This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) at 14:14, 18 August 2022 (Added UNII). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 14:14, 18 August 2022 by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) (Added UNII)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)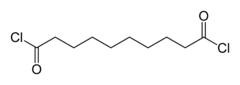 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Decanedioyl dichloride | |
| Other names Sebacoyl dichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.495 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C061659 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H16Cl2O2 |
| Molar mass | 239.14 g/mol |
| Density | 1.12 g cm |
| Melting point | −2.5 °C (27.5 °F; 270.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Sebacoyl chloride (or sebacoyl dichloride) is a di-acyl chloride, with formula (CH2)8(COCl)2. A colorless oily liquid with a pungent odor, it is soluble in hydrocarbons and ethers. Sebacoyl chloride is corrosive; like all acyl chlorides, it hydrolyzes, evolving hydrogen chloride. It is less susceptible to hydrolysis though than shorter chain aliphatic acyl chlorides.
Preparation
Sebacoyl chloride can be prepared by reacting sebacic acid with an excess of thionyl chloride. Residual thionyl chloride can be removed by distillation.
Use
Sebacoyl chloride can be polymerized with hexamethylenediamine yielding nylon-6,10.
See also
References
- Morgan, Paul W.; Kwolek, Stephanie L. (April 1959). "The nylon rope trick: Demonstration of condensation polymerization". Journal of Chemical Education. 36 (4): 182. Bibcode:1959JChEd..36..182M. doi:10.1021/ed036p182.
- Erdmann, L.; Uhrich, K.E. (October 2000). "Synthesis and degradation characteristics of salicylic acid-derived poly(anhydride-esters)". Biomaterials. 21 (19): 1941–1946. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00073-9. PMID 10941915.
- Enkelmann, Volker; Wegner, Gerhard (1976-11-01). "Mechanism of interfacial polycondensation and the direct synthesis of stable polyamide membranes". Die Makromolekulare Chemie. 177 (11): 3177–3189. doi:10.1002/macp.1976.021771106. ISSN 0025-116X.
| Diacyl chlorides (-COCl)2 | ||
|---|---|---|
|  | |
| Category:Acyl chlorides | ||