This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Rjwilmsi (talk | contribs) at 21:19, 28 July 2011 (→Occurrence in nature: Journal cites:, added 1 PMID, using AWB (7794)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 21:19, 28 July 2011 by Rjwilmsi (talk | contribs) (→Occurrence in nature: Journal cites:, added 1 PMID, using AWB (7794))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Β-Carboline" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 9H-β-carboline | |
| Other names 9H-pyridoindole | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.418 |
| MeSH | norharman |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C11H8N2 |
| Molar mass | 168.20 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
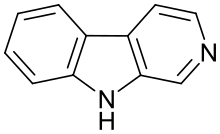
β-Carboline (9H-pyridoindole) is an organic amine that is the prototype of a class of compounds known as β-carbolines.
Pharmacology
β-Carboline alkaloids are widespread in plants and animals, and frequently act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI). As components of the liana Banisteriopsis caapi, the β-carbolines harmine, harmaline, and tetrahydroharmine play a pivotal role in the pharmacology of the indigenous hallucinogenic drug ayahuasca by preventing the breakdown of dimethyltryptamine in the gut by inhibiting monoamine oxidase, thus making it psychoactive upon oral administration. Some β-carbolines, notably tryptoline and pinoline, are formed naturally in the human body. The latter is implicated along with melatonin in the role of the pineal gland in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. The β-carboline can link to cerebral benzodiazepine receptors and induce inverse agonist effect.
United States Patent Number 5591738 describes a method for treating various chemical dependencies via the administration of beta-carbolines.
Structure
β-Carbolines belong to the group of Indole alkaloids. They consist of an indole skeleton and various side chains. The structure of β-carboline is similar to that of tryptamine, with the ethylamine chain re-connected to the indole ring via an extra carbon atom, to produce a three-ringed structure. Indeed, biosynthesis of β-carbolines is believed to follow this route from analogous tryptamines. Different levels of saturation are possible in the third ring, which is indicated here in the structural formula by colouring the optionally double bonds red and blue:
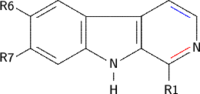
Examples of β-carbolines
Some of the more important β-carbolines are tabulated by structure below.
| Short Name | R1 | R6 | R7 | Structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Carboline |  | |||||
| Tryptoline |  | |||||
| Pinoline |  | |||||
| Harmane |  | |||||
| Harmine | 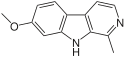 | |||||
| Harmaline |  | |||||
| Tetrahydroharmine |  |
Occurrence in nature
| This article may contain citations that do not verify the text. Please check for citation inaccuracies. (December 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
"There are presently 64 known β-carboline alkaloids dispersed throughout at least eight plant families." The seeds of Peganum harmala (Syrian Rue) are a good source of beta-carbolines, since they contain about 2-6% alkaloids, most of which is harmaline.
As a result of the presence of β-carbolines in the cuticle of scorpions, their skin is known to fluoresce when exposed to certain wavelengths of ultraviolet light such as that produced by a blacklight.
Several β-carbolines have actions opposite to those of benzodiazepines: convulsive, anxiogenic and memory enhancing.
See also
References
- ^ Method of treating chemical dependency using .beta.-carboline alkaloids, derivatives and salts thereof
- The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and its Applications. Ratsch, Christian. Park Street Press c. 2005
- www.amazing-nature.com
- Stachel, Shawn J (1999). "The fluorescence of scorpions and cataractogenesis". Chemistry & Biology. 6. Cell Press: 531–539. doi:10.1016/S1074-5521(99)80085-4. PMID 10421760. Retrieved 2008-06-17.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Venault P, Chapouthier G (2007). "From the behavioral pharmacology of beta-carbolines to seizures, anxiety, and memory". ScientificWorldJournal. 7: 204–23. doi:10.1100/tsw.2007.48. PMID 17334612.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
External links
- TiHKAL #44
- TiHKAL in general
- Beta-Carbolines at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Beta-carbolines in Coffee
- Farzin D, Mansouri N (2006). "Antidepressant-like effect of harmane and other beta-carbolines in the mouse forced swim test". Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 16 (5): 324–8. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2005.08.005. PMID 16183262.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)