This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Jc3s5h (talk | contribs) at 11:55, 27 April 2015 (Undid revision 659450467 by 156.61.250.250 (talk) Contrary to sources and talk page consensus.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 11:55, 27 April 2015 by Jc3s5h (talk | contribs) (Undid revision 659450467 by 156.61.250.250 (talk) Contrary to sources and talk page consensus.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) "GMT" redirects here. For other uses, see GMT (disambiguation). "Greenwich Time" redirects here. For the Greenwich, Connecticut, newspaper, see Greenwich Time (newspaper).| This article's factual accuracy is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help to ensure that disputed statements are reliably sourced. (April 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

| Light Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Western European Summer Time / British Summer Time / Irish Standard Time (UTC+1) | |
| Red | Central European Time (UTC+1) |
| Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) | |
| Yellow | Eastern European Time / Kaliningrad Time (UTC+2) |
| Ochre | Eastern European Time (UTC+2) |
| Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+3) | |
| Green | Moscow Time / Turkey Time (UTC+3) |
| Turquoise | Armenia Time / Azerbaijan Time / Georgia Time / Samara Time (UTC+4) |
▉▉▉ Dark colours: Summer time observed
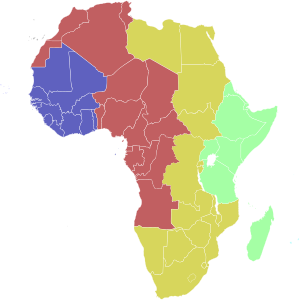
| Light Blue | Cape Verde Time (UTC−1) |
| Blue | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Red | (UTC+1) |
| Ochre | (UTC+2) |
| Green | East Africa Time (UTC+3) |
| Turquoise | (UTC+4) |
Mauritius and the Seychelles are to the east and north-east of Madagascar respectively.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) means the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London. GMT was formerly used as international civil time standard, now superseded in that function by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is always is kept within 0.9 seconds of GMT (or rather, of UT1, the successor of GMT as an astronomical standard) by inserting or removing leap seconds when necessary.
Because of Earth's uneven speed in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt, noon (12:00:00) GMT is rarely the exact moment the sun crosses the Greenwich meridian and reaches its highest point in the sky there. This event may occur up to 16 minutes before or after noon GMT, a discrepancy calculated by the equation of time. Noon GMT is the annual average (i.e. "mean") moment of this event, which accounts for the word "mean" in "Greenwich Mean Time".
Originally, astronomers considered a GMT day to start at noon, while almost everyone else it to start at midnight. To avoid confusion, the name Universal Time was introduced to denote GMT as counted from midnight. Astronomers preferred the old convention to simplify their observational data, so that each night was logged under a single calendar date. Universal Time has since been refined as UT1, an astronomical time standard used in many technical fields.
The term "GMT" is commonly misused as a synonym of UTC, especially in the United Kingdom and its institutions (such as the BBC World Service, the Royal Navy, and the Met Office); in countries of the Commonwealth, including Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, Pakistan and Malaysia; and in many other countries of the eastern hemisphere. In order to avoid ambiguity, it is preferable to use one of the modern terms rather than "GMT". In scientific and technical fields, the use of the term "GMT" has been discouraged for decades.
History
Main article: History of longitude
As the United Kingdom grew into an advanced maritime nation, British mariners kept at least one chronometer on GMT to calculate their longitude from the Greenwich meridian, which was by convention considered to have longitude zero degrees, internationally adopted in the International Meridian Conference of 1884. Synchronisation of the chronometer on GMT did not affect shipboard time, which was still solar time. But this practice, combined with mariners from other nations drawing from Nevil Maskelyne's method of lunar distances based on observations at Greenwich, led to GMT being used worldwide as a standard time independent of location. Most time zones were based upon GMT, as an offset of a number of hours (and possibly a half-hour) "ahead of GMT" or "behind GMT".
Greenwich Mean Time was adopted across the island of Great Britain by the Railway Clearing House in 1847, and by almost all railway companies by the following year, from which the term "railway time" is derived. It was gradually adopted for other purposes, but a legal case in 1858 held "local mean time" to be the official time. This changed in 1880, when Greenwich Mean Time was legally adopted throughout the island of Great Britain. GMT was adopted on the Isle of Man in 1883, Jersey in 1898 and Guernsey in 1913. Ireland adopted GMT in 1916, supplanting Dublin Mean Time. Hourly time signals from Greenwich Observatory were first broadcast on 5 February 1924, rendering the time ball at the observatory obsolete in the process.
The daily rotation of the Earth is somewhat irregular (see ΔT) and is slowing down slightly; atomic clocks constitute a much more stable timebase. On 1 January 1972, GMT was superseded as the international civil time standard by Coordinated Universal Time, maintained by an ensemble of atomic clocks around the world. Universal Time (UT), a term introduced in 1928, represents mean time at Greenwich determined in the traditional way to accord with the originally defined universal day; from 1 January 1956 (as decided by the IAU at Dublin, 1955, at the initiative of William Markowitz) this "raw" form of UT was re-labeled UT0 and effectively superseded by refined forms UT1 (UT0 equalised for the effects of polar wandering) and UT2 (UT1 further equalised for annual seasonal variations in earth rotation rate).
Indeed, even the Greenwich meridian itself is not quite what it used to be—defined by "the centre of the transit instrument at the Observatory at Greenwich". Although that instrument still survives in working order, it is no longer in use and now the meridian of origin of the world's longitude and time is not strictly defined in material form but from a statistical solution resulting from observations of all time-determination stations which the BIPM takes into account when co-ordinating the world's time signals. Nevertheless, the line in the old observatory's courtyard today differs no more than a few metres from that imaginary line which is now the prime meridian of the world.
— Howse, D. (1997). Greenwich time and the longitude. London: Philip Wilson.
Ambiguity in the definition of GMT
Historically GMT has been used with two different conventions for numbering hours. The long-standing astronomical convention dating from the work of Ptolemy, was to refer to noon as zero hours (see Julian day). This contrasted with the civil convention of referring to midnight as zero hours dating from the Romans. The latter convention was adopted on and after 1 January 1925 for astronomical purposes, resulting in a discontinuity of 12 hours, or half a day earlier. The instant that was designated 'December 31.5 GMT' in 1924 almanacs became 'January 1.0 GMT' in 1925 almanacs. The term Greenwich Mean Astronomical Time (GMAT) was introduced to unambiguously refer to the previous noon-based astronomical convention for GMT. The more specific terms UT and UTC do not share this ambiguity, always referring to midnight as zero hours.
GMT in legislation
Britain
Legally, the civil time used in the UK is called still "Greenwich mean time" (without capitalisation), according to the Interpretation Act 1978, with an exception made for those periods when the Summer Time Act 1972 orders an hour's shift for daylight saving. In practice, the civil time used in the UK is UTC+0 during winters, and UTC+1 (or British Summer Time (BST)) during summers.
The Interpretation Act 1978, section 9, provides that whenever an expression of time occurs in an Act, the time referred to shall (unless otherwise specifically stated) be held to be Greenwich mean time. Under subsection 23(3), the same rule applies to deeds and other instruments.
During the experiment of 1968-1971, when the British Isles did not revert to UTC+0 during the winter, the continuously used time zone UTC+1 was called British Standard Time (BST), although by definition Standard Time means a time zone with no offset.
In Britain, UTC+0 is disseminated to the general public in winter and UTC+1 in summer, normally by means of the "six pips" broadcast on the hour before selected news bulletins. However, under proposals by the British government to switch off the analogue radio signal, this method is under threat because there is a delay of up to several seconds between the sending and receipt of the signal using digital radio. The radio signal is termed the "Greenwich Time Signal" irrespective of whether the timezone in use is UTC+0 (during winters) or UTC+1 (during summers).
other countries
Several countries define their local time by reference to Greenwich Mean Time. Some examples are:
- Belgium: Decrees of 1946 and 1947 set legal time as one hour ahead of GMT.
- Ireland: Standard Time (Amendment) Act, 1971, section 1, and Interpretation Act 2005, part iv, section 18(i).
- Canada: Interpretation Act, R.S.C. 1985, c. I-21, section 35(1). This refers to 'standard time' for the several provinces, defining each in relation to 'Greenwich time', but does not use the expression 'Greenwich mean time'. Several provinces, such as Nova Scotia (Time Definition Act. R.S., c. 469, s. 1), have their own legislation which specifically mentions either "Greenwich Mean Time" or "Greenwich mean solar time".
Time zone
Those countries marked in dark blue on the map above use BST/Western European Summer Time and advance their clock one hour in summer. In the United Kingdom, this is British Summer Time (BST); in the Republic of Ireland it is called Irish Standard Time (IST)—officially changing to GMT in winter. Those countries marked in light blue keep their clocks on UTC/GMT/WET year round.
Discrepancies between legal GMT and geographical GMT
| Colour | Legal time vs local mean time |
|---|---|
| 1 h ± 30 m behind | |
| 0 h ± 30 m | |
| 1 h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 2 h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 3 h ± 30 m ahead |
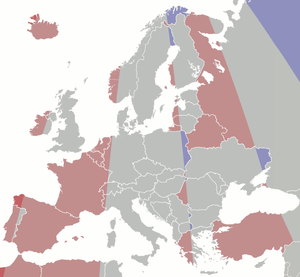
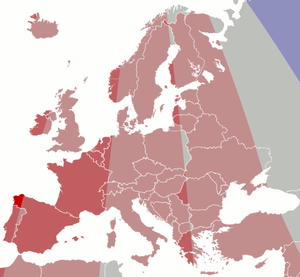
Since legal, political, social and economic criteria in addition to physical or geographical criteria are used in the drawing of time zones, actual time zones do not precisely adhere to meridian lines. The 'GMT' time zone, were it drawn by purely geographical terms, would consist of the area between meridians 7°30'W and 7°30'E. As a result, there are European locales that despite lying in an area with a 'physical' UTC time use another time zone (UTC+1 in particular); conversely, there are European areas that use UTC, even though their 'physical' time zone is UTC−1 (e.g., most of Portugal), or UTC−2 (the westernmost part of Iceland). Because the UTC time zone in Europe is 'shifted' to the west, Lowestoft in Suffolk, East Anglia, England at only 1°45'E is the easternmost settlement in Europe in which UTC is applied. Following is a list of the 'incongruencies':
- Countries (or parts thereof) west of 22°30'W ("physical" UTC−2) that use UTC
- The westernmost part of Iceland, including the northwest peninsula and its main town of Ísafjörður, which is west of 22°30'W, uses UTC. Bjargtangar, Iceland is the westernmost point in which UTC is applied.
- Countries (or parts thereof) west of 7°30'W ("physical" UTC−1) that use UTC
- Canary Islands (Spain)
- Most of Portugal, including Lisbon, Porto, Braga, Aveiro, and Coimbra. (Only the easternmost part, including cities such as Bragança and Guarda, lies east of 7°30'W.) Since the Treaty of Windsor in 1386 (the world's oldest diplomatic alliance), Portugal has maintained close ties to Britain, which possibly explains its choice of UTC. Madeira, even further to the west, also employs UTC. A more likely explanation is that during the mid-1970s, when Portugal was on Central European Time all year round, it did not begin to get light in Lisbon in winter until 08:30.
- Western part of Ireland, including the cities of Cork, Limerick, and Galway.
- Westernmost tip of Northern Ireland, including the county town of County Fermanagh, Enniskillen
- Extreme westerly portion of the Outer Hebrides, west of Scotland; for instance, Vatersay, an inhabited island and the westernmost settlement in Great Britain, lies at 7°54'W. If uninhabited islands or rocks are taken into account St Kilda, west of the Outer Hebrides, at 8°58'W, and Rockall, at 13°41'W, should be included.
- Westernmost island of the Faroe Islands (autonomous region of the Danish Kingdom), Mykines
- Iceland, including Reykjavík
- Northeastern part of Greenland, including Danmarkshavn

- Countries (mostly) between meridians 7°30'W and 7°30'E ("physical" UTC) that use UTC+1
- Spain (except for the Canary Islands, which use UTC). Parts of Galicia lie west of 7°30'W ('physical' UTC−1), whereas there is no Spanish territory east of 7°30'E ('physical' UTC+1). Spain's time is the direct result of Franco's Presidential Order (published in Boletín Oficial del Estado of 8 March 1940) abandoning Greenwich Mean Time and advancing clocks one hour effective 23:00 16 March 1940. This is an excellent example of political criteria used in the drawing of time zones: the time change was passed "in consideration of the convenience from the national time marching in step according to that of other European countries". The Presidential Order (most likely enacted to be in synchrony with Germany and Italy, with which the Franco regime was unofficially allied) included in its 5th article a provision for its future phase out, which never took place. Due to this political decision Spain is two hours ahead of its local mean time during the summer, one hour ahead in winter, which possibly explains the notoriously late schedule for which the country is known. In Portugal, which is a mere one hour behind Spain, the timetable is quite different.
- Most of France, including the cities of Paris, Marseilles and Lyon. Only small parts of Alsace, Lorraine and Provence are east of 7°30'E ("physical" UTC+1).
- Monaco
- Andorra
- Belgium
- Netherlands
- Luxembourg
See also
- 24-hour watch—24-hour wristwatch
- Radio clock
- Marine chronometer—synchronised with GMT, and used by ships to calculate their longitude
- Sandringham Time
- Swatch Internet Time—alternative, decimal measure of time
- Western European Summer Time
Notes
- Hart-Davis, Adam (2011). The Book of Time. London. p. 159. ISBN 978-1-84533-561-8.
UTC is kept within 1 second of GMT by the addition of the occasional leap second.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Whitaker's Almanac 2015. London. 2014. p. 1118. ISBN 978-1-4729-0929-9.
Before 1925 GMT was reckoned in 24 hours commencing at noon; since that date it has been reckoned from midnight. To avoid confusion in the use of the designation GMT before and after 1925, since 1928 astronomers have tended to use the term Universal Time (UT) or Weltzeit (WZ) to denote GMT measured from Greenwich Mean Midnight.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Seidelman, P. Kenneth. (2013). "Introduction to Positional Astronomy" in Sean E. Urban and P. Kenneth Seidelman, Eds. Explananatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac 3rd ed. Mill Valley, CA: University Science Books p. 14. "In the past, the term "Greenwich Mean Time" (GMT) has been used for UTC and UT1. It remains the basis of the civil time for the United Kingdom, and as such, is related to UTC. However, in navigational terminology, GMT means Universal Time. For precise purposes it is recommended that the term "GMT" not be used, since it is ambiguous."
- Greenwich Mean Time, available at .
- What is GMT? at the BBC Radio World Service.
- McCarty and Seidelmann (p. 17) devote most of a page explaining why "the use of the term 'Greenwich Mean Time' or its abbreviation 'GMT' remains a source of confusion today." They point out several times when respected authorities have stopped using GMT or recommended that GMT should no longer be used: the IAU in 1928, the 1939 American Ephemeris, astronomical almanacs after 1960, and another recommendation from the IAU in 1976.
- ^ Myers (2007).
- UT1 as explained on IERS page
- Astronomical Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac. University Science Books. 1992. p. 76. ISBN 0-935702-68-7.
- Howse 1997, p. 157.
- McCarthy & Seidelmann 2009, p. 17.
- ^ Dumortier, Hannelore, & Loncke (n.d.)
- Seago & Seidelmann (c. 2001)
- Standard Time Act, 1968.
- "BOE Orden sobre adelanto de la hora legal en 60 minutos". Retrieved 2 December 2008.
- "B.O.E. #68 03/08/1940 p.1675". Retrieved 2 December 2008.
- ^ "B.O.E. #68 03/08/1940 p.1676". Retrieved 2 December 2008.
- "Hábitos y horarios españoles". Retrieved 27 November 2008.
References
- Dumortier, J, Hannelore, D, & Loncke, M. (n.d.). "Legal Aspects of Trusted Time services in Europe". AMANO. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- Guinot, Bernard (August 2011). "Solar time, legal time, time in use". Metrologica 48 (4): S181–185. Bibcode:2011Metro..48S.181G. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/48/4/S08.
- Howse, D. (1997). Greenwich time and the longitude. London: Philip Wilson.
- Interpretation Act, R.S.C. 1985, c. I-21. (2005). CanLII. (Canadian statute)
- Interpretation Act 1978. UK Law Statute Database. (UK statute)
- Interpretation Act 2005. British and Irish Legal Information Institute. (Irish statute)
- McCarthy, D., and Seidelmann, P. K. (2009). TIME—From Earth Rotation to Atomic Physics. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
- Myers, J. (2007). History of legal time in Britain. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- Seago, J.H., & Seidelmann, P. K. (c. 2001). National Legal Requirements for Coordinating with Universal Time. Steve Allen of University of California Observatories. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- "Six pip salute". BBC News. Retrieved 9 July 2009.
- Standard Time Act, 1968. Irish Statute Book. Office of the Attorney General. (Irish statute)
- Standard Time (Amendment) Act, 1971. British and Irish Legal Information Institute. (Irish statute)
External links
- Greenwich Mean Time
- World Time Zone Map with current time
- International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service
- Royal Observatory, Greenwich
- The original BBC World Service GMT time signal in mp3 format
- Rodgers, Lucy (20 October 2009). "At the centre of time". BBC News. Retrieved 20 October 2009.
| Time measurement and standards | ||
|---|---|---|
| International standards |
|   |
| Obsolete standards | ||
| Time in physics | ||
| Horology | ||
| Calendar | ||
| Archaeology and geology | ||
| Astronomical chronology | ||
| Other units of time | ||
| Related topics | ||
Categories: