This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Dr.K. (talk | contribs) at 15:55, 28 January 2022 (Undid revision 1061784531 by 83.240.63.186 (talk) Not part of the cited definition). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:55, 28 January 2022 by Dr.K. (talk | contribs) (Undid revision 1061784531 by 83.240.63.186 (talk) Not part of the cited definition)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Knife used to remove body hair
A straight razor is a razor with a blade that can fold into its handle. They are also called open razors and cut-throat razors. The predecessors of the modern straight razors include bronze razors, with cutting edges and fixed handles, produced by craftsmen from Ancient Egypt during the New Kingdom (1569 — 1081 BC). Solid gold and copper razors were also found in Ancient Egyptian tombs dating back to the 4th millennium BC.
The first steel-edged cutthroat razors were manufactured in Sheffield in 1680. By the late 1680s, early 1690s, razors with silver-covered handles along with other Sheffield-made products known as "Sheffield wares" were being exported to ports in the Gulf of Finland, approximately 1200 miles (1931km) from Sheffield. From there, these goods were probably sent to Finland and even Russia. By 1740, Benjamin Huntsman was making straight razors complete with decorated handles and hollow-ground blades made from cast steel, using a process he invented. Huntsman's process was adopted by the French sometime later, albeit reluctantly at first due to nationalist considerations. In England, razor manufacturers were even more reluctant than the French to adopt Huntsman's steel-making process and only did so after they saw its success in France.
After their introduction in 1680, straight razors became the principal method of manual shaving for more than two hundred years, and remained in common use until the mid-20th century. Straight razor production eventually fell behind that of the safety razor, which was introduced in the late 19th century and featured a disposable blade. Electric razors have also reduced the market share of the straight razors, especially since the 1950s. A 1979 comparative study of straight and electric razors, performed by Dutch researchers, found that straight razors shave hair approximately 0.002 in. (0.05mm) shorter than electrics.
Since 2012, production of straight razors has increased multifold. Straight razor sales are increasing globally and manufacturers have difficulty satisfying demand. Sales started increasing since the product was featured in the 2012 James Bond film Skyfall and have remained high since. Straight razors are also perceived as a better value and a more sustainable and efficient product. Dovo in Germany reports that since a production low of less than 8,000 units per year in 2006, the company sells 3,000 units per month, and has 110,000 orders with production lead time of three years. The increased sales have also led to an increase in the number of associated trades and artisans such as bladesmiths, leather craftsmen, and potters.
Forums and outlets provide products, directions, and advice to straight razor users. Straight razor manufacturers exist in Europe, Asia, and North America. Antique straight razors are also actively traded. Straight razors require considerable skill to hone and strop, and require more care during shaving. Straight razor design and use was once a major portion of the curriculum in barber colleges.
History

Various forms of razors were used throughout history, which are different in appearance but similar in use to modern straight razors. In prehistoric times clam shells, shark's teeth, and flint were sharpened and used to shave with. Drawings of such blades were found in prehistoric caves. Some tribes still use blades made of flint to this day. Excavations in Egypt have unearthed solid gold and copper razors in tombs dating back to the 4th millennium BC. The Roman historian Livy reported that the razor was introduced in ancient Rome in the 6th century BC by legendary king Lucius Tarquinius Priscus. Priscus was ahead of his time because razors did not come to general use until a century later.
The first narrow-bladed folding straight razors were listed by a Sheffield, England manufacturer in 1680. By the late 1680s, early 1690s, razors with silver-covered handles along with other Sheffield-made products known as "Sheffield wares" were being exported by John Spencer (1655—1729) of Cannon Hall, a wealthy landowner and industrialist, to ports in the Gulf of Finland, approximately 1200 miles (1931km) from Sheffield. From there, these goods were probably sent to Finland and even Russia. By 1740, Benjamin Huntsman was making straight razors complete with decorated handles and hollow-ground blades made from cast steel, using a process he invented. Huntsman's process was adopted by the French sometime later; albeit reluctantly at first due to nationalist sentiments. The English manufacturers were even more reluctant than the French to adopt the process and only did so after they saw its success in France.

Sheffield steel, a highly polished steel, also known as 'Sheffield silver steel' and famous for its deep gloss finish, is considered a superior quality steel and is still used to this day in France by such manufacturers as Thiers Issard. After their introduction in 1680, straight razors became the principal method of manual shaving for more than two hundred years, and remained in common use until the mid-20th century. Electric razors have also cut into the straight razor's market share, especially since the 1950s.
Straight razors eventually fell out of fashion. Their first challenger was manufactured by King C. Gillette: a double-edged safety razor with replaceable blades. These new safety razors did not require any serious tutelage to use. The blades were extremely hard to sharpen, and were meant to be thrown away after one use, and rusted quickly if not discarded. They also required a smaller initial investment, although they cost more over time. Despite its long-term advantages, the straight razor lost significant market share. As shaving became less intimidating and men began to shave themselves more, the demand for barbers providing straight razor shaves decreased.
Since 2012, production of straight razors has increased multifold. Straight razor sales are increasing globally and manufacturers have difficulty satisfying demand. Straight razor sales are increasing because they are perceived as a better value and more efficient product.
Dovo in Germany reports that since a production low of less than 8,000 units per year in 2006, the company sells 3,000 units per month, and has 110,000 orders with production lead time of three years. The Dovo spokesman commented that around 2006, “we were producing less than 8,000 straight razors per year, The tradition of straight razor manufacturing had almost come to an end.” Dovo explains, that after the 2012 James Bond film Skyfall, sales of straight razors increased multifold, and that "built into a wave of sustained overdemand that we are still riding today". The increased sales have also led to an increase in the number of associated trades and artisans such as bladesmiths, leather craftsmen, and potters.
Design criteria
The design of the straight razor is based on the grind of the blade, the width and length of the blade, the handle, which also affects the balance of the razor, the material of the blade, and the finish and degree of polish of the blade material.
Parts description

The parts of a straight razor and their function are described as follows: The narrow end of the blade rotates on a pin called the pivot, between two protective pieces called the scales or handle. The upward curved metal end of the narrow part of the blade beyond the pivot is called the tang and acts as a lever to help raise the blade from the handle. One or two fingers resting on the tang also help stabilize the blade while shaving. The narrow support piece between the tang and the main blade is called the shank, but this reference is often avoided because it can be confusing since the shank is also referred to as tang. The shank sometimes features decorations and the stamp of the brand. The top side and the underside of the shank can sometimes exhibit indentations known as fluting, or jimps for a more secure grip. The curved lower part of the main blade from the shank to the cutting edge is called the shoulder. The point where the shoulder joins the cutting edge is called the heel. The endpoint of the cutting edge at the front of the blade, opposite to the heel, is called the toe.

A thick strip of metal running transversely at the junction where the main blade attaches to the shank is called the stabiliser. The stabiliser can be double, single, or can be absent in some razor models. The first stabiliser is usually very narrow and thicker and runs at the shank-to-blade junction, covering the shank and just spilling over to the shoulder. The second stabiliser can be distinguished since it is considerably wider, thinner, and longer, appearing after the first stabiliser and running lower toward the heel.
The arched, non-cutting top of the blade is called the back or the spine while the cutting part of the blade opposite the back is called the cutting edge. Finally the other free end of the blade, at the opposite end of the tang on the spine, is called the point and, sometimes, the head or the nose.
There are usually two, but sometimes three, pins in the handle. The middle pin, if present, is plastic coated and is called the centre plug. Its function is to stabilise the sides of the handle so that they cannot be squeezed in the middle and acts as a bridge between them. When folded into the scales, the blade is protected from accidental damage, and the user is protected from accidental injury. During folding, the back of the blade, being thick and normally with a curved cross-section, acts as a natural stopper and prevents further rotation of the blade out of the handle from the other side. The frictional force between the scales and the tang applied about the pivot is called the Tension and it determines how freely the blade rotates about the point of rotation. A proper amount of tension should be present, for safety reasons, to ensure that the blade does not spin freely when opening or closing.
Construction
Straight razors consist of a blade sharpened on one edge and a handle attached to the blade through a pin. The blade can then rotate in and out of the handle. The blade can be made of either stainless steel, which is resistant to rust but can be more difficult to hone, or high-carbon steel, which is much easier to hone, obtains a sharper edge but will rust more easily than stainless steel if neglected. Cheap stainless steel straight razors from Asia and more expensive stainless steel and carbon steel razors from Europe are available.
A razor blade starts as a shape called the blank supplied by the steel manufacturer.
Forging

The blank of the blade is produced by forging steel ingots or steel available in other forms such as wire, springs, etc.. After the blank is formed, the first step is to clean it using a heavy forge. The material used for open razors is steel with a minimum carbon content of 0.6%. This percentage of carbon content ensures optimum hardness, flexibility and resistance to wear. Following the forging stage, a hole is drilled in the tang at the pivot point. This is a crucial step, since after the steel hardening process it would be impossible to drill. This process requires great skill.
Hardening and tempering
The steel is hardened through a special process where the forged steel blade is heated up to approximately 760 °C (1,400 °F) dependent on the specific steel. This heating enables fast and uniform heating of the steel at the optimum temperature for maximum hardness. The tempering stage follows the hardening process, where the blade is heated in a bath of oil at a temperature between 200–400 °C (392–752 °F). Tempering imparts the steel its flexibility and toughness according to the phase diagrams for steel. There are three types of steel blade according to the level of tempering it has received. Hard-tempered, medium-tempered and soft-tempered. Hard-tempered edges last longer but sharpening them is difficult. The converse is true for soft-tempered blades. The characteristics of medium-tempered blades are in-between the two extremes. Carbon steel blades can reach a maximum hardness of 61 HRC on a Rockwell scale.
Grinding
Following the processes of hardening and tempering, the blanks are ground, according to the two fundamental blade cross sectional area profiles.
Finishing

Subsequent to grinding, the blade is polished to various degrees of gloss. The finest finish, used in the most expensive razors, is the mirror finish. Mirror finish is the only finish used if gold leafing is to be part of the decoration of the blade.
Satin finish requires less polishing time and therefore is not as expensive to produce. This finish is mostly used with black acid etching. Satin finish can sometimes be applied, as a compromise, to the back of the blade while the mirror finish and gold leafing are applied to the more visible front of the blade. This way the blade will not be as expensive as a fully mirror finished one. Metal plating, using nickel or silver, is also used, but it is not preferred; the plating eventually erodes through use, revealing the underlying metal, which is often of inferior quality. Nickel-plated blades are very difficult to hone repeatedly and are made for mainly aesthetic reasons though lacking functionality.
Blade decoration
The blade is decorated by engraving or gold leafing depending on the price. Less expensive blades undergo an electrolytic black acid engraving process. For more expensive blades, gold leafing applied by hand is employed, following a traditional process.
Sharpening

Sharpening is the final stage in the process. At first the blade is sharpened on a grinding wheel. Following that the blade can be honed by holding the blades against the flat side of rotating round stones, or by drawing the blade across stationary flat stones. The cutting edge is finished using a strop. Sharpening is usually not completed during manufacturing, instead being done after purchase.
Handle materials and their properties

Handle scales are made of various materials, including mother-of-pearl, Bakelite, celluloid, bone, plastic, wood, horn, acrylic, ivory and tortoise shell. Celluloid can spontaneously combust at elevated temperatures. Buffalo horn tends to deform with time and it possesses form memory so it tends to warp. Mother of pearl is a brittle material and can exhibit cracks after some use. Resin impregnated wooden handles are water resistant, do not deform and their weight complements the blade's to provide good overall balance for the razor. Snakewood, Brosimum guianense, is also suitable for long term and intensive use.
The mechanical properties of bone make it a good handle material. Handles were once made of elephant ivory, but this has been discontinued, though fossil ivory, such as mammoth, is still sometimes used, and antique razors with ivory scales are occasionally found (it is illegal to kill elephants for their ivory, but it is legal to buy an ivory-handled razor made before 1989).
Blade geometry and characteristics
The geometry of the blade can be categorised according to the following three factors: First according to the shape of the profile of the point of the razor, second according to the type of grinding method used for the blade; the degree of curvature, and therefore hollowness (or thinness), of the sides of the cross section of the razor blade depends on the grinding method. Finally the blades are categorised according to their width and weight.
Point types

Straight razors are, at first, categorised according to their blade profiles, from the head of the spine to the blade toe, based on their point, or nose, type. The following are the main types of blade profiles called points, or nose shapes:
- Square, spike or sharp point, so-called because the blade profile is straight and terminates at a very sharp point at the toe, perpendicular to the cutting edge of the razor. This type of blade is used for precise shaving in small areas but, at the risk of pinching the skin, it requires some experience in handling. Spike point differs from square point as the angle at the edge of the blade is less than 90 degrees. resulting in a blade profile which appears slanted backwards at the toe. The spike end point of the profile at the toe may be ground by the user to make it rounder, but that may indicate a lack of skill in handling the razor.
- Barber's notch. The Barber's notch point features a large rounded tip at the toe of the blade followed by a short concave and rounded arch, while its upper edge at the head of the spine is rounded and smaller in size than the curve at the toe. The upper, rounded, edge of Barber's notch was designed to aid in pulling the blade from the scales. Barber's notch is essentially a round-nose blade profile with a concave arch (notch) on its upper part to aid in lifting the blade from the scales.
- Round point (or Dutch). As the name implies the point profile is symmetrically curved from head to toe in a circular arc shape and therefore it lacks any sharp end points. As such it is a more forgiving blade than the other types and, although lacking pinpoint accuracy at the blade toe, it is more forgiving, and is recommended for relatively inexperienced users. There are also secondary edge types that derive from a combination of round nose characteristics, such as half round point incorporating round edges joined by a linear segment.
- French (or oblique) point. Its point profile is asymmetrically curved from head to toe, and resembles a quarter circle or ellipse, but with a sharper-angled curve near the head of the blade than the other points. The end line of the profile, at the toe of the blade, can vary between spike and curved. Compared to the rest of the points, the French point may help shave "difficult spots" such as under the nose, due to its sharply angular profile at the head which creates more clearance in tight areas.
- Spanish point. The profile of the Spanish point has a small, rounded tip at the head, followed by a long concave arch, ending in a small rounded edge at the toe. This point should be used with care when shaving or stropping, as it tends to "bite" due to its pronounced edges.
Grinding method

The second category refers to the type of grinding method used and, since it affects the curvature of the blade cross section, includes the following two main types of blade grinds:
- Hollow grind, indicating that the sides of the blade cross section are concave.
- Flat or straight grind, indicating that the sides of the blade cross section are linear. This cross section most closely resembles a wedge and therefore this blade is sometimes called the wedge.
The combination of the types found in these two classification categories can, in theory, lead to a wide variety of blade types such as round point hollow ground, square point flat ground etc., but in practice some points are combined with a specific grind. As an example, a French point blade is usually flat ground.
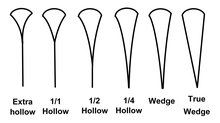
A hollow grind produces a thinner blade than the flat grind because it removes more material from the blade (hollows or thins the blade more). The hollow-ground blade flexes more easily and provides more feedback on the resistance the blade meets while cutting the hair, which is an indicator of blade sharpness. Hollow-ground blades are preferred by most barbers and some high-end razor manufacturers limit their production exclusively to hollow ground razors.
Blade width

The third and final category refers to blade width. The width of the blade is defined as the distance between the back of the blade and the cutting edge. It is expressed in units of eighth of an inch. The sizes vary from 3⁄8 in (9.5 mm) up to 7⁄8 in (22 mm), rarely 8⁄8 in (25 mm). A wider blade can carry more lather, much like a scoop, during multiple successive shaving strokes and thus it allows the user more shaving time and minimises blade rinse cycles. The disadvantage of the wider blade is that it is not as manoeuvrable as a narrower blade. A narrow blade can shave tight facial spots such as under the nose, but it must be rinsed more often. The most popular blade width size is 5⁄8 in (16 mm). The width of the blade can also affect its sharpness. The wider the blade, the greater the thermal deformation that can occur due to changing temperatures, a fact that can lead to loss of edge sharpness.
Blade weight
The weight of the blade is inversely proportional to the pressure that is applied during shaving. The heavier the blade, the lighter the pressure that needs to be applied during shaving.
Length, stability, and balance
The degree of hollowness and thus the cross sectional area (thickness) of the blade vary depending on the grinding method used. Higher degree of hollowness in the blade implies a thinner cross section and this affects the stability (bending or buckling properties) of the blade; the thinner the blade the more flexible it is. The length and weight of the blade and handle and their relation to each other determines the balance of the straight razor. The cutting area of the razor is proportional to the length of the blade, therefore, a longer blade requires less frequent honing since its cutting edge does not deplete as fast as that of a shorter blade.
Transverse stabiliser

For hollow-ground blades stability is augmented by a transverse stabiliser in the form of one or two narrow strips of thicker metal running from the back of the blade to the end of the shoulder (at the junction where the blade meets the shank). This piece, if present, is simply called the stabiliser (single or double) and indicates a hollow ground blade, since a flat ground blade is massive and stable enough to not need a stabiliser. A double stabiliser implies 1⁄1 (full) hollow ground blade. The stabiliser protects the blade from torsional bending in the transverse direction (transverse spine).
Longitudinal stabiliser

In addition to the transverse stabiliser, a longitudinal stabiliser is sometimes created in the form of a ridge parallel to the cutting edge and the blade is ground in two areas or bevels, each with different degrees of hollowness or curvature; the area between the back of the blade and the ridge is typically less hollow featuring a larger radius of curvature, also called the "belly", and the area between the ridge and the cutting edge which is more hollow i.e. with a smaller radius of curvature. These two beveled areas have different curvatures and in a well-made razor they transition seamlessly in the ridge (belly) and the cutting edge respectively. Sometimes there are three bevels.
The ridge stabilizes the blade against torsional flexing in a direction perpendicular to its longitudinal axis by acting as a lengthwise spine for the blade. The distance between the ridge and the back of the blade is inversely proportional to the hollowness of the blade and is described in fractional terms in ascending steps of 1⁄4 as, for example, 1⁄4 hollow, 1⁄2 hollow, or 4⁄4 or 1⁄1 (full hollow). Full hollow indicates that the stabilizing ridge is very close to the midsection of the blade and the farthest from the cutting edge compared to the other grades. This is considered the most expensive blade.
At the highest end of hollow ground, more hollow than even the 1⁄1 grade, is the so-called singing razor, so named because its blade produces a specific resonant tone when plucked, similar to a guitar string, however such use is not recommended as it can distort the cutting edge. Its manufacturing process is so demanding that a full 25% of the blades get rejected as not meeting standards.
Stability and sharpness

There is a tradeoff between stability and long term blade sharpness. A full hollow ground (1⁄1) blade can keep a very sharp edge even after a great number of honing cycles because of its high degree of hollowness but it is more susceptible to torsional bending because it is thinner. A partially hollow blade (1⁄2 or 1⁄4 for example) cannot sustain the same degree of sharpness for as long, because as the cutting edge erodes it can eventually reach the stabilising ridge faster where there is more material and thus the cutting-edge bevel cannot be maintained without excessive honing of the stabilising ridge to remove the additional material, which could also destabilise the rest of the blade. However, the partially hollow blade is more stable because its additional material makes it stiffer, and thus more resistant to deformation. In addition a flat ground blade, since by definition is not hollow (curved) at all, is the most stable of the blades but because its cross sectional area is the largest it also feels heavier than hollow ground and this can affect the feel and balance of the razor.
Balance
A razor is well balanced if when opened it balances about its pivot pin, indicating that the torques about the pivot point, caused by the corresponding weight distributions of the blade and the handle about the pivot pin, counterbalance each other. A well-balanced razor is both safer to handle when open and easier to shave with.
Effects of blade geometry on performance
The characteristics of each blade type determine the type of recommended uses for each blade as well as their performance and maintenance routines.
Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses depending on the requirements of use.

Extra hollow blades such as singing blades are the thinnest and therefore they provide the best possible shave from all the other types. However they are also very flexible and therefore not suitable for tasks requiring increased pressure to the blade such as heavy beard growth etc. Care should also be taken when stropping so that the thin blade will not be overly stressed, since it cannot withstand abuse as well as lower grades. Flat ground razors are very stable and as such they can handle tough shaving jobs since they do not easily deform under pressure and they can take rough handling such as heavy stropping and honing.
Although a wider blade is not as manoeuvreable as a narrower one, especially in tight spots, it is better to purchase a wider blade, since honing eventually reduces the width of the blade with use, a fact that can shorten the life of a straight razor with a narrow blade. On the other hand, the width of the blade is proportional to the blade distortion that can occur due to temperature fluctuations; this can lead to more frequent stropping and honing, because blade deformation due to thermal stress can lead to loss of cutting edge sharpness.
Usage

Shaving is done with the blade at approximately an angle of thirty degrees to the skin and in a direction perpendicular to the edge; an incision requires the movement of the blade to be sideways or in a direction parallel to the edge. These circumstances are always avoided by the shaver, who always shaves in a direction perpendicular to the cutting edge of the blade.
To be most effective, a straight razor must be kept extremely sharp. The edge is delicate, and inexpert use may bend or fold over the razor's edge. To unfold and straighten the microscopic sharp edge, one must strop the blade on leather periodically. A 1979 comparative study of straight and electric razors, performed by Dutch researchers, found that straight razors shave hair approximately 2/1000 in. (0.05mm) shorter than electrics.
To sharpen or finish the blade using a suspended strop, the razor is pushed toward the suspension ring while both the back and the cutting edge lie flat on the strop and with the back of the blade. No pressure should be applied on the cutting edge. A strop may be two sided with leather on one side and cloth on the other side. The cloth is used for blade alignment and sharpening. The leather is for finishing.

The stropping process involves sliding the razor blade flat on the strop; upon reaching the end of the cloth or leather near the suspension ring, the blade is turned about its back (clockwise for a right-handed barber; counter-clockwise for a left-handed one) until the cutting edge touches the strop. It is then pulled toward the rectangular handle of the strop with back and cutting edge flat on the strop as before. The blade is moved in a slightly diagonal direction so to give every point of the edge a chance to touch the strop, without applying too much pressure. This process aligns the cutting edge properly with the back of the blade, avoiding "bumps" on the cutting edge. Rotating the blade on the strop about the cutting edge can damage it because such use will impact the micro-alignment of the edge. Depending on use and condition, the blade can be sharpened occasionally by using a razor hone. Strops prepared with pastes containing fine grit are also used for honing but are not recommended for the inexperienced user, as they can easily rake off the edge if they apply the wrong amount or exert too much pressure.
Some strops have a linen or canvas back.
Shaving soap in a cup is traditionally lathered and applied using a rotating in-and-out motion of a shaving brush, usually made of boar or badger bristles. In the heyday of straight razor shaving, wealthy users maintained a weekly "rotation" of seven razors to reduce wear on any one piece. Straight razors were often sold in special boxes of seven labelled for the days of the week.
Modern use


Straight razors are still manufactured. DOVO, of Solingen, Germany, and Thiers Issard of France are two of the best-known European manufacturers. Boeker of Solingen is yet another cutlery manufacturer known for their straight razors. Wusthof and Henckels are two prominent knife manufacturers in Solingen who also produced straight razors. Thiers Issard and Hart Steel are famous for their decorated blades and their Damascus steel. Feather Safety Razor Co. Ltd. of Osaka, Japan, makes a razor with the same form as a traditional straight, but featuring a disposable blade that can be installed through an injector-type system. Artisans also make handcrafted custom straight razors based on their own designs, the designs of their customers, or by finishing old blanks of blades.
Modern straight-razor users are known to favor them for a variety of reasons. Some are attracted to the nostalgia of using old and traditional methods of shaving. Others wish to avoid the waste of disposable blades.
Still others argue that straight razors provide a superior shave through a larger blade and greater control of the blade, including the blade angle. Straight razors cover a much greater area per shaving stroke, because their cutting edge is much longer than any of the multi-blade razors.
They also do not have to be rinsed as often, because their blade acts like a scoop and carries the lather on it during multiple shaving strokes, while the multi-blade razors are not nearly as efficient at such a task because of their considerably smaller blade geometry.
Straight razors are also much easier to clean and can handle tougher shaving tasks, such as longer facial hair, than modern multi-blade razors, which tend to trap shaving debris between their tightly packed blades and are easily clogged, even with relatively short stubble.
In addition, multi-edge razors can irritate the skin due to their multi-blade action, and this can lead to a condition known as pseudofolliculitis barbae, colloquially known as razor bumps. One of the recommended actions for those so affected is to switch to single blade use.
Others simply like the good results and the satisfaction of maintaining the blade themselves. Yet others cite aesthetic reasons in addition to the practical ones. A well-made blade, in a nice handle with a well-crafted etching and decorated shank, carries a sense of craftsmanship and ownership difficult to associate with a disposable blade cartridge.
Finally, a well-kept razor can last for decades, and can become a family heirloom that can be passed from parent to child. For all of these reasons, devotees of the straight razor make for an active market.

Owing to health concerns, some areas require barbers who provide straight-razor shaving to use a version that employs a disposable or changeable blade system. In this type of straight razor the razor blade is changed and disposed of after each service. In places such as Turkey, Australia, New Zealand, Ontario, Pennsylvania, Denver, Boston, Texas and San Diego, however, the professional use of straight razors in barber shops is legal.
The 2012 James Bond film, Skyfall, has renewed interest in straight razors due to a scene when the agent shaves with one and his co-star Naomie Harris helps him finish shaving while remarking that “sometimes the old ways are the best”. Online straight razor retailers have reported increased sales ranging from 50% to over 400% due to the exposure generated by the film.
The increase in sales is part of an overall growth in demand for straight razors, since about 2008, which has also seen an increase in the number of barbers offering straight razor shaves. The phenomenon seems to be driven by renewed nostalgia for things retro such as the straight razor which evokes simpler notions of the past such as the "macho" image associated with its use and also the skill required to shave with it which can be a source of pride.
Cost
As compared to the disposable and cartridge razors, straight razors are more economical, despite a higher initial cost due to the fact that if properly cared for, no additional cost is incurred, as compared to disposable razors where new cartridges must be periodically procured.
Environment
Straight razors are more environmentally friendly than other types of razors since the latter come with packaging that may have to be thrown away along with the razors, and, in the case of electric razors, batteries that are typically disposed of after they expire. Straight razors produce no waste and they require only a strop for honing.
Handling and honing
The various straight razor honing and stropping directions and handling techniques are illustrated by the drawings below.
-
 Razor honing directions on a whetstone
Razor honing directions on a whetstone
-
 Razor honing directions on a whetstone diagonally
Razor honing directions on a whetstone diagonally
-
 Razor handling technique
Razor handling technique
-
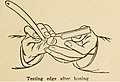 Testing edge after honing by pushing the cutting edge on a moist nail to test its grip
Testing edge after honing by pushing the cutting edge on a moist nail to test its grip
-
 Stropping technique on a hanging strop
Stropping technique on a hanging strop
-
 Testing edge after stropping by touching the cutting edge with a finger
Testing edge after stropping by touching the cutting edge with a finger
-
 Representation of shaving with a straight razor from a book about the art of shaving from 1846
Representation of shaving with a straight razor from a book about the art of shaving from 1846
-
 Paris ca. 1760, the first safety straight razor invented by French master cutler Jean-Jacques Perret
Paris ca. 1760, the first safety straight razor invented by French master cutler Jean-Jacques Perret
References
- "Cambridge Dictionary definition". Dictionary.cambridge.org. 2019-05-08. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- "Merriam Webster definition". Merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ "Government of New Zealand" (PDF). Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- "Collins Dictionary definition". Dictionary.reverso.net. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ "Dovo Solingen via Web archive". Archived from the original on 2007-02-22. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ ohiokids.org by the Ohio Historical Society, 1982 Velma Ave. Columbus, OH 43211-2497 (through the Internet Archive) quote: "Today, men usually shave with disposable razors or electric razors, but that has not always been the case. For more than two hundred years, most American men who wanted to shave used a straight razor, also known as a straight-edge razor. This type of razor first appeared in England in the 1700s, and remained the mainstay of men's razors until the twentieth century.
- ^ The Editors. "Encyclopædia Britannica online". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Hearst Magazines (February 1983). "Popular Mechanics". Popular Mechanics Magazine. Hearst Magazines: 107. ISSN 0032-4558.
- ^ Matt Jancer (29 September 2016). "The Straight-Razor Start-Up Package". outsideonline.com.
- ^ "Beard-Loving Hipsters Give Razor Sales a Shave". Time.
The straight razor is also making a comeback, as it's a better value and more efficient, although requires greater care when shaving.
- ^ "Traditional straight-razor shaving faces a resurgence". Journal Sentinel.
- ^ "msnbc.msn.com". msnbc.msn.com. 2019-05-01. Archived from the original on 2005-02-04. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ Sidney Coyne Thorpe (1967). Practice and Science of Standard Barbering: A Practical and Complete Basic Course of Training on the Science and Practice of Barbering for Students in Training and Professional Barbers. Milady Publishing Corporation. p. 49. Retrieved 15 August 2013.
The full concave grind is generally preferred by most barbers. ...A straight razor is properly balanced when the weight of the blade is equal to that of the handle. Proper balance means greater ease in shaving with the straight razor. ...The finish of a razor is the condition of its surface which may be either plain steel, crocus (polished steel) or metal plated (nickel or silver). Of these types, the crocus finish is the choice of the discriminating barber. Although the crocus finish is more costly, it usually lasts longer and does not show any signs of rusting. The metal plated razors are undesirable because they wear off quickly and often hide a poor quality steel.
- Charles Welch (1923). History of the Cutlers' Company of London and of Minor Cutlery Crafts: With Biographical Notices of Early London Cutlers. Privately printed for the Cutlers' Company. p. 56.
The first appearance of razors in the Sheffield Company's records is in 1680
- Joseph Beeston Himsworth (1953). The Story of Cutlery: From Flint to Stainless Steel. Benn. p. 171.
(Razors first appeared in the Sheffield Company's records in 1680)
- How in the World?. Reader's Digest Association. 1990. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-89577-353-1.
The world's first steel-edged cut-throat' razors were introduced in Sheffield in 1680.
- Myriam Zaoui; Eric Malka (25 February 2009). The Art of Shaving. Potter/TenSpeed/Harmony. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-307-48163-4.
...first manufactured in Sheffield, England, around 1680.
- ^ Melvyn Jones (30 September 2004). The Making of Sheffield. Wharncliffe. p. 75. ISBN 978-1-78340-089-8.
In the late 1680s and early 1690s he is known to have been exporting 'Sheffield wares' including knives, penknives, spring knives and forks, some with tortoiseshell and others with horn handles, razors with silver capped handles, inkpots and ...
- ^ Classic shaving: The Thiers-Issard Story 28 Mar 2004 through the Internet Archive
- Gordon C. McKibben (1998). Cutting Edge: Gillette's Journey to Global Leadership. Harvard Business Press. pp. 5–15. ISBN 978-0-87584-725-2. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- ^ A. B. Moler (1911). Standardized Barbers' Manual. [Chicago, Ill. pp. 5–13.
- ^ "Parts naming from Razor central". En.nassrasur.com. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ Dovo Solingen Meisterwerke (Masterworks) from Internet Archive: (Parts of a razor)
- ^ menessentials from web archive (Parts of a razor) and: "Hold the razor at a 30 degree angle to the surface of your skin and shave your first even stroke"
- ^ "The-Straight-Razor-Shave" (PDF). Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- "Nose" is used by Thiers Issard in description labels on their razor boxes
- ^ "Straight razor dictionary". Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Hearst Magazines (July 1992). "Popular Mechanics". Popular Mechanics Magazine. Hearst Magazines: 68. ISSN 0032-4558.
- Martha Stewart (2006). Martha Stewart's Homekeeping Handbook: The Essential Guide to Caring for Everything in Your Home. Clarkson Potter Publishers. p. 111. ISBN 978-0-517-57700-4.
- Paul S. Auerbach (31 October 2011). Wilderness Medicine E-Book: Expert Consult Premium Edition - Enhanced Online Features. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1880. ISBN 978-1-4557-3356-9.
- ^ "HOW DO RAZORS ACTUALLY DIFFER? HOW TO FIND THE RIGHT ONE!". Dovo Stahlwaren. 19 March 2019.
- "Classic Shaving through Internet Archive". Archived from the original on 2011-11-22. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ Knife center Razor Sharpening And Using Tips (through Internet Archive) quote: "The disadvantage of this second step without a ridge was, that the ultra thin biconcave blades were unstable in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the blade. Therefore the third step was to create a ridge parallel to the cutting edge, dividing the blade in two parts: an upper part between back and ridge, and a lower part between ridge and cutting edge. The ridge is created by grinding the raw triangular basic form with successive different wheel diameters: the greater wheel for the part between ridge and back; the smaller wheel for the part between ridge and cutting edge."
- ^ "Executive Shaving through Internet Archive". Archived from the original on 2013-03-10. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- "Snakewood". The Wood Database.
- Dan Brownell (15 October 2009). Antique Trader Antiques & Collectibles 2010 Price Guide. Krause Publications. p. 594. ISBN 978-1-4402-0361-9. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
Ivory does not have to be antique (100 years old) to be legal, just pre-1989. It can be ... Some Animal Products Covered by Law African elephant ivory (AEI), hippo tusks, and warthog tusks are among the products covered by laws such as the ...
- Esmond Martin and Daniel Stiles Drawings by Andrew Kamiti (2008). Ivory Markets in the USA (PDF). Care for the Wild International and Save the Elephants. pp. 90–91. ISBN 978-9966-9683-5-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-12-02.
- Esmond Martin and Daniel Stiles Drawings by Andrew Kamiti (2005). Ivory Markets of Europe (PDF). Care for the Wild International and Save the Elephants. p. 73. ISBN 9966-9683-4-2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-12-02.
- "Straight Razors". Royal Shave.
- ^ "Blade points from Razor central". En.nassrasur.com. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- Milady (6 June 2016). Milady Standard Barbering. Cengage Learning. pp. 119–126. ISBN 978-1-305-10055-8.
- ^ Blade diagrams from Classic shaving through Internet Archive
- Lorin Shields-Michel (9 November 2001). Hair Care & Styling for Men: A Guide to Healthier Looking Hair. Cengage Learning. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-7668-3817-8. Retrieved 15 August 2013.
- "How to Shave with a Straight Razor (and Not Suffer)". GQ Magazine. 9 March 2017.
- ^ Hearst Magazines (July 1935). "Popular Mechanics". Popular Mechanics Magazine. Hearst Magazines: 114–117. ISSN 0032-4558. Retrieved 23 November 2012.
- Stephanie Henderson-Brown; Catherine Avadis (2004). Advanced Hairdressing. Nelson Thornes. pp. 155–156. ISBN 978-0-7487-9024-1. Retrieved 15 August 2013.
- Napoleon Le Blanc (14 October 2018). Essay on barbers' razors, razor hones, razor strops and razor honing. Napoleon Le Blanc. p. 19. GGKEY:D2D6661QAKC.
- Benjamin Kingsbury (razor-maker.) (1810). A treatise on razors. p. 19. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- Steve Bottorff (1 January 2002). Sharpening Made Easy: A Primer on Sharpening Knives and Other Edged Tools. Knife World Publications. pp. 59–60. ISBN 978-0-940362-19-2. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- premiumknives: "Some manufacturers do produce a professional abrasive in yellow, red, brown, black pastes/rouges or chalky white pastes, however these pastes can be difficult to use properly."
- Milady (6 June 2016). Milady Standard Barbering. Cengage Learning. p. 125. ISBN 978-1-305-10055-8.
- Karen Roemuss; Martin Green; Leo Palladino (1 September 2018). Professional Hairdressing: Australian and New Zealand Edition 2ed. Cengage AU. p. 613. ISBN 978-0-17-041592-7.
- Brian Boyd (16 March 2004). "Cut-throat battle about the best a man can get". The Irish Times. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
In 1900 most men were shaved by their local barber or did it themselves at home. The barber's better-off customers would have personal sets of seven razors, labelled with the days of the week.
- ^ Rene Alexander Disini Orquiza (18 April 2019). "The advantages of a closer shave (and how to achieve it)". ABS-CBN.
- "German 'blade city' has edge in straight razor revival". Hindustan Times. 1 June 2016.
- Joe Kertzman (19 September 2016). Knives 2017: The World's Greatest Knife Book. F+W Media. p. 287. ISBN 978-1-4402-4825-2.
- motherearthnews: "..Shaving with a straight razor is a very simple idea that will preserve your face and, in some small measure, the environment, as well."
- ^ Safety razor Website Archived 2008-01-31 at the Wayback Machine: "..it's a disposable razor or a permanent razor with disposable razor cartridges, the problem is that the defoliated whiskers get caught between the two blades of a twin-bladed razor, and no amount of rinsing can get them all out."
- Weblog: "I am skeptical of this product, though, because the Mach 3 does clog up badly and the blades of the new razor are allegedly even closer together."
- New Zealand Dermatological Society Incorporated: "When you resume shaving, use a single blade razor. Double blade razors cut the hairs too short allowing them to grow in."
- John McCain; Mark Salter (14 August 2007). Hard Call: Great Decisions and the Extraordinary People Who Made Them. Grand Central Publishing. p. 132. ISBN 978-0-446-19871-4. Retrieved 15 August 2013.
- STATE BOARD OF BARBER EXAMINERS of Pennsylvania via the Internet Archive
- "San Diego Health Regulations" (PDF). Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- New York Times SAVING FACE September 16, 1990
- TEXAS DEPARTMENT OF LICENSING AND REGULATION Archived 2007-11-20 at the Wayback Machine
- "Hairdressing and Barbering fact sheet from www.toronto.ca" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-10-08. Retrieved 2010-09-09.
- ^ E.B. (November 8, 2012). "James Bond and male grooming Getting stroppy". The Economist: Blighty Britain. Retrieved 23 November 2012.
Yet the latest cut-throat boomlet is part of a growing demand for classic razors and kit. Mr Mulreany notes that sales at his company have risen 240% in three years. He adds that he spends much of his time teaching grooming basics to men of all ages. "It used to be that dad would take his son into the bathroom and show him what to do," he says. "I now meet men who have never shaved properly in their life." More barbers are offering cut-throat shaves as well.
- ^ "How to master a cut-throat razor". GQ Magazine. 19 March 2014.

