This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Slof (talk | contribs) at 01:06, 24 March 2007 (→Law and government: refs). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:06, 24 March 2007 by Slof (talk | contribs) (→Law and government: refs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)- "Salt Lake City" redirects here. For similarly named places, see Salt Lake (disambiguation).
| Salt Lake City, Utah | |
|---|---|
| File:092102 03.jpg | |
| Nickname(s): Crossroads of the West, SLC | |
 Location of Salt Lake City in Salt Lake County, Utah Location of Salt Lake City in Salt Lake County, Utah | |
| County | Salt Lake |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Rocky Anderson |
| Elevation | 1,288 m (4,226 ft) |
| Population | |
| • City | 181,743 |
| • Metro | 1,005,232 |
| Time zone | UTC-7 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-6 (Mountain) |
| Website | http://www.slcgov.com |
Salt Lake City is the capital and the most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. The name of the city is often shortened to Salt Lake, or its initials, S.L.C. It was originally known as Great Salt Lake City.
Salt Lake City has a population of 178,097. The Salt Lake City metropolitan area spans Salt Lake, Summit and Tooele counties, and has a total estimated population of 1,034,484. Salt Lake City is further situated in a larger urban area known as the Wasatch Front, and until 2003 the Ogden-Clearfield metro area within it was considered part of the Salt Lake City metropolitan area. The total estimated population of the Wasatch Front is approximately 2,150,017.
The city was founded in 1847 by a group of Mormon pioneers led by their prophet, Brigham Young, who fled hostility from the midwest. Salt Lake City is now the headquarters of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (the L.D.S. or Mormon Church).
Mining booms and the construction of the first transcontinental railroad initially brought economic growth, and the city became nicknamed the Crossroads of the West. In the 21st century the city has developed a strong outdoor recreation industry, become the industrial banking center of the U.S, and served as host to the 2002 Winter Olympics.
History
Main article: History of Salt Lake CityBefore Western settlement, the Shoshone, Ute, and Paiute had dwelled in the Salt Lake Valley for thousands of years. However, these tribes dwelt only on a temporary basis near streams emptying from Canyons into the Salt Lake Valley. The first Caucasian in the Salt Lake area is believed to be the explorer Jim Bridger in 1825, although other Caucasians had been in Utah earlier, some as far north as the nearby Utah Valley. U.S. Army officer John C. Frémont surveyed the Great Salt Lake and the Salt Lake Valley in 1843 and 1845. The Donner party, a group of ill-fated pioneers, had traveled through the Great Salt Lake Valley in August 1846.
The first Europeans to settle in the valley were the Latter-day Saints on July 24, 1847. They had traveled beyond the boundaries of the United States seeking an isolated area to practice their religion, away from the hostility they had faced in the East. Upon arrival, President of the Church Brigham Young is recorded as stating, "this is the right place," later abbreviated to simply "this is the place," after reportedly seeing the area in a vision. They found the large valley empty of any human settlement.
Only four days after arriving in the Salt Lake Valley, Brigham Young designated the site for the Salt Lake Temple, the third temple of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Constructed on Temple Square, in the center of the city, the temple took 40 years to complete, being started in 1853 and dedicated on April 6, 1893. The temple has become iconic of the city.
The Mormon pioneers organized a new state called Deseret and petitioned for its recognition in 1849. The United States Congress rebuffed the settlers in 1850 and established the Utah Territory, vastly reducing its size (it formerly encompassed all of Nevada and a great deal of southern California). Great Salt Lake City replaced Fillmore as the territorial capital in 1858, and the name was subsequently abbreviated to Salt Lake City. The city's population swelled with an influx of religious converts, making it one of the most populous cities in the American Old West.
Disputes with the federal government ensued over the widespread Mormon practice of polygamy. A climax occurred in 1857 when President James Buchanan declared the area in rebellion after Brigham Young refused to step down as governor, beginning the Utah War. A division of the United States Army, commanded by Albert Sidney Johnston, later a general in the army of the Confederate States of America, marched through the city and found that it had been evacuated. This division set up Camp Floyd approximately 40 miles (65 km) southwest of the city. Another military installation, Fort Douglas, was established in 1862 to maintain Union allegiance during the American Civil War. Many area leaders were incarcerated at the territorial prison in Sugar House in the 1880s for violation of anti-polygamy laws. The LDS Church conceded in 1890, releasing "The Manifesto," which officially renounced polygamy in the church. This paved the way for statehood in 1896, when Salt Lake City became the state capital.
The First Transcontinental Railroad was completed in 1869 at Promontory Summit on the north side of the Great Salt Lake. A railroad was connected to the city from the Transcontinental Railroad in 1870, making travel less burdensome. Mass migration of different groups followed. They found economic opportunities in the booming mining industries. These groups constructed the Greek Orthodox Holy Trinity Cathedral in 1905 and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of the Madeleine in 1909. This time period also saw the creation of Salt Lake City's now defunct Red-light district that employed 300 courtesans at its height before being closed down in 1911.
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, an extensive streetcar system was constructed throughout the city with the first streetcar running in 1872 and electrification of the system in 1889. As in the rest of the country, the automobile usurped the streetcar and the last trolley ran in 1945. Rail transit was re-introduced when TRAX, a light rail system, opened in 1999.
The city's population began to stagnate during the 20th century as population growth shifted to suburban areas north and south of the city. Few of these areas were annexed to the city, while nearby towns incorporated and expanded themselves. As a result, the population of the surrounding metropolitan area greatly outnumbers that of Salt Lake City. A major concern of recent government officials has been combating inner-city commercial decay. The city lost population from the 1960s through the 1980s, but experienced some recovery in the 1990s. Presently, the city is losing population again (though that of the metro area continues to grow), having lost an estimated 2 percent of its population since the year 2000.
The city has experienced significant demographic shifts in recent years. Hispanics now account for approximately 19% of residents and the city has a large gay community. There is also a large Pacific Islander population, mainly made up of Samoans and Tongans; they compose roughly 1% of the population of the Salt Lake Valley area.
 In the past 20 years the skyline of Salt Lake City has expanded greatly. Picture taken in 2004.
In the past 20 years the skyline of Salt Lake City has expanded greatly. Picture taken in 2004.
Salt Lake City was selected to host the 2002 Winter Olympics in 1995. The games were plagued with controversy. A bid scandal surfaced in 1998 alleging that bribes had been offered to secure the city for the 2000 games location. During the games, other scandals erupted over contested judging scores and illegal drug use. Despite the controversies, the games were heralded as a financial success, being one of the few in recent history to profit. In preparation major construction projects were initiated. Local freeways were expanded and repaired, and a light rail system was constructed. Olympic venues are now used for local, national, and international sporting events and Olympic athlete training. Tourism has increased since the Olympic games, but business did not pick up immediately following them.
Salt Lake City hosted the 16th Winter Deaflympic games in 2007, taking place in the venues in Salt Lake City and Park City, and Rotary International has designated the city as the site of their 2007 convention, which will be the largest single gathering since the 2002 Winter Olympics. The U.S. Volleyball Association convention in 2005 drew 39,500 attendees.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Salt Lake City The Salt Lake Valley urban area, called the Wasatch Front.
The Salt Lake Valley urban area, called the Wasatch Front.


Salt Lake City is located at 40°45′N 111°53′W / 40.750°N 111.883°W / 40.750; -111.883. The total area is 110.4 square miles (285.9 km²) and has an average elevation of 4,327 feet (1,320 m) above sea level. The lowest point within the boundaries of the city is 4,210 feet near the Jordan River and the Great Salt Lake, and the highest is Grandview Peak, at 9,410 feet.
The city is located in the northeast corner of the Salt Lake Valley surrounded by the Great Salt Lake to the northwest, and the steep Wasatch and Oquirrh mountain ranges, on the eastern and western border respectively. Its encircling mountains contain many narrow glacially and volcanically carved canyons, among them City Creek, Emigration, Millcreek, and Parley's border Salt Lake proper.
The Great Salt Lake is separated from Salt Lake City by extensive marshlands and mudflats. The decomposition of plants and animals in the lake results in a phenomenon known as "lake stink", a scent reminiscent of foul poultry eggs, two to three times per year for a few hours. The Jordan River flows through the city and is a drainage of Utah Lake that empties into the Great Salt Lake.
The highest mountaintop visible from Salt Lake City is Twin Peaks, which reaches 11,489 feet (3502 m). Twin Peaks is located southeast of Salt Lake in the Wasatch Range. The Wasatch Fault is found along the western base of the Wasatch and is considered overdue for an earthquake as large as 7.5. Catastrophic damage is predicted in the event of an earthquake with major damage resulting from the liquefaction of the clay- and sand-based soil and the possible permanent flooding of portions of the city by the Great Salt Lake.
The second-highest mountain range are the Oquirrhs, reaching a maximum height of 10,620 feet (3,237 m) at Flat Top. The Traverse Mountains to the south extend to 6,000 feet (1,830 m), nearly connecting the Wasatch and Oquirrh Mountains. The mountains near Salt Lake City are easily visible from the city and have sharp vertical relief caused by massive ancient earthquakes, with a maximum difference of 7,099 feet (2164 m) being achieved with the rise of Twin Peaks from the Salt Lake Valley floor.
The Salt Lake Valley floor is the ancient lakebed of Lake Bonneville which existed at the end of the last Ice Age. Several Lake Bonneville shorelines can be distinctly seen on the foothills or benches of nearby mountains .
Layout
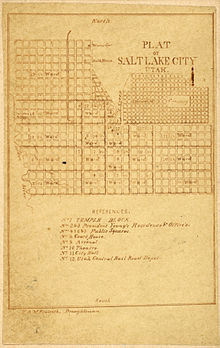
The city, as well as the county, is laid out on a grid plan; Most major streets run very nearly north-south and east-west. There is about a fourteen to fifteen minute of arc variation of the grid from true north. Its origin is the southeast corner of Temple Square, the block containing the Salt Lake Temple of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Addresses are coordinates within the system. This is similar to latitude and longitude. One hundred units are equal to 1/8th of a mile (200 m), the length of blocks in downtown Salt Lake City. The streets are relatively wide, a vision of the original settlers, who wanted them wide enough that a wagon team could turn around.
Joseph Smith, founder of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, planned it in the "Plat of the City of Zion." In his plan the city was to be developed into 135 10-acre lots. However, the blocks became irregular during the late 19th century when the LDS Church lost authority over growth and before zoning ordinances in the 1920s. The original 10-acre blocks allowed for large garden plots, and many were supplied with irrigation water from ditches that ran approximately where modern curb and gutter is laid. The original water supply was from City Creek. Subsequent development of water resources was from successively more southern streams flowing from the mountains to the east of the city. Some of these irrigation ditches are still visible in the eastern suburbs.
There are three distinct street patterns in Salt Lake City, the first of which are the initial square blocks crisscrossed by later small streets. The second distinct pattern are the 2.5 acre (10,100 m²) blocks in the Avenues. The final section is the rectangular blocks south from 900 South.
Neighborhoods

Salt Lake City has many informal neighborhoods. The eastern portion of the city has higher property values than its western counterpart. This is a result of the railroad being built in the western half as well as scenic views from inclined grounds in the eastern portion. Housing is more affordable on the west side, which results in demographic differences. Interstate 15 was also built in a north-south line, further dividing east and west sides of the city.
The west side of the city has historically been a working-class neighborhood, but recently the more affordable nature of the area has enticed many professionals to the neighborhood. For example, the small, increasingly trendy Marmalade District on the west side of Capitol Hill, once considered seedy as few as 5–10 years ago, was heavily gentrified and is now thought of as an eclectic and desirable location. During the 1980s, gang activity was also centered in the western neighborhoods of Rose Park, Poplar Grove, and Glendale. Recently, however, these neighborhoods have made recoveries while other areas of town, such as the Central City, have come to be known as the poorer areas of town, despite the more balanced demographics.
Just northeast of Downtown is The Avenues, a neighborhood outside of the regular grid system on much smaller blocks. This area is nearly entirely residential, and contains much of the young student-aged population. The Avenues are situated on the upward-sloping bench in the foothills of the Wasatch Range, with property values generally increasing with elevation. The Upper Avenues, along with Federal Heights, just to the east and north of the University of Utah, and the East Bench, south of the University, contain gated communities, large, multi-million dollar houses, and fantastic views of the valley.
Climate
Main article: Climate of Salt Lake City
The climate of Salt Lake City is characterized by four distinct seasons. Both summer and winter are long, with hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters, and with spring and fall serving as brief but comfortable transition periods. The city receives 16.50 in (419 mm) of precipitation annually. Spring is the wettest season, and another "rainy season" occurs in fall. Snow occurs on average from November 6 to April 18, producing a total average of 62.7 in (159 cm), while the city's watersheds in nearby mountains accumulate averages as high as 500 in (1,270 cm). The period without freezing temperatures usually lasts an average of 167 days, from April 30 to October 15.
During the winter months cold fronts typically originate in the Gulf of Alaska and move southeastward into the area. The nearby Great Salt Lake produces lake-effect snow approximately 6 to 8 times per year, some of which can drop excessive snowfalls. The lake-effect also contributes to some rain storms, and it is estimated that about 10% of the annual precipitation in the city can be attributed to the lake effect. During mid-winter, strong areas of high pressure often situate themselves over the Great Basin, leading to strong temperature inversions. This causes air stagnation and thick smog in the valley for several days to weeks at a time and can result in the worst air-pollution levels in the U.S. reducing air quality to unhealthy levels. The all-time record low temperature is -30 °F (-34 °C), which occured on February 9, 1933.
In the spring, most of the storms originate in the Pacific Ocean from the Pineapple Express, bringing in the most moisture of the entire year. Larger and cooler storms in the spring can lead to heavy overnight snowfall. Measurable snow has occurred as late as May 18.
The summers of the city are marked by hot weather and are mostly dry. The monsoon rises from the Gulf of California from approximately mid-July into September, producing localized severe afternoon thunderstorms. Due to the low daytime humidity, virga, lightning, and microbursts can lead to wildfire problems. During active monsoon periods, widespread thunderstorms carrying excessive precipitation are common. High temperatures of at least 100°F(38°C) occur on average five times a year, but usually on days with low humidity. The record high temperature is 107 °F (41 °C), which occurred first on July 26, 1960 and again on July 13, 2002.
During October, the Pacific Ocean once again becomes active, bringing in more precipitation, occasionally in the form of the remnants of tropical cyclones. The remnants of Hurricane Olivia helped bring the record monthly precipitation of 7.04 in (179 mm) in September 1982. The first measurable snowfall usually occurs in early November, but has occurred as early as September 17.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record Daily High | °F | 63 | 69 | 78 | 86 | 99 | 104 | 107 | 106 | 100 | 89 | 75 | 69 |
| Average Daily High | °F | 37 | 43 | 53 | 61 | 71 | 82 | 91 | 89 | 78 | 64 | 49 | 38 |
| Average Daily Low | °F | 21 | 26 | 33 | 39 | 47 | 56 | 63 | 62 | 52 | 41 | 30 | 22 |
| Record Daily Low | °F | -22 | -30 | 2 | 14 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 37 | 27 | 16 | -14 | -21 |
| Data is for Salt Lake International Airport | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record Precipitation | in. | 3.23 | 4.89 | 3.97 | 4.90 | 4.76 | 3.84 | 2.57 | 3.66 | 7.04 | 3.91 | 3.34 | 4.37 |
| Average Precipitation | in. | 1.37 | 1.33 | 1.91 | 2.02 | 2.09 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 1.33 | 1.57 | 1.40 | 1.23 |
| Average Snowfall | in. | 13.6 | 9.9 | 9.1 | 4.9 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 12.0 |
| Record Snowfall | in. | 50.3 | 32.1 | 41.9 | 26.4 | 7.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 20.4 | 33.3 | 35.2 |
| Data is for Salt Lake International Airport | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Salt Lake City's racial demographics against those of Utah: | ||
| Utah | Salt Lake City | Ethnicity |
| 85.3% | 79.20% | White |
| 0.8% | 1.89% | Black |
| 1.3% | 1.34% | Native American |
| 1.7% | 3.62% | Asian |
| 0.7% | 1.89% | Pacific Islander |
| N/A | 8.52% | Other race |
| 2.1% | 3.54% | Two or more races |
| 9.0% | 18.85% | Hispanic |
| Note: Hispanics may be of any race. | ||
As of the censusTemplate:GR of 2000, there are 181,743 people (up from 159,936 in 1990), 71,461 households, and 39,803 families residing in the city. This amounts to 8.1% of Utah's population, 20.2% of Salt Lake County's population, and 13.6% of the Salt Lake metropolitan population. Salt Lake City proper covers 14.2% of Salt Lake County. Salt Lake City is more densely populated than the surrounding metro area with a population density of 643.3/km² (1,666.1/mi²). There are 77,054 housing units at an average density of 272.7/km² (706.4/mi²).
The Salt Lake City-Ogden metropolitan area, which included Salt Lake, Davis, and Weber counties, had a population of 1,333,914 in 2000, a 24.4% increase over the 1990 figure of 1,072,227. Since the 2000 Census, the Census Bureau has added Summit and Tooele counties to the Salt Lake City metropolitan area, but removed Davis and Weber counties and designated them as the separate Ogden-Clearfield metropolitan area. Together with the Provo-Orem metropolitan area, which lies to the south, a roughly continuous urban corridor along the Wasatch Front is formed, which has a combined population of well over 2 million.
There are 71,461 households, out of which 27.0% have children under the age of 18 living with them, 41.1% are married couples living together, 10.2% have a female householder with no husband present, and 44.3% are nonfamilies. Of the 71,461 households, 3,904 were reported to be unmarried partner households: 3,047 heterosexual, 458 same-sex male, and 399 same-sex female. 33.2% of all households are made up of individuals, and 9.7% have someone living alone who is 65 years of age or older. The average household size is 2.48, and the average family size is 3.24.
In the city the population is spread out with:
- 23.6% under the age of 18
- 15.2% from 18 to 24
- 33.4% from 25 to 44
- 16.7% from 45 to 64
- 11.0% who are 65 years of age or older
The median age is 30 years. For every 100 females there are 102.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there are 101.2 males. The median income for a household in the city is $36,944, and the median income for a family is $45,140. Males have a median income of $31,511 versus $26,403 for females. The per capita income for the city is $20,752. 15.3% of the population and 10.4% of families are below the poverty line. Out of the total population, 18.7% of those under the age of 18 and 8.5% of those 65 and older are living below the poverty line.
| Historical Population | |
|---|---|
| Year | Population |
| 1860 | 8,236 |
| 1870 | 12,854 |
| 1880 | 20,768 |
| 1890 | 44,843 |
| 1900 | 53,531 |
| 1910 | 92,777 |
| 1920 | 116,110 |
| 1930 | 140,267 |
| 1940 | 149,934 |
| 1950 | 182,121 |
| 1960 | 189,454 |
| 1970 | 175,885 |
| 1980 | 163,034 |
| 1990 | 159,936 |
| 2000 | 181,743 |
| 2005 | 178,097 |
Large family sizes and low housing vacancy rates, which have inflated housing costs along the Wasatch Front, have led to one out of every six residents living below the poverty line.
Less than 50% of Salt Lake City's residents are members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. This is a much lower proportion than in Utah's more rural municipalities; altogether, LDS members make up about 62% of Utah's population.
The Rose Park and Glendale sections are predominantly Spanish-speaking with Latinos accounting for 60% of public school-children. The Centro Civico Mexicano acts as a community gathering point for the Wasatch Front's estimated 300,000 Latinos, Mexican President Vicente Fox began his U.S. tour in the city in 2006, and the largest supermarket chain of Mexico, Supermercados Gigante, is planning a location, the first in the U.S. outside of California. Bosnian, Sudanese, Afghani, Somali, and Russian refugees have settled in the city under government programs. There is also a large Pacific Islander population, mainly made up of Samoans and Tongans. Many of the Pacific Islanders are members of the LDS Church.
Salt Lake City has been considered one of the top 51 "gay-friendly places to live" in the U.S. The city is home to a large, business savvy, organized, and politically supported gay community. Leaders of the Episcopal Church's Diocese of Utah, Utah's largest Jewish congregation, the Salt Lake Kol Ami, and three elected representatives of the city, two members of the state house and one in the senate, all identify as gay. These developments have attracted controversy from socially conservative officials representing other regions of the state. State Senator Chris Buttars of West Jordan publicly denounced Mayor Rocky Anderson for having "attracted the entire gay community to come and live in Salt Lake County" after a Dan Jones poll indicated strong support for allowing domestic partnerships. In the 2004 election, 63% of the city population voted against banning same-sex marriage, in agreement with Mayor Anderson.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Salt Lake CityThe modern economy of Salt Lake City is service-oriented. In the past, nearby steel, mining and railroad operations provided a strong source of income with Geneva Steel, Kennecott Copper Mine, and oil refineries. Today the city's major industries are government, trade, transportation, utilities, and professional and business services. The city is known as the "Crossroads of the West" for its central geography in the western United States. As a result, Interstate 15 is a major corridor for freight traffic and the area is host to many regional distribution centers.
Local, state, and federal governments have their largest presence in the city proper itself, and trade, transportation, and utilities also take up a significant portion of employment, with the major employer being the western North America Delta Air Lines hub at Salt Lake City International Airport. Equally significant are the professional and business services, while health services and health educational services also serve as significant areas of employment. Other major employers include the University of Utah, Sinclair Oil Corporation, and The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Besides its central offices, the LDS Church owns and operates a profit division, Deseret Management Corporation and its subsidiaries, which are headquartered in the city. Other notable firms headquartered in the city include AlphaGraphics and Smith's Food and Drug (owned by national grocer Kroger). Notable firms based in the metropolitan area include Arctic Circle Restaurants, Franklin-Covey, and Overstock.com. Metropolitan Salt Lake was also once the headquarters of Kentucky Fried Chicken (the first ever KFC is located in South Salt Lake), American Stores, the Skaggs Companies, and ZCMI, one of the first-ever department stores; it is currently owned by Federated Department Stores. Former ZCMI stores now operate under the Macy's label. Suburban Salt Lake was also the first location for Sears Grand (at the Jordan Landing shopping center in West Jordan).
Since Utah is one of seven states that allow the establishment of commercially-owned industrial banks, the vast majority of industrial banks in the U.S. have established their headquarters in the Salt Lake City area. High-tech firms with a large presence in the suburbs include e-Bay, Unisys, Siebel, Micron and 3M.
Other economic activities include tourism, conventions, and major suburban call centers. Tourism has increased since the 2002 Olympic Winter Games, and many hotels and restaurants were built for the events. The convention industry has expanded since the construction of the Salt Palace convention center in the late 1990s, which hosts trade shows and conventions, including the annual Outdoor Retailers meeting and Novell's annual BrainShare convention.
In 2006, the largest potato producer in Idaho, the United Potato Growers of America, announced that it would re-locate its headquarters to Salt Lake City, citing its need for a large international airport, being that Salt Lake City International is the 18th busiest in the world in terms of combined freight and passengers. The announcement led some members of the Idaho legislature to propose legislation changing the state license plate, which currently reads "Famous Potatoes".
In 2005, it was found the downtown area was experiencing rapid population growth. The number of residential units in the central business district has increased by 80% since 1995, and is forecasted to nearly double in the next decade. The City Creek development of the LDS Church will be adding 300 units in its first phase including the 415 ft. tall City Creek condominium tower, Allen Millo Associates currently has two projects under construction and two more planned, all 200 units have been sold before construction of a seven-story condominium planned by Wood Property, a residential tower is planned for Trolley Square, and this is after the recent completion of the Northgate Apartments and 12-story condominiums at Gateway with two more buildings finished nearby and the Liberty Metro apartments near Library Square.
Office vacancy rates are low in the downtown region. In response, two new large buildings are being constructed. The first is eight stories and located in the Gateway District, while the second will be 22 stories high and is currently under construction on Main Street. In addition, the historic Walker Bank Building is currently undergoing major renovations that will enable it to achieve Class A office space status. Construction of the Gateway District, light rail, and planned commuter rail service have supported the revival of downtown.
Law and government
Since 1979 Salt Lake City has had a nonpartisan mayor-council form of government. The mayor and the seven councilors are elected to four-year terms. Mayoral elections are held the same year as three of the councilors. The other four councilors are staggered two years from the mayoral. Council seats are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each councilor represents approximately 26,000 citizens. Officials are not subject to term limits. The most recent election was held in 2005.
The city has elected Democratic Party mayoral candidates since the 1970s. Councilors are elected under specific issues and are usually well-known. Labor politics play no significant role. The city has two elected openly gay women and an openly gay man, representing the city in the State House and Senate, respectively.
The separation of church and state was the most heated topic in the days of the Liberal Party and People's Party of Utah, when many candidates would be LDS Bishops and Mark Twain referred to Brigham Young as "the only monarch in America." Non-Mormons are commonly called "gentiles". This tension is still reflected today with the Bridging the Religious Divide campaign. This campaign was initiated when some city residents complained that the Utah political establishment was unfair in its dealings with non-LDS residents by giving the LDS Church preferential treatment, while LDS residents perceived a growing anti-Mormon bias in city politics.
| Elected officials of Salt Lake City as of 2004 | ||
| Official | Position | Term ends |
| Rocky Anderson (D) | Mayor | 2007 |
| City Council members | ||
| Carlton Christensen | 1st district | 2009 |
| Van Blair Turner | 2nd district | 2007 |
| Eric Jergensen | 3rd district | 2009 |
| Nancy Saxton | 4th district | 2007 |
| Jill Remington Love | 5th district | 2009 |
| David Buhler | 6th district | 2007 |
| Søren Simonsen | 7th district | 2009 |
The current mayor is Ross C. "Rocky" Anderson, who gained international attention for actively organizing a protest against President George W. Bush during his visit to Salt Lake City for the 2005 Veterans of Foreign Wars convention. He again held a protest against President Bush when the president addressed the 2006 American Legion convention. He is supportive of same-sex marriage, the Kyoto Treaty, transit-oriented urban planning, alternative energy sources, and the relaxation of Utah state liquor laws. He has also been accused of abusive and demanding working conditions by former staffers and inflammatory remarks towards the LDS Church, and has been criticized for spending city funds on the purchase of alcohol for dignitaries and guests. He also worked with environmentalists to block construction of the Legacy Highway, accusing UDOT of a sloppy environmental impact statement, which was ruled as incomplete. Rocky maintains wide public support within Salt Lake City. He has supported civil rights and hate crimes legislation.
The city is home to several non-governmental think-tanks and advocacy groups such as the conservative Sutherland Institute, the gay-rights group Equality Utah, and the quality-growth advocates Envision Utah. Salt Lake hosted many foreign dignitaries during the 2002 Winter Olympics, and in 2006 the President of Mexico began his U.S. tour in the city and Israel's ambassador to the United States opened a cultural center. President George W. Bush visited in 2005 and again in 2006 for national veterans' conventions, both visits of which were protested by Mayor Rocky Anderson. Other political leaders such as Howard Dean and Harry Reid gave speeches in the city in 2005.
See also: List of mayors of Salt Lake CityEducation
Main article: Education in Salt Lake City
In 1847 pioneer Jane Dillworth held the first classes in her tent for the children of the first LDS families. In the last part of the 1800s, there was much controversy over how children in the area should be educated. LDS and non-LDS could not agree on the level of religious influence in schools. Today, many LDS youths in grades 9 through 12 attend some form of religious instruction, referred to as seminary.
Because of high birth rates and large classrooms, Utah spends less per student than any other state yet simultaneously spends more per capita than any state with the exception of Alaska. Money is always a challenge, and many businesses donate to support schools. Several districts have set up foundations to raise money. Recently, money was approved for the reconstruction of more than half of the elementary schools and one of the middle schools in the Salt Lake City School District, which serves most of Salt Lake City proper. There are twenty-three elementary schools, five middle schools, three high schools (Highland, East, and West, with the former South High being converted to the South City campus of the Salt Lake Community College, and an alternative high school (Horizonte) located within the school district. In addition, Highland has recently been selected as the site for the charter school Salt Lake School for the Performing Arts (SPA), while Salt Lake City proper also holds many Catholic schools, including Judge Memorial High School. Rowland Hall-St. Mark's School is the area's premier independent school.
Postsecondary educational options in Salt Lake City include the University of Utah, Westminster College, Salt Lake Community College, BYU Salt Lake Center, and LDS Business College. There are also many trade and technical schools such as the Utah College of Massage Therapy.
- See also: Salt Lake County - Education
Culture
Arts

The Utah Museum of Fine Arts, Utah Museum of Natural History, and the Museum of Church History and Art are some of the museums located in Salt Lake City. Other museums include the Utah State Historical Society, Daughters of Utah Pioneer Memorial Museum, Fort Douglas Military Museum, and the Social Hall Heritage Museum. Clark Planetarium at the Gateway Mall houses an IMAX theater.
Salt Lake City provides many venues for both professional and amateur theatre. The city attracts many traveling Broadway and off-Broadway performances. Local professional acting companies include the Pioneer Theatre Company, Salt Lake Acting Company, and Plan-B Theatre Company.
Salt Lake City is the home of the Mormon Tabernacle Choir, founded in 1847. The Choir's weekly program, called Music and the Spoken Word, is the longest-running continuous network broadcast in the world. Salt Lake City is also the home to the Utah Symphony Orchestra, which was founded in 1940 by Maurice Abravanel and has become widely renowned. The orchestra's original home was the Salt Lake Tabernacle, but since the 1990s has performed at Abravanel Hall in the western downtown area.
The city also has a local music scene dominated by blues, rock and roll, punk, and emo groups. There are also many clubs which offer musical venues. Popular groups or persons who started in the Wasatch Front area or were raised and influenced by it include The Used, Shedaisy, and the lead singer of The Killers, Brandon Flowers. In 2004 over 200 bands submitted tracks for a compilation by a local music zine, SLUG ("Salt Lake Underground"). The 15-year-old free monthly zine trimmed the submissions to 59 selections featuring diverse music types such as hip-hop, jazz, jazz-rock, punk, and a variety of rock and roll.
The University of Utah is home to two highly-ranked dance departments, the Ballet Department and the Department of Modern Dance. Professional dance companies in Salt Lake City include Ballet West, Rire Woodbury, and Repertory Dance Theatre.
Many films, music videos, commercials, and TV shows have been recorded in the Salt Lake metropolitan area. They include: SLC Punk!, Touched By An Angel, Everwood, Big Love, Dawn of the Dead, Drive Me Crazy, High School Musical, Unaccompanied Minors, Dumb and Dumber, Independence Day, Poolhall Junkies, The Brown Bunny, The World's Fastest Indian, Carnival of Souls, and The Postal Service's "Such Great Heights". In 2006 it was revealed that Dan Brown, the author of The DaVinci Code, was in the city studying the symbols on the Salt Lake LDS Temple and the Masonic Temple, among other historical buildings, for inclusion in an upcoming book.
Events

Although the city is often stereotyped as a predominantly LDS city, it is culturally and religiously diverse. The city is the location of many cultural activities, Mormon and otherwise. A major state holiday is Pioneer Day, July 24, the anniversary of the Mormon pioneers' entry into the Salt Lake Valley. It is celebrated each year with a week's worth of activities, including a children's parade, a horse parade, the featured Days of '47 Parade (one of the largest parades in the United States), a rodeo, and a large fireworks show at Liberty Park.
Salt Lake City has a significant gay population, and the second-largest parade in the city is a gay pride parade, part of the annual Utah Pride Festival held every June.
First Night on New Year's Eve, a celebration emphasizing family-friendly entertainment and activities held at Rice-Eccles Stadium at the University of Utah, culminates with a fireworks display at midnight.
The Greek Festival, held the weekend after Labor Day, celebrates Utah's Greek heritage and is located at the downtown Greek Orthodox Church. The 3-day event includes Greek music, dance groups, Cathedral tours, booths and a large buffet. Attendance ranges from 35,000 - 50,000.
The Utah Arts Festival has been held annually since 1977 with an average attendance of 80,000. About 130 booths are available for visual artists and there are five performance venues for musicians.
Salt Lake City also hosts portions of the Sundance Film Festival. The festival, which is held each year, brings many cultural icons, movie stars, celebrities, and thousands of film buffs to see the largest independent film festival in the United Sates. However, the main location of the event is in nearby Park City.
Beginning in 2004, Salt Lake City has been the host of the international Salt Lake City Marathon. In 2006 Real Madrid and many of the nation's best cyclist had engagements.
Salt Lake City was host to the 2002 Winter Olympics. At the time of the 2002 Olympics, Salt Lake City was the most populated area to hold a Winter Olympic games. The event put Salt Lake City in the international spotlight and is regarded by many as being one of the most successful winter olympics ever.
Media
Salt Lake City has many diverse media outlets. Most of the major television and radio stations are based in or near the city. The Salt Lake City metropolitan area is ranked as the 31st largest radio and 36th largest television market in the United States.
Print media include two major daily newspapers, The Salt Lake Tribune and the Deseret Morning News, and the alternative weekly, Salt Lake City Weekly. Other more specialized publications include Nuestro Mundo of the Spanish-speaking community and Salt Lake Metro, QSaltLake and The Pillar for the LBGT community. There are many local magazines, such as Salt Lake Magazine (a bimonthly lifestyle magazine), Wasatch Woman Magazine (a bimonthly magazine spotlighting the successes of local women), and Salt Lake Underground (SLUG)], an alternative underground music magazine. The popular online music festival, Rippyfest, is owned by Salt Lake City-based indie record label Rippyfish records.
KSL-TV is one of Utah's oldest television stations. KSL has downtown studios at "Broadcast House" in the Triad Center office complex. Most other television stations had until recently moved out of the downtown core and relocated in the suburbs. However, KUTV was recently given a Redevelopment Agency (RDA) grant, and moved its studios to Main Street. Its news desk overlooks the street, with a large window behind the anchor desk.
Because television and radio stations serve a larger area (usually the entire state of Utah, as well as parts of western Wyoming, southern Idaho, parts of Montana, and eastern Nevada), ratings returns tend to be higher than those in similar-sized cities. Some Salt Lake radio stations are carried on broadcast translator networks throughout the state.
Salt Lake City has become a case of market saturation on the FM dial; one cannot go through more than about two frequencies on an FM radio tuner before encountering another broadcasting station. A variety of companies, most notably Millcreek Broadcasting and Simmons Media, have constructed broadcast towers on Humpy Peak in the Uinta Mountains to the east. These towers allow frequencies allocated to nearby mountain communities to be boosted by smaller, low-powered FM transmitters along the Wasatch Front.
Sites of interest and City Architecture
Main article: Buildings and sites of Salt Lake City, UtahAs Salt Lake City is the headquarters for LDS Church, there are many historic and actual LDS sites around the city. The largest is Temple Square, which includes the Salt Lake Temple and visitors’ centers that are open to the public, free of charge. Temple Square also includes the historic Tabernacle, home of the world-famous Mormon Tabernacle Choir. The modern LDS Conference Center is across the street to the north. The Family History Library, the world’s largest genealogical library in the world, is located just west of Temple Square. It is run by the LDS Church and is open to the public and free of charge.
The Salt Lake City Public Library was named Library of the Year by the American Library Association and features a distinctive, unique architectural style. The roof of the building serves as a viewpoint for the Salt Lake Valley. The Utah State Capitol Building offers marble floors and a dome similar to that of the building that houses the U.S. Congress. Other notable historical buildings include the City and County Building, built in 1894, and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of the Madeleine, built in 1909.
Near the mouth of Emigration Canyon lies This Is The Place Heritage Park, which re-creates typical 19th-century LDS pioneer life. Hogle Zoo is located across the street from the park. The city’s largest public park, at over 100 acres, Liberty Park features a lake with an island in the middle and the Tracy Aviary. The park is home to a large number of birds, both wild and in the aviary.
Salt Lake City is also home to a few major shopping centers. Trolley Square is an indoor and outdoor mall with many independent art boutiques, restaurants, and national retailers. The buildings housing the shops are renovated trolley barns with cobblestone streets. The Gateway District, an outdoor shopping mall, is the city’s newest major shopping center and has many national restaurants, clothing retailers, a movie theater, the Clark Planetarium, a music venue called The Depot, and a 2002 Olympic Park.
On October 3, 2006, the LDS Church, who owns the ZCMI Center Mall and Crossroads Mall, both on Main Street, announced plans to demolish the malls, a skyscraper, and several other buildings to make way for the $1 billion City Creek Center redevelopment. It will combine several new office and residential buildings (one of which will be the third-tallest building in the city) around an outdoor shopping center featuring a stream, fountain, and other outdoor amenities, and is expected to be completed in 2011. Sugar House is a neighborhood with a small town main street shopping area and numerous old parks. Sugar House Park is the second largest park in the city, and is host to frequent outdoor events and the primary Fourth of July fireworks in the city.
Other attractions within proximity of Salt Lake City include the Golden Spike National Historic Site (where the world's first transcontinental railroad was joined), the Lagoon Amusement Park, the Great Salt Lake, the Bonneville Salt Flats, Gardner Historic Village, ski resorts such as Park City Mountain Resort and Snowbird, resort towns such as Park City, one of the largest dinosaur museums in the U.S. at Thanksgiving Point in Lehi, and the world’s largest man-made excavation at Kennecott Copper Mine.

Sports and recreation
Winter sports, such as skiing and snowboarding, are popular activities in the Wasatch Mountains east of Salt Lake City. Eight ski resorts lie within 50 miles (80 km) of the city. Alta, Brighton, Solitude, and Snowbird are located in Big and Little Cottonwood Canyons to the southeast, Deer Valley, The Canyons, and Park City Resort are located to the east, near Park City in Summit County, and Sundance is located to the southeast in Utah County. The ski resorts see frequent storms that deposit light, dry snow due to a phenomenon known as the lake effect, where storms amplified by the warm waters of the Great Salt Lake precipitate in the Wasatch Mountains. Alta and Deer Valley only allow skiing, while the others allow both skiing and snowboarding. The popularity of the ski resorts has increased nearly 29% since the 2002 Winter Olympics.
Most of the ski resorts also offer summer activities. The mountains surrounding Salt Lake City are very popular for hiking, camping, rock climbing, mountain biking, and other related outdoor activities. In addition, the many small reservoirs and rivers in the Wasatch Mountains are popular for boating, fishing, and other water-related activities. Salt Lake City is the primary jumping-off point for exploring the national parks and monuments and rugged terrain of the southern half of the state, as it contains the only international airport in the state.
Salt Lake City is home to the NBA team Utah Jazz, which plays at EnergySolutions Arena, and Real Salt Lake of Major League Soccer that began play in 2005 and currently plays at Rice-Eccles Stadium at the University of Utah. An as-of-yet unnamed soccer-specific stadium for Real Salt Lake has been approved for the suburb of Sandy and will finish construction by the 2008 season after undergoing nearly 2 years of funding difficulties. Salt Lake City also received an Arena Football League team known as the Utah Blaze in 2006, who were popular in their first season in Utah, recording the highest average attendance in the league. It is also the home of the Salt Lake Bees minor league baseball team, a Los Angeles Angels Triple A affiliate that plays in the Pacific Coast League. Nearby West Valley City has the Utah Grizzlies of the ECHL. The new ABA league has twice attempted to expand into the city, first with the Utah Snowbears in the 2004-05 season (which folded after reaching the quarterfinals of the playoffs) and later with the Salt Lake Dream (who folded before ever playing a game). The Continental Basketball Association (CBA) also attempted an expansion with the Utah Eagles, who folded halfway through the 2006-07 season. The Utah Starzz of the WNBA were once located within the city, but moved to San Antonio and became the Silver Stars.
Because Utah lacks a professional football team of its own, college football is very popular in the state. The University of Utah and Brigham Young University both maintain large and faithful followings in the city, and rivalries are intense during the annual game between the two universities. This is sometimes referred to as the Holy War, despite the fact that Utah is a secular university.
Transportation
Main article: Transportation in Salt Lake CityRoads

There are four major freeways located within Salt Lake City. Interstate 15 runs north-south just west of downtown, while Interstate 80 enters near the airport and briefly merges with I-15 west of downtown before heading east through residential neighborhoods into Parley's Canyon. Utah State Route 201 (the 2100 South freeway) runs east-west along the border with West Valley City; and Interstate 215, a beltway, traverses the city's northwest and west neighborhoods and encircles the city's southern suburbs. SR-201, I-15, and I-80 bisect one another at the "spaghetti bowl" just south of the city in neighboring South Salt Lake.

An additional freeway, known as the Mountain View Corridor, which is part of the Legacy Highway system, is proposed to reduce growing congestion and accommodate rapidly-growing population along the west side of the Salt Lake Valley, with construction set to begin as early as 2008 and completion after 2015. The first portion of the Legacy Highway system, known as Legacy Parkway, has begun construction as of November 2006 and will connect into I-215 just north of the city borders by 2008. This highway is expected to significantly reduce congestion on I-15 into Davis County. Utah State Route 154 (Bangerter Highway) is an expressway that provides access to the rapidly growing western and southern cities of the Salt Lake Valley, beginning at Salt Lake City International Airport. U.S. Highway 89 enters from Davis County parallel to I-15 before heading southeast into downtown. In downtown, U.S. 89 becomes State Street and extends south as the main surface street through the center of the city. Both S.R. 154 and U.S. 89 connect to I-15 at the far south end of the valley.
Public transportation

Salt Lake City's mass transit service is operated by the Utah Transit Authority (UTA) and includes light rail and bus routes (with the addition of commuter rail in 2008). The 19-mile light rail system, called TRAX, consists of two lines originating downtown. Daily ridership averages 53,400, nearly four times original projections, and is the ninth-most ridden light rail system in the country.
Both lines begin at the EnergySolutions Arena near the western edge of downtown and head east to Temple Square. From there they turn south; near the courthouse, the University Line heads east to the University of Utah. The Sandy Line continues south to Sandy, and has a total of 18 stations. The University Line heads east to the University of Utah and ends at the University Medical Center. The line has a total of 11 stations.
TRAX began service on December 4, 1999, and the University Line opened in 2001 and was extended in 2003 to its current terminus at the University Medical Center. The Mid-Jordan Line to the Daybreak Community in South Jordan and the Draper lines have been approved, as well. An additional two stations were recently approved west of the EnergySolutions Arena through the Gateway District and will end at the Intermodal Hub located on 600 West between 200 South and 300 South. A sales tax hike for road improvements, light rail, and commuter rail was approved on November 7, 2006. A commuter rail line, FrontRunner, running north from Salt Lake City into Davis and Weber Counties, is currently under construction and is expected to be completed in the spring of 2008.
In addition, a non-UTA, non-profit vintage rail trolley system is being planned for the Sugar House neighborhood.
UTA also operates an extensive bus system that extends throughout the Wasatch Front from Brigham City in the north to Santaquin in the south and as far west as Grantsville. UTA also operates routes to the ski resorts in Big and Little Cottonwood Canyons during the ski season (typically November to April).
Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, provides service to Salt Lake City, operating its California Zephyr daily in both directions between Chicago and Emeryville, California across the bay from San Francisco. Greyhound Bus Lines serves Salt Lake City as well, providing access north-to-south through Utah along the I-15 corridor. Salt Lake City International Airport is located 7 mi (11 km) west of downtown. Delta Air Lines has hub operations at the airport and is currently expanding its Salt Lake City service. Ute Cab, City Cab, and Yellow Cab are the major taxi services.
Sister cities
Salt Lake City has several sister cities, including:
 Chernivtsi (Ukraine)
Chernivtsi (Ukraine) Keelung City (Taiwan)
Keelung City (Taiwan) Matsumoto (Japan)
Matsumoto (Japan) Oruro (Bolivia)
Oruro (Bolivia) Quezon City (Philippines)
Quezon City (Philippines) Thurles (Ireland)
Thurles (Ireland) Turin (Italy)
Turin (Italy)
See also

- 2002 Winter Olympics
- Great Salt Lake
- List of famous Salt Lakers
- Salt Lake City Tornado
- Trolley Square shooting
Sources
- Salt Lake City population estimate. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- "Metropolitan Area Definitions". United States Department of Labor - Bureau of Labor Statistics. March 2005. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|note=ignored (help) - FDIC Industrial Banks. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (2004-06-25). Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- Alexander, Thomas G. "Utah History to Go - Fremont's Exploration". Utah State Historical Society. Retrieved 2006-12-15.
- Salt Lake Temple. LDSChurchTemples.com. Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- Sillitoe, Linda. A History of Salt Lake County, p. 138.
- Money, Marti. Utah Street Tramways - History of trams in Salt Lake City. Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- Population Estimates for Places over 100,000: 2000 to 2005. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- Haya El Nasser (2006-09-15). "Immigrants turn Utah into mini-melting pot". USA Today.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Salt Lake City Has High Gay Population", KUTV.com. Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- Sullivan, Tim (2005-09-08). "The Gangs of Zion". Retrieved 2007-01-13.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Lisa Riley Roche (2006-10-05). "Big incentive helps lure speedskating group". Deseret Morning News.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Gorrell, Mike (2006-03-30). "Convention numbers best since Olympics; S.L. County conventions post big year". The Salt Lake Tribune.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Mike Gorrell (2004-02-15). "Olympic windfall unseen". The Salt Lake Tribune.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - 2007 Winter Deaflympics - Official Website: About Us. Winter Deaflympics (2007). Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- "SLC to land Rotarians in '07", The Salt Lake Tribune.
- "Area Information - Frequently Asked Questions". Salt Lake City Corporation. Retrieved 2006-12-11.
- Utah’s Infamous “Lake Stink”. Utah Department of Environmental Quality. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- ^ Arave, Lynn. "Mountains High: Utah abounds with high peaks in all counties", Deseret Morning News, 2005-03-31. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- Davidson, Lee. "It's 2008 — and 'the big one' slams Utah", Deseret Morning News, 2006-04-16. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- Husarik, Theresa. Navigating Utah's Streets. About.com. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- William E. Hill (1996). The Mormon Trail: yesterday and today. Logan, Utah: Utah State University Press. ISBN 0-87421-202-2 p. 26
- The Disaster Center Ranking of Tornado Risk by State. The Disaster Center. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- NWS Salt Lake City - Average precipitation. National Weather Service. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- NWS Salt Lake City - Average snowfall. National Weather Service. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- NWS Salt Lake eCity - Freeze data. National Weather Service. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- Bauman, Joe. "Lake has great impact on storms, weather", Deseret Morning News, 1999-08-05. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- Fahys, Judy. "Winter's bad air still choking Utah", The Salt Lake Tribune, 2007-03-07. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- Olympic Air. ACFnewsource (2002-01-28). Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- NWS Salt Lake City - Extreme low temperatures. National Weather Service. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- NWS Salt Lake City - Earliest and latest measurable snowfall. National Weather Service. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- NWS Salt Lake City - Extreme maximum temperatures. National Weather Service. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- Remnants of Hurricane Olivia - September 23-28, 1982. Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- NWS Salt Lake City - Record high and low precipitation for each month. National Weather Service. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- Matt Canham (2005-06-22). "Mormon portion of Utah population steadily shrinking". Salt Lake Tribune.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "School ranks thinned by 'Day Without Immigrants' ", The Salt Lake Tribune, 2006-05-01.
- "Latinos eye Utah for 2009 meeting", The Salt Lake Tribune, 2006-07-31.
- "Latino shops wary of Gigante", The Salt Lake Tribune, 2006-03-27, p. A1.
- Sullivan, Tim. Somali Bantu refugees started arriving in Salt Lake City, Utah. The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- Lattin, Don (1996-04-10). "New Mormon Melting Pot, Church transcends its racist history". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved 2007-03-21.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Stewart, Erin. "Travel book to highlight Salt Lake as 'gay-friendly place to live'", Deseret Morning News, 2005-11-09. Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- Perkins, Nancy. "Utah Episcopalians support gay bishop", Deseret Morning News, 2003-10-26. Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- "Bishop explains ousting of gay Episcopal bishop", Deseret News, 2004-05-22. Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- Davis, Kristy. "Eye on the Rabbi", Salt Lake City Weekly, 2003-11-27. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- "The Thumb", The Salt Lake Tribune, 2005-10-23.
- "Potato growers group leave Idaho for Utah", Deseret News, 2006-03-24. Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- "Population Is Up Downtown", Salt Lake Tribune, October 21, 2002.
- City Creek housing data. Downtown Rising (2006). Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- Allen Millo housing. Allen Millo Associates (2005). Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- Metro Condominiums. Wood Property Development, LC (2006). Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- Anderton, Dave. "Office space hard to find", Deseret Morning News, 2006-06-29. Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- Hamilton Partners: Location Overview Hamilton Partners (2007). Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- Projects: Walker Tower Downtown Rising (2006). Retrieved on 2007-03-23. Downtown Rising Web Site
- Official Utah State Capitol history page
- Roche, Lisa Riley. "State's first gay senator is sworn in", Deseret Morning News, 2005-02-08. Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- Stack, Peggy Fletcher. "Mormons, non-Mormons clear the air", The Salt Lake Tribune.
- Bernick Jr., Bob; Roche, Lisa Riley. "Rocky calls for Bush protest", Deseret Morning News, 2005-08-20. Retrieved on 2007-03-23.
- Burr, Thomas; May, Heather. "Protesting President Bush's visit", The Salt Lake Tribune.
- Lori Buttars (2006-6-21). "Rocky on liquor rules: 'Asinine'". The Salt Lake Tribune.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help), but Anderson's position on alcohol predates the 2002 Olympics, see also Greg Burton and Joe Baird (2001-08-05). "Alcohol Angst ; Utah isn't the only prudish state when it comes to drinking. We surely aren't the stingiest when it comes to liquor licenses. We don't even have the highest sin tax. So why does the world believe it can't get a drink here and why do Utah drinkers gripe so much?". The Salt Lake Tribune. - Anderson, Rocky (2005-10-18). "News' reporting 'reckless and deceptive'". Deseret Morning News.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Matt Canham (2006-05-19). "Let's be partners, Israel's ambassador urges governor" (PDF). The Salt Lake Tribune.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Music & the Spoken Word — Choir History
- Greater Salt Lake City Annual Events (2005). EventGuide.network.
- Utah Arts Festival
- Jared Eborn (2006-10-06). "Tour of Utah takes step forward". Deseret Morning News.
- "The Salt Lake City Games were by all accounts the most successful Winter Olympics ever." — Linda Fantin (2002-09-11). "Games Helped to Heal a Nation". Salt Lake Tribune.; " Controversies aside, the 2002 Salt Lake games may prove to be the most successful Winter Olympics in recent history." — Betsy Streisand (2002-02-25). "Hey, baby, it's gold outside". U.S. News & World Report..
- Radio Stations - Arbitron Radio Market Rankings (2005). Arbitron. Retrieved January 1, 2005
- Nielsen Media Research Local Universe Estimates (US). Nielsen Media Research. Retrieved December 29, 2004.
- Salt Lake City system is named Library of the Year. Tammy Walquist, Deseret Morning News.
- Downtown rebound: LDS Church unveils plans for 20-acre development. Doug Smeath, Deseret Morning News.
- Mike Gorrell (2006-05-16). "Utah's ski industry chalks up another record year for visitors". The Salt Lake Tribune.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Salt Lake County plays ball, OKs a deal with Real. Leigh Dethman, Deseret Morning News.
- Blaze burn bright with optimism
- Trax and taxes: Would expanded light rail be worth the price?. Nicole Warburton, Deseret Morning News.
- Transit measures approved. Nicole Warburton, Deseret Morning News.
- Sugar House trolley
- Online Directory: Utah, USA (2005). Sister Cities International.
References
- Alexander, Thomas G. (2001). Grace & Grandeur: A History of Salt Lake City. Heritage Media Corp. ISBN 1-886483-60-4.
- Thomas G. Alexander and James B. Allen (1984). Mormons & Gentiles: A History of Salt Lake City. Pruett Publishing Co. ISBN 0-87108-664-6.
- Bagley, Will (2004). World Book Encyclopedia (S-Sn ed.). World Book Inc. pp. 76-76a. ISBN 0-7166-0104-4.
- McCormick, John S. (2000). The Gathering Place: An Illustrated History of Salt Lake City. Signature Books. ISBN 1-56085-132-5.
- Rainey, Virginia (2004). Insiders' Guide: Salt Lake City (4th ed.). Globe Pequot Press. ISBN 0-7627-2836-1.
- Stober, Daniel (2004). Utah Street Names. Retrieved 2004.
- McCarthy, Terry (February 03, 2002). "The New Utah". Time.com.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Area Information - Salt Lake City's Climate (1991). slcgov.com. Retrieved March 2005.
- Area Information - Employment (2002). slcgov.com. Retrieved March 2005.
- Area Information - FAQ (2005). slcgov.com. Retrieved March 2005.
- Cities and Counties of Utah Census Brief (May 2001). Retrieved April 15, 2005 (PDF file).
- Comparative Climatic Data Publication - Data Tables. NOAA National Data Centers - NOAA Satellites and Information. Retrieved November 2004.
- Salt Lake City History (2004). slcgov.com. Retrieved September 2004.
- Salt Lake City (2005). Encarta Encyclopedia. Retrieved March 2005.
- The Official Site of the Mormon Tabernacle Choir. Official Website of the Mormon Tabernacle Choir. Retrieved May 2006.
External links
- Salt Lake City government website
- Salt Lake City Chamber of Commerce
- The Downtown Alliance (tourist, resident, and potential resident guide to downtown area)
- Downtown Rising (information on the current $1.5 billion construction projects in downtown)
- artTix (fine-art events information)
- The Utah Office of Tourism
- National Weather Service - Salt Lake City
- Template:Wikitravelpar
| Salt Lake City | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topics | |||||
| Education |
| ||||
| Neighborhoods | |||||
| Sports | |||||
| Transportation | |||||
| Capitals of the United States by jurisdiction | |
|---|---|
|
Nation: States:
Territories: |
| Winter Olympic Games host cities | |
|---|---|
| |
| Cancelled due to World War II
|