic analysis, among other modern techniques, helps to compensate for an often incomplete and fragmentary fossil record.
Classification
Main article: Dinosaur classification
Dinosaurs are archosaurs, like modern crocodilians. Archosaurs' diapsid skulls have two holes located where the jaw muscles attach, called temporal fenestrae. Most reptiles are diapsids; mammals, with only one temporal fenestra, are called synapsids; and turtles, with no temporal fenestra, are anapsids. Anatomically, dinosaurs share many other archosaur characteristics, including teeth that grow from sockets rather than as direct extensions of the jawbones. Within the archosaur group, dinosaurs are differentiated most noticeably by their gait. Dinosaur legs extend directly beneath the body, whereas the legs of lizards sprawl out to either side. All dinosaurs were land animals.
Many other types of reptiles lived at the same time as the dinosaurs. Some of these are commonly, but incorrectly, thought of as dinosaurs, including plesiosaurs (which are not closely related to the dinosaurs) and pterosaurs, which developed separately from reptilian ancestors in the late Triassic period.
Collectively, dinosaurs are usually regarded as a superorder or an unranked clade. They are divided into two orders, the Saurischia and the Ornithischia, on the basis of their hip structure. Saurischians ('lizard-hipped', from the Greek sauros (σαυρος) meaning 'lizard' and ischion (ισχιον) meaning 'hip joint') are dinosaurs that originally retained the hip structure of their ancestors. They include all the theropods (bipedal carnivores) and sauropods (long-necked herbivores). Ornithischians ('bird-hipped', from the Greek ornitheos (ορνιθειος) meaning 'of a bird' and ischion (ισχιον) meaning 'hip joint') is the other dinosaurian order, most of which were quadrupedal herbivores.
-
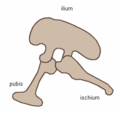 Saurischian pelvis structure (left side)
Saurischian pelvis structure (left side)
- Tyrannosaurus pelvis (showing saurischian structure - left side) Tyrannosaurus pelvis (showing saurischian structure - left side)
-
 Ornithischian pelvis structure (left side).
Ornithischian pelvis structure (left side).
- Edmontosaurus pelvis (showing ornithischian structure - left side) Edmontosaurus pelvis (showing ornithischian structure - left side)
The following is a simplified classification of dinosaur families. A more detailed version can be found at List of dinosaur classifications.
The dagger (†) is used to indicate taxa that are extinct.
Order Saurischia
- †Infraorder Herrerasauria
- Suborder Theropoda
- †Superfamily Coelophysoidea
- †Infraorder Ceratosauria
- †Family Abelisauridae
- (unranked) Tetanurae
- †Superfamily Megalosauroidea
- †Infraorder Carnosauria
- Infraorder Coelurosauria
- †Family Coeluridae
- †Superfamily Tyrannosauroidea
- †(unranked) Ornithomimosauria
- (unranked) Maniraptora
- †(unranked) Oviraptoriformes
- †(unranked) Therizinosauria
- †(unranked) Oviraptorosauria
- †(unranked) Deinonychosauria
- †Family Troodontidae
- †Family Dromaeosauridae
- †(unranked) Oviraptoriformes
- †Suborder Sauropodomorpha
- †Thecodontosaurus
- †Infraorder Prosauropoda
- †Infraorder Sauropoda
- †Superfamily Diplodocoidea
- †Superfamily Titanosauriformes
- †Family Brachiosauridae
- †(unranked) Titanosauria
Order Ornithischia
- †Suborder Thyreophora
- †Infraorder Stegosauria
- †Infraorder Ankylosauria
- †(unranked) Cerapoda
- †Family Heterodontosauridae
- †Suborder Marginocephalia
- †Infraorder Pachycephalosauria
- †Infraorder Ceratopsia
- †Family Psittacosauridae
- †Family Protoceratopsidae
- †Family Ceratopsidae
- †Suborder Ornithopoda
- †Family Hypsilophodontidae
- †Infraorder Iguanodontia
- †Family Iguanodontidae
- †Family Hadrosauridae
Evidence for Cenozoic dinosaurs
In 2002, paleontologists Zielinski and Budahn reported the discovery of a single hadrosaur leg bone fossil in the San Juan Basin, New Mexico. The formation in which the bone was discovered has been dated to the early Paleocene epoch approximately 64.5 million years ago. If the bone was not re-deposited into that stratum by weathering action, it would provide evidence that some dinosaur populations may have survived at least a half million years into the Cenozoic Era.
Bringing dinosaurs back to life

There has been much speculation about the use of technology to bring dinosaurs back to life. In Michael Crichton's book Jurassic Park (later adapted into a movie), which popularized the idea, scientists use blood from fossilized mosquitos that have been suspended in tree sap since the Mesozoic to reconstruct the DNA of dinosaurs, filling chromosomal gaps with modern frog genes. It is probably impossible to resurrect dinosaurs in this manner. One problem with the amber extraction method is that DNA decays over time by exposure to air, water and radiation, making it unlikely that such an approach would recover any useful DNA (DNA decay can be measured by a racemization test).
The successful extraction of ancient DNA from dinosaur fossils has been reported on two separate occasions, but upon further inspection and peer review, neither of these reports could be confirmed. However, a functional visual peptide of a (theoretical) dinosaur has been inferred using analytical phylogenetic reconstruction methods on gene sequences of still-living related species (reptiles and birds).
Even if dinosaur DNA could be reconstructed, it would be exceedingly difficult to "grow" dinosaurs using current technology since no closely related species exist to provide zygotes or a suitable environment for embryonic development.
Soft tissue in dinosaur fossils
One of the best examples of soft tissue impressions in a fossil dinosaur was discovered in Petraroia, Italy. The discovery was reported in 1998, and described the specimen of a small, very young coelurosaur, Scipionyx samniticus. The fossil includes portions of the intestines, colon, liver, muscles, and windpipe of this immature dinosaur.
In the March 2005 issue of Science, Dr. Mary Higby Schweitzer and her team announced the discovery of flexible material resembling actual soft tissue inside a 68-million-year-old Tyrannosaurus rex leg bone from the Hell Creek Formation in Montana. After recovery, the tissue was rehydrated by the science team.
When the fossilized bone was treated over several weeks to remove mineral content from the fossilized bone marrow cavity (a process called demineralization), Schweitzer found evidence of intact structures such as blood vessels, bone matrix, and connective tissue (bone fibers). Scrutiny under the microscope further revealed that the putative dinosaur soft tissue had retained fine structures (microstructures) even at the cellular level. The exact nature and composition of this material are not yet clear, although many news reports immediately linked it with the movie Jurassic Park. Interpretation of the artifact is ongoing, and the relative importance of Dr. Schweitzer's discovery is not yet clear.
History of discovery
Dinosaur fossils have been known for millennia, although their true nature was not recognized. The Chinese, whose own word for dinosaur is konglong (恐龍, or "terrible dragon"), considered them to be dragon bones and documented them as such. For example, Hua Yang Guo Zhi, a book written by Zhang Qu during the Western Jin Dynasty, reported the discovery of dragon bones at Wucheng in Sichuan Province.. In Europe, dinosaur fossils were generally believed to be the remains of giants and other creatures killed by the Great Flood.
Megalosaurus was the first dinosaur to be formally described, in 1677, when part of a bone was recovered from a limestone quarry at Cornwell near Oxford, England. This bone fragment was identified correctly as the lower extremity of the femur of an animal larger than anything living in modern times. The second dinosaur species to be identified, Iguanodon, was discovered in 1822 by the English geologist Gideon Mantell, who recognized similarities between his fossils and the bones of modern iguanas. Two years later, the Rev William Buckland, a professor of geology at Oxford University, unearthed more fossilized bones of Megalosaurus and became the first person to describe dinosaurs in a scientific journal.
The study of these "great fossil lizards" soon became of great interest to scientists, and in 1842 the English paleontologist Richard Owen coined the term "dinosaur". He recognized that the remains that had been found so far, Iguanodon, Megalosaurus and Hylaeosaurus, shared a number of distinctive features, and so decided to present them as a distinct taxonomic group. With the backing of Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha, the husband of Queen Victoria, Owen established the Natural History Museum in South Kensington, London, to display the national collection of dinosaur fossils and other biological and geological exhibits.
In 1858, the first known American dinosaur was discovered, in marl pits in the small town of Haddonfield, New Jersey (although fossils had been found before, their nature had not been correctly discerned). The creature was named Hadrosaurus foulkii, after the town and the discoverer, William Parker Foulke. It was an extremely important find; Hadrosaurus was the first nearly complete dinosaur skeleton found and it was clearly a bipedal creature. This was a revolutionary discovery as, until that point, most scientists had believed dinosaurs walked on four feet, like other lizards. Foulke's discoveries sparked a wave of dinosaur mania.

Dinosaur mania was exemplified by the fierce rivalry between Edward Drinker Cope and Othniel Charles Marsh, both of whom raced to be the first to find new dinosaurs in what came to be known as the Bone Wars. The feud probably originated when Marsh publicly pointed out that Cope's reconstruction of an Elasmosaurus skeleton was flawed; Cope had inadvertently placed the plesiosaur's head at what should have been the animal's tail end. The fight between the two scientists lasted for over 30 years, ending in 1897 when Cope died after spending his entire fortune on the dinosaur hunt. Marsh won the contest primarily because he was better funded through a relationship with the US Geological Survey. Unfortunately, many valuable dinosaur specimens were damaged or destroyed due to the pair's rough methods; for example, their diggers often used dynamite to unearth bones (a method modern paleontologists would find appalling). Despite the pair's unrefined methods, their contributions to paleontology were vast; Marsh unearthed 86 new species of dinosaur and Cope discovered 56, for a total of 142 new species. Cope's collection is now at the American Museum of Natural History in New York, while Marsh's is on display at the Peabody Museum of Natural History at Yale University.
Since 1897, the search for dinosaur fossils has extended to every continent, including Antarctica. The first Antarctic dinosaur to be discovered, the ankylosaurid Antarctopelta oliveroi, was found on Ross Island in 1986, although it was 1994 before an Antarctic species, the theropod Cryolophosaurus ellioti, was formally named and described in a scientific journal.
Current dinosaur "hot spots" include southern South America (especially Argentina) and China.
In popular culture
By human standards, dinosaurs were creatures of fantastic appearance and often enormous size. As such, they have captured people's imagination and become an enduring part of human popular culture. Dinosaur exhibitions, parks and museum exhibits around the world both cater to and reinforce the public's interest. The popular preoccupation with dinosaurs is also reflected in a broad array of fictional and non-fictional works.
Notable examples of older fictional works featuring dinosaurs include Arthur Conan Doyle's book The Lost World; the 1933 film King Kong; and Godzilla.
Religious views
Main article: Religious perspectives on dinosaursVarious religious groups have views about dinosaurs that differ from those held by scientists. While many mainstream scientists respect these views as faith positions, they argue that religiously-inspired interpretations of dinosaurs do not withstand serious scientific scrutiny. See the referenced article for specific examples and further context.
See also
- Dinosaur classification
- Fossils
- List of dinosaurs
- Prehistoric life
- Prehistoric reptiles
- Senckenberg Museum - The Senckenberg Museum in Frankfurt, Germany boasts the largest exhibition of large dinosaurs in Europe.
Notes and references
- * Owen, Richard. 1842. "Report on British Fossil Reptiles." Part II. Report of the British Association for the Advancement of Science, Plymouth, England.
- Fountain, Henry. "Many more dinosaurs still to be found." New York Times: 12 Sept. 2006.
- Wang, S.C., and Dobson, P. (2006). Estimating the Diversity of Dinosaurs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 103:37, pp. 13601-13605.
- Dinosaur size varied in different periods Working hypothesis for body size.
- Origin of Dinosaurs and Mammals - Erickson Soruce of Erickson quote.
- Johan Yans, Jean Dejax, Denise Pons, Christian Dupuis, Philippe Taquet.(2005) Palaeontological and geodynamical implications of the palynological dating of the wealden facies sediments of Bernissart (Mons Basin, Belgium). C. R. Palevol 4 (2005) 135–150.
- Deposition of Iguanodon skeletons ocurred in at least 3 different events.
- Day, J.J. and Upchurch, P. (2002). Sauropod Trackways, Evolution, and Behavior. Science 296:1659. See commentary on the article
- Lessem, D. and Glut, D.F. (1993). The Dinosaur Society's Dinosaur Encyclopedia. Random House Inc. ISBN 0-679-41770-2. See commentary on the article
- Juvenile Tyrannosaur A juvenile Tyrannosaur skeleton was found.
- Oviraptor nesting Oviraptor nests or Protoceratops?
- Dinosaur family tracks Footprints show maternal instinct after leaving the nest.
- Joined forever in death The discovery of two fossil dinosaurs entangled together proved many theories.
- Cannibalistic Dinosaur The mystery of a dinosaur cannibal.
- Rogers, R.R., Krause, D.W. and Rogers, K.C. (2003). Cannibalism in the Madagascan dinosaur Majungatholus atopus. Nature 422:515-518.See commentary on the article.
- Gait and Dinosaur speed Gait and his formula on estimating a dinosaur's speed.
- Calculate your own Dinosaur speed More on Gait and his speed calculations.
- Douglas, K. and Young, S. (1998). The dinosaur detectives. New Scientist 2130:24. See commentary on the article.
- Hecht, J. (1998). The deadly dinos that took a dive. New Scientist 2130. See commentary on the article.
- Henderson, D.M. (2003). Effects of stomach stones on the buoyancy and equilibrium of a floating crocodilian: A computational analysis. Canadian Journal of Zoology 81:1346-1357. See commentary on the article.
- Citation for Permian/Triassic extinction event, percentage of animal species that went extinct. See commentary
- Another citation for P/T event data. See commentary
- Hayward, T. (1997). The First Dinosaurs. Dinosaur Cards. Orbis Publishing Ltd. D36040612.
- Sereno, P.C., C.A. Forster, R.R. Rogers, and A.M. Monetta. 1993. Primitive dinosaur skeleton from Argentina and the early evolution of Dinosauria. Nature 361:64-66.
- ^ Dal Sasso, C. and Signore, M. (1998). Exceptional soft-tissue preservation in a theropod dinosaur from Italy. Nature 292:383-387. See commentary on the article
- Schweitzer, M.H., Wittmeyer, J.L. and Horner, J.R. (2005). Soft-Tissue Vessels and Cellular Preservation in Tyrannosaurus rex. Science 307:1952 - 1955. See commentary on the article
- Evans, J. (1998). Ultimate Visual Dictionary - 1998 Edition. Dorling Kindersley Books. 66-69. ISBN 1-871854-00-8.
- Fassett, J, R.A. Zielinski, & J.R. Budahn. (2002). Dinosaurs that did not die; evidence for Paleocene dinosaurs in the Ojo Alamo Sandstone, San Juan Basin, New Mexico. In: Catastrophic events and mass extinctions; impacts and beyond. (Eds. Koeberl, C. & K. MacLeod): Special Paper - Geological Society of America 356: 307-336.
- Wang, H., Yan, Z. and Jin, D. (1997). Reanalysis of published DNA sequence amplified from Cretaceous dinosaur egg fossil. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 14:589-591. See commentary on the article.
- Chang, B.S.W., Jönsson, K., Kazmi, M.A., Donoghue, M.J. and Sakmar, T.P. (2002). Recreating a Functional Ancestral Archosaur Visual Pigment. Molecular Biology and Evolution 19:1483-1489. See commentary on the article.
- Schweitzer, M.H., Wittmeyer, J.L. and Horner, J.R. (2005). Soft-Tissue Vessels and Cellular Preservation in Tyrannosaurus rex. Science 307:1952-1955. Also covers the Reproduction Biology paragraph in the Feathered dinosaurs and the bird connection section. See commentary on the article
- Dong Zhiming (1992). Dinosaurian Faunas of China. China Ocean Press, Beijing. ISBN 3-540-52084-8.
- Williams, P. (1997). The Battle of the Bones. Dinosaur Cards. Orbis Publishing Ltd. D36040607.
General references
- Kevin Padian, and Philip J. Currie. (1997). Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-226810-5. (Articles are written by experts in the field).
- Paul, Gregory S. (2000). The Scientific American Book of Dinosaurs. St. Martin's Press. ISBN 0-312-26226-4.
- Paul, Gregory S. (2002). Dinosaurs of the Air: The Evolution and Loss of flight in Dinosaurs and Birds. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-6763-0.
- Weishampel, David B. (2004). The Dinosauria. University of California Press; 2nd edition. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
External links
Listen to this article(2 parts, 42 minutes)
- For children
- Dinosaur Time Machine from MantyWeb Educational Software From MantyWeb Educational Software. Kid's site, facts, games.
- Dinopedia From Yahooligans! Science. Glossaries, dino cards and indexes.
- Zoom Dinosaurs From Enchanted Learning. Kid's site, info pages, theories, history.
- 30 Dinosaur pictures for painting so the dinos get into your fingers, also for adults.
- Dinosaur Interplanetary Gazette Award-winning online children's science magazine.
- Popular
- Dinosaurs & other extinct creatures From the Natural History Museum. London popular site, well illustrated dino directory.
- Dinosaurs: They Certainly Were Big Humorous educational video about the dinosaur basics.
- Dinosaurnews The Dino-headlines from around the world. Recent news on dinosaurs, including finds and discoveries, lots of links.
- The Dinosaur Lady The Discoveries of Dr. Joan Wiffen, New Zealand's Dinosaur Lady
- History of Dinosaur discovery Timeline of the discovery of Dinosaurs.
- Dinosaurs: Facts and Fiction From the United States Geological Survey. Popular overview.
- Dinosaurs From the BBC. Popular site, very well illustrated.
- Discussions From DinoData. Summaries of modern debates about dinosaurs.
- Dinosauria From UC Berkeley Museum of Paleontology Detailed information - scroll down for menu.
- OPUS: Dinosaur by Daniel Bensen A gallery of dino-paintings.
- Fossilized dinosaurs in mid-battle
- #dinosaurs is an IRC channel on EFnet devoted to the discussion of dinosaurs.
- Technical
- Putting Dinosaurs' Noses Back Where They Really Were
- Prehistoric Planet From PaleoClones. Current dino news.
- A Fiery Death for Dinosaurs? by Amit Asaravala From Wired. Article on the rapid extinction of dinosaurs.
- The Rex Files From the New Scientist. Articles, latest news but out of date.
- Palaeontologia Electronica From Coquina Press. Online technical journal.
- TeV scale gravity, mirror universe, and ... dinosaurs Article from Acta Physica Polonica B by Z.K. Silagadze.
- Very technical
- DinoData Technical site, essays, classification, anatomy.
- Dinosauria On-Line Technical site, essays, pronunciation, dictionary.
- The Dinosauricon By T. Michael Keesey. Technical site, cladogram, illustrations and animations.
- Thescelosaurus! By Justin Tweet. Includes a cladogram and small essays on each relevant genera and species.
- Dinosauromorpha Cladogram From Palaeos. A detailed and wonderful amateur site about all things paleo.
- Dinobase A dinosaur database with dinosaur lists, classification, pictures, and more.
- Planet Dinosaur A very extensive site regarding dinosaur information.
- Bird-dinosaur and dinosaur warm-bloodedness discussion
- DinoBuzz Are birds Dinosaurs?
- Dinosauria Site focusing on the dinosaur-bird relationship.
- Feathered dinosaurs
- Fossilized dinosaur heart
- Fossilized dinosaur eggs and nests
- Dinosaur eggs inside pregnant dinosaur
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: