This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Moalli (talk | contribs) at 07:55, 10 February 2021 (The Encyclopedia of Bilingualism source lists German and Portuguese as world languages; these two are also widely used in international affairs and outside national/ethnic lines). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 07:55, 10 February 2021 by Moalli (talk | contribs) (The Encyclopedia of Bilingualism source lists German and Portuguese as world languages; these two are also widely used in international affairs and outside national/ethnic lines)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
A world language is one that is spoken internationally and learned and spoken by numerous people as a second language. A world language is characterized not only by the total number of speakers (native and second language speakers) but also by geographical distribution and its use in international organizations and diplomatic relations.
English is the foremost—and by some accounts only—world language. French is also a world language. Beyond that, there is no academic consensus about which languages qualify; other possible world languages include, Spanish, Arabic, Russian, and Standard Chinese.
Overview
Asian languages
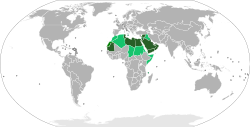
Arabic
Arabic gained international prominence because of the medieval Islamic conquests and the subsequent Arabization of the Middle East and North Africa, and it is also a liturgical language amongst Muslim communities outside the Arab World.
Chinese
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese or Standard Northern Mandarin is the direct replacement of Classical Chinese, which was a historical lingua franca in East Asia, also referred to academically as the East Asian cultural sphere in terms of culture, until the early 20th century, and today serves as a common language between speakers of other varieties of Chinese not only within China proper (between the Han Chinese and other unrelated ethnic groups), but in overseas Chinese communities. It is also widely taught as a second language internationally. Standard Mandarin is also an official language in many international organizations such as the United Nations, ASEAN, and the Shanghai Pact, etc.
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese used to be a historical common language in East Asia or the Sinosphere. It was usually used as a written language in official documents and letters.
European languages
English
In addition to 370 million native speakers, English is estimated to have over 610 million second-language speakers, including anywhere between 200 and 350 million learners/users in China alone, at varying levels of study and proficiency, though this number is difficult to accurately assess. English is also increasingly becoming the dominant language of scientific research and papers worldwide, having even outpaced national languages in Western European countries, including France, where a recent study showed that English has massively displaced French as the language of scientific research in "hard" as well as in applied sciences. It is the most common of the languages used on the Internet. As of 2019, according to one survey, English is used by 54% of the world's top 10 million websites, and according to another survey, 25.5% of all Internet users are English speakers.
French
During the 19th and early 20th centuries, French was the language of communication and diplomacy, and the favoured second language among the elite and the educated classes in Europe (including Russia, Romania, Bulgaria, and Greece) — as well as in many Middle East and North African countries such as Syria, Egypt, Ottoman Turkey and Iran. In addition, French enjoyed high status in its colony in Indochina, and in several South American ones like Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Uruguay. However, French has declined steadily since World War I, being gradually displaced by English - although in Lebanon, Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco, French continues to be the favoured second language, as well as enjoying co-official status in Canada, Switzerland and Belgium. Moreover, French still remains one of the working languages of many international organizations, including the United Nations, NATO, European Union and NAFTA. French is the principal working language of the European Court of Justice. French is also internationally recognized to be of high linguistic prestige, still used in diplomacy and international commerce, as well as having a significant portion of second language speakers throughout the world.
German
German is the most spoken native language in the European Union and one of the three "procedural languages" of its institutions alongside English and French. It also historically, and to some extent still serves, as a lingua franca throughout much of Eastern and Northern Europe, as well as the former African colony of Namibia. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, German (along with English) has also been increasingly favored over Russian as a popular first foreign language in many former Soviet states and is the second most learned language in Russia itself.
Within the international scientific community and in technology, it is used as a major working language. As of 2019, it is the third most commonly used language for website content, with 5.8% of the world's top 10 million websites using it, and 2.1% of all Internet users are German speakers.
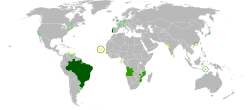
Portuguese
Portuguese is the sole official language of Portugal, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde, São Tomé and Príncipe, and Brazil while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau.
Russian
Russian is the largest native language in Europe, the most geographically widespread language in Eurasia, one of the six official languages of the United Nations, and one of two official languages aboard the International Space Station. As of 2019, it is the second most commonly used language for website content, with 5.9% of the world's top 10 million websites using it, and 2.5% of all Internet users are Russian speakers.
Russian was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, and its teaching was made compulsory in the Eastern Bloc countries. However, the use and teaching of Russian has declined sharply in both the former Eastern bloc and the near abroad since the break up of the Soviet Union and Russia's deputy education minister was quoted as saying in December 2013 that the number of Russian speakers had fallen by 100 million since that date. It is still widely spoken throughout the Caucasus, Central Asia, Eastern Europe and the Baltic states.
Spanish
Spanish is the world's second-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese. Spanish was used in the Spanish Empire and today is in use in Spain, in Latin American countries (except Brazil, French Guiana and Haiti), and is widely spoken in many parts of the United States, particularly in Florida and the states that border Mexico. As of 2011, around 13% of the US population spoke Spanish fluently. Indeed, by 2016 Spanish was the most widely taught non-English language in American secondary schools and schools of higher education. It is also an official language of the United Nations. As of 2019, Spanish had the third-largest number of internet users by language with 7.9%, after English with 25.2% and Chinese with 19.3%.
Properties
Some sources define a living world language as having the following properties:
- numerous speakers
- a substantial fraction of non-native speakers (function as lingua franca)
- official status in several countries
- use across several regions in the world
- a linguistic community not defined strictly along ethnic lines (multiethnic, pluricentric language)
- one or more standard registers which are widely taught as a foreign language
- association with linguistic prestige
- use in international trade relations
- use in international organizations
- use in the academic community
- significant body of literature
Living world languages
Languages which are often considered world languages include:
| Language | Family | Branch | Writing system | First language (L1) | Second language (L2) | Total No. of speakers |
Geographical distribution | Official status distribution | Global distribution map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Indo-European | Germanic | English (Latin) alphabet | 369.7 million | 898.4 million | 1.268 billion | Geographical distribution of English speakers | List of territorial entities where English is an official language | 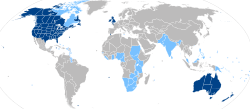
|
| French | Indo-European | Romance | French (Latin) alphabet | 77.3 million | 199.3 million | 276.6 million | Geographical distribution of French speakers | List of territorial entities where French is an official language | 
|
Other sources denote the following languages as world languages, whilst stricter sources list them only as supra-regional languages:
See also
- Global language system
- International auxiliary language
- International English
- Lingua franca
- List of languages by number of native speakers
- List of languages by total number of speakers
- National language
- Translanguaging
- Universal language
- World economy
- World Englishes
- World population
- World religion
Notes
- ^ In contrast to other pluricentric languages (e.g., Arabic or Malay), Ethnologue only lists "Standard German", thereby excluding Swiss German and numerous other varieties of German. Summing up Standard German as well as all undisputed German dialects/varieties (see ISO-list in infobox at German language) that are not listed under "Standard German" results in ca. 90 M native speakers. Furthermore, Ammon (2014) points out that Ethnologue overestimates L2 speakers, thus underestimating L1 speakers, in Germany by 5M --> 95M L1 speakers.
References
- ^ Fischer Weltalmanach. S. Fischer Verlag. Archived from the original on September 4, 2009.
- ^ Baker, Colin; Jones, Sylvia Prys (1998). Encyclopedia of Bilingualism and Bilingual Education. Multilingual Matters. ISBN 9781853593628 https://books.google.com/books?id=YgtSqB9oqDIC.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - https://ask.un.org/faq/14463
- Benrabah, Mohamed (2014-01-02). "Competition between four "world" languages in Algeria". Journal of World Languages. 1 (1): 38–59. doi:10.1080/21698252.2014.893676. ISSN 2169-8252.
- Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Wei, Rining; Jinzhi Su (2012). "The statistics of English in China". English Today. 28 (3): 10–14. doi:10.1017/s0266078412000235.
- Crystal, David (2006). "9 - English worldwide". In Hogg, Richard; Denison, David (eds.). A History of the English Language. Cambridge University Press. pp. 420–439.
- Héran, François (June 2013). "No English please! Survey on the languages used for research and teaching in France" (PDF). Population & Sociétés (501).
- ^ "Usage Statistics of Content Languages for Websites". W3Techs. Retrieved July 14, 2019.
- ^ "Number of Internet Users by Language". Internet World Stats. Retrieved 2019-07-14.
- "Official Languages". United Nations. Retrieved 2016-10-29.
- "European Commission - Press releases - Frequently asked questions on languages in Europe". europa.eu. Retrieved 2017-03-11.
- ^ von Polenz 1999, pp. 192–194, 196. sfn error: no target: CITEREFvon_Polenz1999 (help)
- Singer, Marshall. Language Follows Power: The Linguistic Free Market in the Old Soviet Bloc, Foreign Policy, Jan 1998.
- "Russian: Eurasia's Most Geographically Widespread Language". Day Translations Blog. 4 August 2014.
- Blank, Stephen (9 January 2015). "Russia's Waning Soft Power in Central Asia". The Diplomat.
- "Kyrgyzstan's Russian-Language Teaching Getting Squeezed Out". Eurasianet. 15 December 2014.
- Brooke, James (17 October 2012). "English Replaces Russian as Top Foreign Language of Study in Ex-Soviet Georgia". VOA News.
- Language Use in the United States: 2011 (Table 3, p.9). Census.gov.
- Goldberg, David; Looney, Dennis; Lusin, Natalia (February 2019), Enrollments in Languages Other Than English in United States Institutions of Higher Education, Summer 2016 and Fall 2016: Preliminary Report (PDF), Modern Language Association of America, retrieved March 4, 2019
- "What Is a World Language? (with pictures)". wisegeek.com.
- Wallraff, Barbara. "What Global Language?".
- Ammon, Ulrich (1989). Status and Function of Languages and Language Varieties. W. de Gruyter. ISBN 9780899253565.
- Mazrui, Ali AlʼAmin (1976). A World Federation of Cultures: An African Perspective. Free Press.
- "Summary by language size". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2019-03-01.
- English at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- French at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- "Summary by language size". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2019-03-01.
- Spanish at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- Arabic at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- Russian at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- https://blog.lingoda.com/en/most-spoken-languages-in-the-world-in-2020
- Chinese at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- Portuguese at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- German, Standard at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

- Ammon, Ulrich - Die Stellung der deutschen Sprache in der Welt (de Gruyter Mouton; ISBN 978-3-11-019298-8)