This is an old revision of this page, as edited by VaudevillianScientist (talk | contribs) at 05:41, 16 July 2022 (added Category:Iodides using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 05:41, 16 July 2022 by VaudevillianScientist (talk | contribs) (added Category:Iodides using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)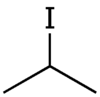
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Iodopropane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 1098244 |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.782 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | isopropyl+iodide |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2392 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H7I |
| Molar mass | 169.993 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.703 g mL |
| Melting point | −90.00 °C; −130.00 °F; 183.15 K |
| Boiling point | 88.8 to 89.8 °C; 191.7 to 193.5 °F; 361.9 to 362.9 K |
| Solubility in water | 1.4 g L (at 12.5 °C) |
| Solubility in chloroform | Miscible |
| Solubility in ethanol | Miscible |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | Miscible |
| Solubility in benzene | Miscible |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
890 nmol Pa kg |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4997 |
| Viscosity | 6.971 mPa (at 20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 137.3 J K mol |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−77.2–−72.6 kJ mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H302 |
| Flash point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanes | |
| Related compounds | Diiodohydroxypropane |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Isopropyl iodide is the organoiodine compound with the formula (CH3)2CHI. It is colorless, flammable, and volatile. Organic iodides are light-sensitive and take on a yellow colour upon storage, owing to the formation of iodine.
Preparation
Isopropyl iodide is prepared by iodination of isopropyl alcohol using hydrogen iodide or, equivalently, with a mixture of glycerol, iodine, and phosphorus. An alternative preparation involves the reaction of 2-propyl bromide with an acetone solution of sodium iodide (Finkelstein reaction):
- (CH3)2CHBr + NaI → (CH3)2CHI + NaBr
References
- "isopropyl iodide - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 3 March 2012.
- Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs, 9th ed., monograph 5074
- Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall, 1989
This article about an organic halide is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |