This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Future Perfect at Sunrise (talk | contribs) at 06:04, 31 March 2009 (standard naming). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 06:04, 31 March 2009 by Future Perfect at Sunrise (talk | contribs) (standard naming)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) | |
| Continent | Europe |
|---|---|
| Region | South Europe (Balkan Peninsula) |
| Coordinates | 39°00′N 22°00′E / 39.000°N 22.000°E / 39.000; 22.000 |
| Area | Ranked 96th |
| • Total | 131,940 km (50,940 sq mi) |
| • Land | 99.1% |
| • Water | 0.9% |
| Coastline | 15,021 km (9,334 mi) |
| Borders | Total land borders: 1,935 km (1,201.635 miles) Albania: 282 km (175.122 miles) Bulgaria: 494 km (306.774 miles) Turkey: 931 km (578.151 miles) Rep. Macedonia: 228 km (141.588 miles) |
| Highest point | Mount Olympus: 2,919 m |
| Lowest point | Mediterranean Sea: 0 m |
| Longest river | Haliacmon: 322 km (200 miles) |
| Largest lake | Trichonida: 98.6 km² (38 miles²) |
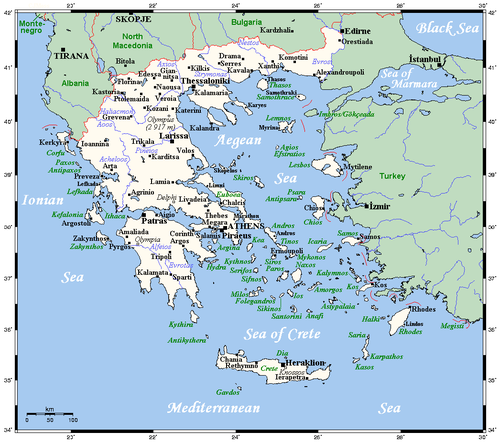
The country of Greece is located in southern Europe, on the southern end of the Balkan peninsula. Greece is surrounded on the north by Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia and Albania; to the west by the Ionian Sea; to the south by the Mediterranean Sea and to the east by the Aegean Sea and Turkey. The country ranges approximately in latitude from 35°00′N to 42°00′N and in longitude from 19°00′E to 28°30′E. As a result, it has considerable climatic variation, as discussed below. The country consists of a large mainland; the Peloponnese, a peninsula connected to the southern tip of the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth; and around 3000 islands, including Crete, Rhodes, Corfu, the Dodecanese and the Cyclades. Greece has 15000 kilometres (9300 miles) of coastline.
80% of Greece is mountainous, and the country is one of the most mountainous countries of Europe. The Pindus chain of mountain lies across the center of the country in a northwest-to-southeast direction, with a maximum elevation of 2 637 m. Extensions of the same mountain range stretch across the Peloponnese and underwater across the Aegean, forming many of the Aegean islands including Crete, and joining with the Taurus Mountains of southern Turkey. Central and Western Greece contain high and steep peaks dissected by many canyons and other karstic landscapes, including the Meteora and the Vikos Gorges - the latter being one of the largest of the world and the second deepest after the Grand Canyon, plunging vertically for more than 1100 meters. Mount Olympus is the highest point of Greece and the fourth highest in relative topographical prominence in Europe, rising to 2 919 m above sea level. The Rhodope Mountains form the border between Greece and Bulgaria; that area is covered with vast and thick forests. Plains also are found in Eastern Thessaly, in central Macedonia and in Thrace. Western Greece contains lakes and wetlands.
Climate
Greece's climate is divided into three classes:
- A Mediterranean climate features mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Temperatures rarely reach extremes, although snowfalls do occur occasionally even in Athens, Cyclades or Crete during the winter.
- An alpine climate is found primarily in Western Greece (Epirus, Central Greece, Thessaly, Western Macedonia as well as central parts of the Peloponnese like Achaea, Arkadia and parts of Lakonia where the Alpine range pass by).
- A temperate climate is found in Central and Eastern Macedonia as well as in Thrace at places like Komotini, Xanthi and northern Evros; with cold, damp winters and hot, dry summers.
The southern suburbs of Athens are in the Mediterranean zone, while northern suburbs have a temperate climate.
Details
|
|
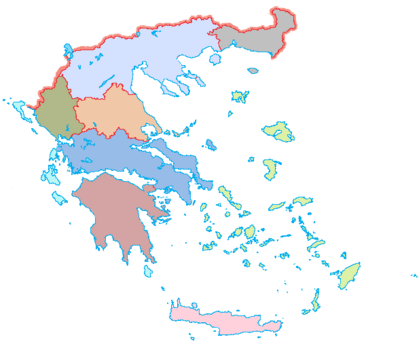
| Cities and islands of Greece |
Location:
Southern Europe, bordering the Ionian Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea, between Albania and Turkey Geography - note: strategic location dominating the Aegean Sea and southern approach to Turkish Straits; a peninsular country, possessing an archipelago of about 3,000 islands. The Country can be divided in three main geographic areas. The mainland, the islands and the Aegean basin.
Area
Total:
131 940 km²
Land:
130 800 km²
Internal waters:
(Lakes and rivers): 1 140 km²
Boundaries
Land:
1 935 km
Border countries:
Albania 282 km, Bulgaria 494 km, Turkey 931 km (206 km in the Evros river at NE Greece and 725 km in the Aegean from Thrace to Rhodes), the FYR Macedonia 228 km
Coastline:
15 021 km
Maritime claims:
Continental shelf:
200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Territorial sea:
12 nautical miles (22 km)
(Turkey only recognises 6 nautical miles)
Climate
Three well defined climatological areas; Mediterranean, Alpine, and Mid-European Temperate.
Terrain
Mostly mountains with ranges extending into the sea as peninsulas or chains of islands with 13 regions. It also includes of rocky conditions and mountainous terrain. However the surrounding bodies of water fed the surplus olives and grapes in Greece.
Land use
1.) Arable land:
19%
2.) Permanent crops:
8%
3.) Forests and woodland:
50%
4.) Other:
23% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land:
13 140 km² (1993 est.)
Environment
1.) Natural hazards: severe earthquakes, droughts, wildfires
2.) Current issues: air pollution/water pollution
3.) International agreements:
party to:
Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
See also
References
- CIA World Fact Book,
| Geography of Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
| Other entities | |
Category: