This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Evolution and evolvability (talk | contribs) at 02:59, 10 June 2018 (→Nutritional value: update from v:WikiJournal_of_Science/Lysine:_biosynthesis,_catabolism_and_roles). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 02:59, 10 June 2018 by Evolution and evolvability (talk | contribs) (→Nutritional value: update from v:WikiJournal_of_Science/Lysine:_biosynthesis,_catabolism_and_roles)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Lysine | |||
| Other names 2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid; 2,6-Diammoniohexanoic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.673 | ||
| IUPHAR/BPS | |||
| KEGG | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C6H14N2O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 146.190 g·mol | ||
| Solubility in water | 1.5 kg/L @ 25 °C | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| ATC code | B05XB03 (WHO) | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Lysine (data page) | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Lysine (symbol Lys or K), encoded by the codons AAA and AAG, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it and thus it must be obtained from the diet.
Lysine is a base, as are arginine and histidine. The ε-amino group often participates in hydrogen bonding and as a general base in catalysis. The ε-ammonium group (NH3) is attached to the fourth carbon from the α-carbon, which is attached to the carboxyl (C=OOH) group.
Common posttranslational modifications include methylation of the ε-amino group, giving methyl-, dimethyl-, and trimethyllysine (the latter occurring in calmodulin); also acetylation, sumoylation, ubiquitination, and hydroxylation – producing the hydroxylysine in collagen and other proteins. O-Glycosylation of hydroxylysine residues in the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus is used to mark certain proteins for secretion from the cell. In opsins like rhodopsin and the visual opsins (encoded by the genes OPN1SW, OPN1MW, and OPN1LW), retinaldehyde forms a Schiff base with a conserved lysine residue, and interaction of light with the retinylidene group causes signal transduction in color vision (See visual cycle for details). Deficiencies may cause blindness, as well as many other problems due to its ubiquitous presence in proteins.
Lysine was first isolated by the German biological chemist Ferdinand Heinrich Edmund Drechsel (1843–1897) in 1889 from the protein casein in milk. He named it "lysin". In 1902, the German chemists Emil Fischer and Fritz Weigert determined lysine's chemical structure by synthesizing it.
Biosynthesis
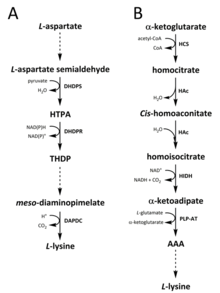
Two different pathways have been identified in nature for the synthesis of lysine. The diaminopimelate (DAP) pathway (Fig. 2A) belongs to the aspartate derived biosynthetic family, which is also involved in the synthesis of threonine, methionine and isoleucine. Whereas the α-aminoadipate (AAA) pathway (Fig. 2B) is part of the glutamate biosynthetic family.
The DAP pathway (Fig. 2A) is found in both prokaryotes and plants and begins with the dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS) (E.C 4.2.1.52) catalysed condensation reaction between the aspartate derived, L-aspartate semialdehyde, and pyruvate to form (4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(2S)-dipicolinic acid (HTPA) (Fig. 2A). The product is then reduced by dihydrodipicolinate reductase (DHDPR) (E.C 1.3.1.26), with NAD(P)H as a proton donor, to yield 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate (THDP) (Fig. 2A). From this point on, there are four pathway variations found in different species, namely the acetylase, aminotransferase, dehydrogenase, and succinylase pathways. Both the acetylase and succinylase variant pathways use four enzyme catalysed steps, the aminotransferase pathway uses two enzymes, and the dehydrogenase pathway uses a single enzyme. These four variant pathways converge at the formation of the penultimate product, meso‑diaminopimelate, which is subsequently enzymatically decarboxylated in an irreversible reaction catalysed by diaminopimelate decarboxylase (DAPDC) (E.C 4.1.1.20) to produce L-lysine (Fig. 2A). The DAP pathway is regulated at multiple levels, including upstream at the enzymes involved in aspartate processing as well as at the initial DHDPS catalysed condensation step. Lysine imparts a strong negative feedback loop on these enzymes and, subsequently, regulates the entire pathway.
The AAA pathway (Fig. 2B) involves the condensation of α-ketoglutarate and acetyl-CoA via the intermediate AAA for the synthesis of L-lysine. This pathway has been shown to be present in several yeast species, as well as protists and higher fungi. It has also been reported that an alternative variant of the AAA route has been found in Thermus thermophilus and Pyrococcus horikoshii, which could indicate that this pathway is more widely spread in prokaryotes than originally proposed. The first and rate-limiting step in the AAA pathway is the condensation reaction between acetyl-CoA and α‑ketoglutarate catalysed by homocitrate-synthase (HCS) (E.C 2.3.3.14) to give the intermediate homocitryl‑CoA, which is hydrolysed by the same enzyme to produce homocitrate (Fig. 2B). Homocitrate is enzymatically dehydrated by homoaconitase (HAc) (E.C 4.2.1.36) to yield cis-homoaconitate. HAc then catalyses a second reaction in which cis-homoaconitate undergoes rehydration to produce homoisocitrate (Fig. 2B). The resulting product undergoes an oxidative decarboxylation by homoisocitrate dehydrogenase (HIDH) (E.C 1.1.1.87) to yield α‑ketoadipate. AAA is then formed via a pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP)-dependent aminotransferase (PLP-AT) (E.C 2.6.1.39), using glutamate as the amino donor (Fig. 2B). From this point on, the AAA pathway differs depending on the kingdom. In fungi, AAA is reduced to α‑aminoadipate-semialdehyde via AAA reductase (E.C 1.2.1.95) in a unique process involving both adenylation and reduction that is activated by a phosphopantetheinyl transferase (E.C 2.7.8.7). Once the semialdehyde is formed, saccharopine reductase (E.C 1.5.1.10) catalyses a condensation reaction with glutamate and NAD(P)H, as a proton donor, and the imine is reduced to produce the penultimate product, saccharopine. The final step of the pathway in fungi involves the saccharopine dehydrogenase (SDH) (E.C 1.5.1.8) catalysed oxidative deamination of saccharopine, resulting in L-lysine. In a variant AAA pathway found in some prokaryotes, AAA is first converted to N‑acetyl-α-aminoadipate, which is phosphorylated and then reductively dephosphorylated to the ε-aldehyde. The aldehyde is then transaminated to N‑acetyl-lysine, which is deacetylated to give L-lysine. However, the enzymes involved in this variant pathway need further validation.
Catabolism
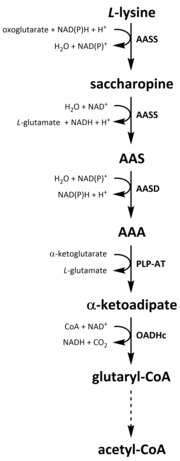
Like all amino acids, catabolism of lysine is initiated from the uptake of dietary lysine or from the breakdown of intracellular protein. Catabolism is also used as a means to control the intracellular concentration of free lysine and maintain a steady-state to prevent the toxic effects of excessive free lysine. There are several pathways involved in lysine catabolism but the most commonly used is the saccharopine pathway (Fig. 3), which primarily takes place in the liver (and equivalent organs) in animals, specifically within the mitochondria. Interestingly, this is the reverse of the previously described AAA pathway (Fig. 2B). In animals and plants, the first two steps of the saccharopine pathway are catalysed by the bifunctional enzyme, α-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase (AASS), which possess both lysine-ketoglutarate reductase (LKR) (E.C 1.5.1.8) and SDH activities, whereas in other organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, both of these enzymes are encoded by separate genes. The first step involves the LKR catalysed reduction of L-lysine in the presence of α-ketoglutarate to produce saccharopine, with NAD(P)H acting as a proton donor (Fig. 3). Saccharopine then undergoes a dehydration reaction, catalysed by SDH in the presence of NAD, to produce AAS and glutamate. AAS dehydrogenase (AASD) (E.C 1.2.1.31) then further dehydrates the molecule into AAA (Fig. 3). Subsequently, PLP-AT catalyses the reverse reaction to that of the AAA biosynthesis pathway, resulting in AAA being converted to α-ketoadipate. The product, α‑ketoadipate, is decarboxylated in the presence of NAD and coenzyme A to yeild glutaryl-CoA, however the enzyme involved in this is yet to be fully elucidated (Fig. 3). Some evidence suggests that the 2-oxoadipate dehydrogenase complex (OADHc), which is structurally homologous to the E1 subunit of the oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (OGDHc) (E.C 1.2.4.2), is responsible for the decarboxylation reaction. Finally, glutaryl-CoA is oxidatively decarboxylated to crotony-CoA by glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase (E.C 1.3.8.6), which goes on to be further processed through multiple enzymatic steps to yield acetyl-CoA; an essential carbon metabolite involved in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA).
Nutritional value
Lysine is one of the nine essential amino acids in humans. The human nutritional requirements varies from ~60 mg·kg in infancy to ~30 mg·kg in adults. This requirement is commonly met in a western society with the intake of lysine from meat and vegetable sources well in excess of the recommended requirement. In vegetarian diets, the intake of lysine is less due to the limiting quantity of lysine in cereal crops compared to meat sources. Given the limiting concentration of lysine in cereal crops, it has long been speculated that the content of lysine can be increased through genetic modification practices. Often these practices have involved the intentional dysregulation of the DAP pathway by means of introducing lysine feedback-insensitive orthologues of the DHDPS enzyme. These methods have met limited success likely due to the toxic side effects of increased free lysine and indirect effects on the TCA cycle. Plants accumulate lysine and other amino acids in the form of seed storage proteins, found within the seeds of the plant, and this represents the edible component of cereal crops. This highlights the need to not only increase free lysine, but also direct lysine towards the synthesis of stable seed storage proteins, and subsequently, increase the nutritional value of the consumable component of crops. Whilst genetic modification practices have met limited success, more traditional selective breeding techniques have allowed for the isolation of ‘Quality Protein Maize’, which has significantly increased levels of lysine (and tryptophan). This increase in lysine content is attributed to an opaque-2 mutation that reduced the transcription of lysine lacking zein related seed storage proteins and, as a result, increased the abundance of other proteins that are rich in lysine. Commonly, to overcome the limiting abundance of lysine in livestock feed, industrially produced lysine is added. The industrial process includes the fermentative culturing of Corynebacterium glutamicum and the subsequent purification of lysine.
Properties
L-Lysine plays a major role in calcium absorption; building muscle protein; recovering from surgery or sports injuries; and the body's production of hormones, enzymes, and antibodies.
Modifications
Lysine can be modified through acetylation (acetyllysine), methylation (methyllysine), ubiquitination, sumoylation, neddylation, biotinylation, pupylation, and carboxylation, which tends to modify the function of the protein of which the modified lysine residue(s) are a part.
Clinical significance
A review cited studies showing that lysine supplementation can decrease herpes simplex cold sore outbreaks and reduce healing time. Original article published at 1978.
However, at 1984 and later the controlled researches don't confirm this for humans and animals.
An authoritative Cochrane Review published in 2015 concluded there is insufficient evidence that lysine supplementation is effective against herpes simplex virus; it has not been approved by the FDA for herpes simplex suppression.
Use of lysine in animal feed
Lysine production for animal feed is a major global industry, reaching in 2009 almost 700,000 tonnes for a market value of over €1.22 billion. Lysine is an important additive to animal feed because it is a limiting amino acid when optimizing the growth of certain animals such as pigs and chickens for the production of meat. Lysine supplementation allows for the use of lower-cost plant protein (maize, for instance, rather than soy) while maintaining high growth rates, and limiting the pollution from nitrogen excretion. In turn, however, phosphate pollution is a major environmental cost when corn is used as feed for poultry and swine.
Lysine is industrially produced by microbial fermentation, from a base mainly of sugar. Genetic engineering research is actively pursuing bacterial strains to improve the efficiency of production and allow lysine to be made from other substrates.
In popular culture
The 1993 film Jurassic Park (based on the 1990 Michael Crichton novel of the same name) features dinosaurs that were genetically altered so that they could not produce lysine. This was known as the "lysine contingency" and was supposed to prevent the cloned dinosaurs from surviving outside the park, forcing them to be dependent on lysine supplements provided by the park's veterinary staff. In reality, no animals are capable of producing lysine (it is an essential amino acid).
Lysine is the favorite amino acid of the character Sheldon Cooper in the television show, The Big Bang Theory. It was mentioned in season 2, episode 13, "The Friendship Algorithm".
In 1996, lysine became the focus of a price-fixing case, the largest in United States history. The Archer Daniels Midland Company paid a fine of US$100 million, and three of its executives were convicted and served prison time. Also found guilty in the price-fixing case were two Japanese firms (Ajinomoto, Kyowa Hakko) and a South Korean firm (Sewon). Secret video recordings of the conspirators fixing lysine's price can be found online or by requesting the video from the U.S. Department of Justice, Antitrust Division. This case served as the basis of the movie The Informant!, and a book of the same title.
The 2002 album Mastered by Guy at The Exchange by Max Tundra features a song called "Lysine".
See also
References
- IUPAC-IUBMB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". Recommendations on Organic & Biochemical Nomenclature, Symbols & Terminology etc. Retrieved 17 May 2007.
- Lysine. The Biology Project, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, University of Arizona.
- Drechsel, E. (1889). "Zur Kenntniss der Spaltungsprodukte des Caseïns" [ to knowledge of the cleavage products of casein]. Journal für Praktische Chemie. 2nd series (in German). 39: 425–429. On p. 428, Drechsel presented an empirical formula for the chloroplatinate salt of lysine – C8H16N2O2Cl2•PtCl4 + H2O – but he later admitted that this formula was wrong because the salt's crystals contained ethanol instead of water. See: Drechsel, E. (1891) "Der Abbau der Eiweissstoffe" , Archiv für Anatomie und Physiologie, 248–278. §2. Drechsel, E. "Zur Kenntniss der Spaltungsproducte des Caseïns" ( to knowledge of the cleavage products of casein), pp. 254–260. From p. 256: " … die darin enthaltene Base hat die Formel C6H14N2O2. Der anfängliche Irrthum ist dadurch veranlasst worden, dass das Chloroplatinat nicht, wie angenommen ward, Krystallwasser, sondern Krystallalkohol enthält, … " ( … the base contained therein has the formula C6H14N2O2. The initial error was caused by the chloroplatinate containing not water in the crystal (as was assumed), but ethanol … )
- Drechsel, E. (1891) "Der Abbau der Eiweissstoffe" , Archiv für Anatomie und Physiologie, 248–278. §4. Fischer, Ernst (1891) "Ueber neue Spaltungsproducte des Leimes" (On new cleavage products of gelatin), pp. 465–469. From p. 469: " … die Base C6H14N2O2, welche mit dem Namen Lysin bezeichnet werden mag, … " ( … the base C6H14N2O2, which may be designated with the name "lysine", … )
- Fischer, Emil; Weigert, Fritz (1902). "Synthese der α,ε – Diaminocapronsäure (Inactives Lysin)" [Synthesis of α,ε-diaminohexanoic acid ( inactive lysine)]. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (in German). 35: 3772–3778.
- ^ Hudson, Andre' O.; Bless, Christine; Macedo, Polliana; Chatterjee, Siba P.; Singh, Bijay K.; Gilvarg, Charles; Leustek, Thomas. "Biosynthesis of lysine in plants: evidence for a variant of the known bacterial pathways". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects. 1721 (1–3): 27–36. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.09.008.
- Velasco, A. M.; Leguina, J. I.; Lazcano, A. (1 October 2002). "Molecular Evolution of the Lysine Biosynthetic Pathways". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 55 (4): 445–449. doi:10.1007/s00239-002-2340-2. ISSN 0022-2844.
- Miyazaki, Takashi; Miyazaki, Junichi; Yamane, Hisakazu; Nishiyama, Makoto (2004). "α-Aminoadipate aminotransferase from an extremely thermophilic bacterium, Thermus thermophilus". Microbiology. 150 (7): 2327–2334. doi:10.1099/mic.0.27037-0.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Xu, Hengyu; Andi, Babak; Qian, Jinghua; West, Ann H.; Cook, Paul F. (1 September 2006). "The α-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis in fungi". Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 46 (1): 43–64. doi:10.1385/cbb:46:1:43. ISSN 1085-9195.
- Atkinson, Sarah C.; Dogovski, Con; Downton, Matthew T.; Czabotar, Peter E.; Dobson, Renwick C. J.; Gerrard, Juliet A.; Wagner, John; Perugini, Matthew A. (1 March 2013). "Structural, kinetic and computational investigation of Vitis vinifera DHDPS reveals new insight into the mechanism of lysine-mediated allosteric inhibition". Plant Molecular Biology. 81 (4–5): 431–446. doi:10.1007/s11103-013-0014-7. ISSN 0167-4412.
- Griffin, Michael D. W.; Billakanti, Jagan M.; Wason, Akshita; Keller, Sabrina; Mertens, Haydyn D. T.; Atkinson, Sarah C.; Dobson, Renwick C. J.; Perugini, Matthew A.; Gerrard, Juliet A. (5 July 2012). "Characterisation of the First Enzymes Committed to Lysine Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana". PLOS ONE. 7 (7): e40318. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040318. ISSN 1932-6203.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Soares da Costa, Tatiana P.; Muscroft-Taylor, Andrew C.; Dobson, Renwick C.J.; Devenish, Sean R.A.; Jameson, Geoffrey B.; Gerrard, Juliet A. "How essential is the 'essential' active-site lysine in dihydrodipicolinate synthase?". Biochimie. 92 (7): 837–845. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.03.004.
- Soares da Costa, Tatiana P.; Christensen, Janni B.; Desbois, Sebastien; Gordon, Shane E.; Gupta, Ruchi; Hogan, Campbell J.; Nelson, Tao G.; Downton, Matthew T.; Gardhi, Chamodi K. Quaternary Structure Analyses of an Essential Oligomeric Enzyme. pp. 205–223. doi:10.1016/bs.mie.2015.06.020.
- Muscroft-Taylor, Andrew C.; Costa, Tatiana P. Soares da; Gerrard, Juliet A. "New insights into the mechanism of dihydrodipicolinate synthase using isothermal titration calorimetry". Biochimie. 92 (3): 254–262. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2009.12.004.
- Christensen, Janni B.; Costa, T. P. Soares da; Faou, Pierre; Pearce, F. Grant; Panjikar, Santosh; Perugini, Matthew A. (15 November 2016). "Structure and Function of Cyanobacterial DHDPS and DHDPR". Scientific Reports. 6 (1). doi:10.1038/srep37111. ISSN 2045-2322.
- McCoy, Andrea J.; Adams, Nancy E.; Hudson, André O.; Gilvarg, Charles; Leustek, Thomas; Maurelli, Anthony T. (21 November 2006). "l,l-diaminopimelate aminotransferase, a trans-kingdom enzyme shared by Chlamydia and plants for synthesis of diaminopimelate/lysine". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 103 (47): 17909–17914. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608643103.
- Hudson, André O.; Gilvarg, Charles; Leustek, Thomas (1 May 2008). "Biochemical and Phylogenetic Characterization of a Novel Diaminopimelate Biosynthesis Pathway in Prokaryotes Identifies a Diverged Form of ll-Diaminopimelate Aminotransferase". Journal of Bacteriology. 190 (9): 3256–3263. doi:10.1128/jb.01381-07. ISSN 0021-9193. PMID 18310350.
- Peverelli, Martin G.; Perugini, Matthew A. "An optimized coupled assay for quantifying diaminopimelate decarboxylase activity". Biochimie. 115: 78–85. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2015.05.004.
- ^ Soares da Costa, Tatiana P.; Costa, Tatiana P. Soares da; Desbois, Sebastien; Dogovski, Con; Gorman, Michael A.; Ketaren, Natalia E.; Paxman, Jason J.; Siddiqui, Tanzeela; Zammit, Leanne M. "Structural Determinants Defining the Allosteric Inhibition of an Essential Antibiotic Target". Structure. 24 (8): 1282–1291. doi:10.1016/j.str.2016.05.019.
{{cite journal}}: no-break space character in|last=at position 10 (help) - ^ Jander, Georg; Joshi, Vijay (1 January 2009). "Aspartate-Derived Amino Acid Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana". The Arabidopsis Book: e0121. doi:10.1199/tab.0121.
- Andi, Babak; West, Ann H.; Cook, Paul F. (1 September 2004). "Kinetic Mechanism of Histidine-Tagged Homocitrate Synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Biochemistry. 43 (37): 11790–11795. doi:10.1021/bi048766p. ISSN 0006-2960.
- Bhattacharjee, J. K. (1985). "alpha-Aminoadipate pathway for the biosynthesis of lysine in lower eukaryotes". Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 12 (2): 131–151. doi:10.3109/10408418509104427. ISSN 1040-841X. PMID 3928261.
- Bhattacharjee, J. K.; Strassman, M. (25 May 1967). "Accumulation of tricarboxylic acids related to lysine biosynthesis in a yeast mutant". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 242 (10): 2542–2546. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 6026248.
- GAILLARDIN, Claude M.; RIBET, Anne-Marie; HESLOT, Henri. "Wild-Type and Mutant Forms of Homoisocitric Dehydrogenase in the Yeast Saccharomycopsis lipolytica". European Journal of Biochemistry. 128 (2–3): 489–494. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06991.x.
- Jaklitsch, W. M.; Kubicek, C. P. (1 July 1990). "Homocitrate synthase from Penicillium chrysogenum. Localization, purification of the cytosolic isoenzyme, and sensitivity to lysine". The Biochemical Journal. 269 (1): 247–253. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1131560. PMID 2115771.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - Ye, Z. H.; Bhattacharjee, J. K. (1 December 1988). "Lysine biosynthesis pathway and biochemical blocks of lysine auxotrophs of Schizosaccharomyces pombe". Journal of Bacteriology. 170 (12): 5968–5970. doi:10.1128/jb.170.12.5968-5970.1988. ISSN 0021-9193. PMID 3142867.
- Kobashi, N.; Nishiyama, M.; Tanokura, M. (March 1999). "Aspartate kinase-independent lysine synthesis in an extremely thermophilic bacterium, Thermus thermophilus: lysine is synthesized via alpha-aminoadipic acid not via diaminopimelic acid". Journal of Bacteriology. 181 (6): 1713–1718. ISSN 0021-9193. PMID 10074061.
- Kosuge, T.; Hoshino, T. (1999). "The alpha-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis is widely distributed among Thermus strains". Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 88 (6): 672–675. ISSN 1389-1723. PMID 16232683.
- ^ Nishida, H. "A Prokaryotic Gene Cluster Involved in Synthesis of Lysine through the Amino Adipate Pathway: A Key to the Evolution of Amino Acid Biosynthesis". Genome Research. 9 (12): 1175–1183. doi:10.1101/gr.9.12.1175.
- ^ Nishida, H.; Nishiyama, M. (September 2000). "What is characteristic of fungal lysine synthesis through the alpha-aminoadipate pathway?". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 51 (3): 299–302. ISSN 0022-2844. PMID 11029074.
- Zabriskie, T. Mark; Jackson, Michael D. (1 January 2000). "Lysine biosynthesis and metabolism in fungi". Natural Product Reports. 17 (1): 85–97. doi:10.1039/a801345d. ISSN 1460-4752.
- ^ Zhu, Xiaohong; Galili, Gad (1 May 2004). "Lysine Metabolism Is Concurrently Regulated by Synthesis and Catabolism in Both Reproductive and Vegetative Tissues". Plant Physiology. 135 (1): 129–136. doi:10.1104/pp.103.037168. ISSN 0032-0889. PMID 15122025.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Blemings, K. P.; Crenshaw, T. D.; Swick, R. W.; Benevenga, N. J. (August 1994). "Lysine-alpha-ketoglutarate reductase and saccharopine dehydrogenase are located only in the mitochondrial matrix in rat liver". The Journal of Nutrition. 124 (8): 1215–1221. ISSN 0022-3166. PMID 8064371.
- Galili, Gad; Tang, Guiliang; Zhu, Xiaohong; Gakiere, Bertrand. "Lysine catabolism: a stress and development super-regulated metabolic pathway". Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 4 (3): 261–266. doi:10.1016/s1369-5266(00)00170-9.
- Arruda, Paulo; Kemper, Edson L; Papes, Fabio; Leite, Adilson. "Regulation of lysine catabolism in higher plants". Trends in Plant Science. 5 (8): 324–330. doi:10.1016/s1360-1385(00)01688-5.
- Sacksteder, Katherine A.; Biery, Barbara J.; Morrell, James C.; Goodman, Barbara K.; Geisbrecht, Brian V.; Cox, Rody P.; Gould, Stephen J.; Geraghty, Michael T. "Identification of the α-Aminoadipic Semialdehyde Synthase Gene, Which Is Defective in Familial Hyperlysinemia". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 66 (6): 1736–1743. doi:10.1086/302919.
- Zhu, Xiaohong; Tang, Guiliang; Galili, Gad (20 December 2002). "The Activity of the Arabidopsis Bifunctional Lysine-ketoglutarate Reductase/Saccharopine Dehydrogenase Enzyme of Lysine Catabolism Is Regulated by Functional Interaction between Its Two Enzyme Domains". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (51): 49655–49661. doi:10.1074/jbc.m205466200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12393892.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Kiyota, Eduardo; Pena, Izabella Agostinho; Arruda, Paulo (November 2015). "The saccharopine pathway in seed development and stress response of maize". Plant, Cell & Environment. 38 (11): 2450–2461. doi:10.1111/pce.12563. ISSN 1365-3040. PMID 25929294.
- Serrano, Guilherme Coutinho de Mello; Rezende e Silva Figueira, Thaís; Kiyota, Eduardo; Zanata, Natalia; Arruda, Paulo (23 March 2012). "Lysine degradation through the saccharopine pathway in bacteria: LKR and SDH in bacteria and its relationship to the plant and animal enzymes". FEBS letters. 586 (6): 905–911. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.02.023. ISSN 1873-3468. PMID 22449979.
- ^ Danhauser, Katharina; Sauer, Sven W.; Haack, Tobias B.; Wieland, Thomas; Staufner, Christian; Graf, Elisabeth; Zschocke, Johannes; Strom, Tim M.; Traub, Thorsten. "DHTKD1 Mutations Cause 2-Aminoadipic and 2-Oxoadipic Aciduria". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 91 (6): 1082–1087. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.10.006.
- Sauer, Sven W.; Opp, Silvana; Hoffmann, Georg F.; Koeller, David M.; Okun, Jürgen G.; Kölker, Stefan (1 January 2011). "Therapeutic modulation of cerebral l-lysine metabolism in a mouse model for glutaric aciduria type I". Brain. 134 (1): 157–170. doi:10.1093/brain/awq269. ISSN 0006-8950.
- Goncalves, Renata L.S.; Bunik, Victoria I.; Brand, Martin D. "Production of superoxide/hydrogen peroxide by the mitochondrial 2-oxoadipate dehydrogenase complex". Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 91: 247–255. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.12.020.
- Goh, Denise L.M; Patel, Ankita; Thomas, George H; Salomons, Gajja S; Schor, Danielle S.M; Jakobs, Cornelis; Geraghty, Michael T. "Characterization of the human gene encoding α-aminoadipate aminotransferase (AADAT)". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 76 (3): 172–180. doi:10.1016/s1096-7192(02)00037-9.
- Härtel, Ulrich; Eckel, Elke; Koch, Jürgen; Fuchs, Georg; Linder, Dietmar; Buckel, Wolfgang (1 February 1993). "Purification of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas sp., an enzyme involved in the anaerobic degradation of benzoate". Archives of Microbiology. 159 (2): 174–181. doi:10.1007/bf00250279. ISSN 0302-8933.
- Sauer, S. W. (October 2007). "Biochemistry and bioenergetics of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency". Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 30 (5): 673–680. doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0678-8. ISSN 1573-2665. PMID 17879145.
- Cite error: The named reference
:3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Wang, Guoping; Xu, Mengyun; Wang, Wenyi; Galili, Gad (19 June 2017). "Fortifying Horticultural Crops with Essential Amino Acids: A Review". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 18 (6): 1306. doi:10.3390/ijms18061306.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Angelovici, Ruthie; Fait, Aaron; Fernie, Alisdair R.; Galili, Gad (January 2011). "A seed high-lysine trait is negatively associated with the TCA cycle and slows down Arabidopsis seed germination". The New Phytologist. 189 (1): 148–159. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03478.x. ISSN 1469-8137. PMID 20946418.
- Edelman, Marvin; Colt, Monica (2016). "Nutrient Value of Leaf vs. Seed". Frontiers in Chemistry. 4. doi:10.3389/fchem.2016.00032. ISSN 2296-2646.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Jiang, Shu-Ye; Ma, Ali; Xie, Lifen; Ramachandran, Srinivasan (28 September 2016). "Improving protein content and quality by over-expressing artificially synthetic fusion proteins with high lysine and threonine constituent in rice plants". Scientific Reports. 6 (1). doi:10.1038/srep34427. ISSN 2045-2322.
- ^ Shewry, Peter R. "Improving the protein content and composition of cereal grain". Journal of Cereal Science. 46 (3): 239–250. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2007.06.006.
- Prasanna, B. M.; Vasal, S. K.; Kassahun, B.; Singh, N. N. (2001). "Quality protein maize". Current Science. 81 (10): 1308–1319.
- ^ Kircher, Manfred; Pfefferle, Walter. "The fermentative production of l-lysine as an animal feed additive". Chemosphere. 43 (1): 27–31. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(00)00320-9.
- Junior, Letti; Alberto, Luiz; Letti, Gilberto Vinícius Melo; Soccol, Carlos Ricardo; Junior, Letti; Alberto, Luiz; Letti, Gilberto Vinícius Melo; Soccol, Carlos Ricardo (00/2016). "Development of an L-Lysine Enriched Bran for Animal Nutrition via Submerged Fermentation by Corynebacterium glutamicum using Agroindustrial Substrates". Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology. 59. doi:10.1590/1678-4324-2016150519. ISSN 1516-8913.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Sadoul K, Boyault C, Pabion M, Khochbin S (February 2008). "Regulation of protein turnover by acetyltransferases and deacetylases". Biochimie. 90 (2): 306–12. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2007.06.009. PMID 17681659.
- Gaby AR (2006). "Natural remedies for Herpes simplex". Altern Med Rev. 11 (2): 93–101. PMID 16813459.
- Griffith RS, Norins AL, Kagan C. (1978). "A multicentered study of lysine therapy in Herpes simplex infection". Dermatologica. 156 (5): 257–267. doi:10.1159/000250926. PMID 640102.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - John J. DiGiovanna, MD; Harvey Blank, MD (1984). "Failure of Lysine in Frequently Recurrent Herpes Simplex Infection: Treatment and Prophylaxis". Dermatology. 120 (1): 48–51. doi:10.1001/archderm.1984.01650370054010. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Sebastiaan Bol, Evelien M Bunnik (2015). "Lysine supplementation is not effective for the prevention or treatment of feline herpesvirus 1 infection in cats: A systematic review". BMC Veterinary Research. 11 (1): 284. doi:10.1186/s12917-015-0594-3.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Ching-Chi Chi1, Shu-Hui Wang, Finola M Delamere, Fenella Wojnarowska, Mathilde C Peters, Preetha P Kanjirath (2015). "Interventions for prevention of herpes simplex labialis (cold sores on the lips)". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (8): CD010095. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010095.pub2. PMID 26252373. CD010095.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Drugs.com. "Herpes Simplex, Suppression Medications". Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "AllAboutFeed – News: Norwegian granted for improving lysine production process". archive.org. 11 March 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- Toride Y. "Lysine and other amino acids for feed: production and contribution to protein utilization in animal feeding". Retrieved 25 January 2011.
- Abelson, Philip (March 1999). "A Potential Phosphate Crisis". Science. 283 (5410): 2015. doi:10.1126/science.283.5410.2015. PMID 10206902.
- Coyne, Jerry A. (10 October 1999). "The Truth Is Way Out There". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- Wu, G (2009). "Amino acids: Metabolism, functions, and nutrition". Amino Acids. 37 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1007/s00726-009-0269-0. PMID 19301095.
- M3ta1 (28 February 2011). "Sheldon's Favourite Amino Acid". Retrieved 14 April 2018 – via YouTube.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Connor, J.M.; "Global Price Fixing" 2nd Ed. Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, 2008. ISBN 978-3-540-78669-6.
- Eichenwald, Kurt.; "The Informant: a true story" Broadway Books: New York, 2000. ISBN 0-7679-0326-9.
Sources
- Much of the information in this article has been translated from German Misplaced Pages.
- Lide, D. R., ed. (2002). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (83rd ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0483-0.
| Encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General topics |  | ||||||||||
| By properties |
| ||||||||||

