This is an old revision of this page, as edited by SporkBot (talk | contribs) at 15:23, 10 December 2022 (Merge table created by User:CX Zoom per TFD outcome). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:23, 10 December 2022 by SporkBot (talk | contribs) (Merge table created by User:CX Zoom per TFD outcome)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Congressional districts in the U.S. state of Ohio| Parts of this article (those related to the map) need to be updated. The reason given is: It needs to be updated to reflect the new map.. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (November 2021) |


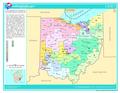
Ohio is divided into 16 congressional districts, each represented by a member of the United States House of Representatives. After the 2010 Census, Ohio lost two House seats due to slow population growth compared to the national average, and a new map was signed into law on September 26, 2011. This map was ruled unconstitutional as partisan gerrymandering, and state Republicans were told to redraw the map before June 14, 2019. However, on October 7, 2019, the U.S. Supreme Court dismissed the challenge to the map, allowing it to stay in effect for the 2020 election.
2021 Redistricting
See also: 2020 United States redistricting cycleStarting in the 2022 midterms, per the 2020 United States census, Ohio will lose a congressional seat. On November 17, 2021, after lengthy discussions, a new map was passed by the Ohio House of Representatives 55-36, along party lines, with no Democrat voting in favor of the map. The map was sent to Governor of Ohio, Mike DeWine, where he accepted it 3 days later on November 20th.
The map has been controversial, as Democrats accuse the map of being purposefully designed to benefit Republicans. By December 7, 2021, six lawsuits had been filed against the new 15-seat congressional map, citing it as "racially discriminatory". The proposed map favors Republican to Democratic districts by a 12-3 margin.
On January 14, 2022, the Ohio Supreme Court declared the map a partisan gerrymander, violating Article XIX of the Constitution of Ohio, in a 4-3 decision. The Ohio General Assembly had 30 days to draw a new map.
On March 16, 2022, the Ohio Supreme Court rejected the new proposed state legislative district map for the third time. The decision will most likely force Ohio to postpone its primary elections, scheduled to take place on May 3, until new maps of both state legislative seats and districts for the United States House of Representatives pass constitutional muster.
Current (until 2023 inauguration) districts and representatives
On May 3, 2019, a three-judge panel from the United States District Court for the Southern District of Ohio declared the Ohio's 2012 district map contrary to Article One of the United States Constitution, as "an unconstitutional partisan gerrymander" and ordered "the enactment of a constitutionally viable replacement" prior to the 2020 elections. An appeal made to the U.S. Supreme Court resulted in the order to redraw the map being nullified.
The following table is a list of members of the Ohio United States House delegation, their terms, their district boundaries, and the districts' political rating according to the CPVI. The delegation has a total of 16 members, with 12 Republicans and 4 Democrats.
| Current U.S. representatives from Ohio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | Member (Residence) |
Party | Incumbent since | CPVI (2021) |
District map |
| 1st |  Steve Chabot (Cincinnati) |
Republican | January 3, 2011 | R+4 | 
|
| 2nd |  Brad Wenstrup (Cincinnati) |
Republican | January 3, 2013 | R+9 | 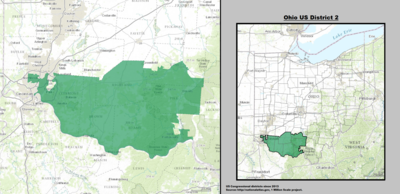
|
| 3rd |  Joyce Beatty (Columbus) |
Democratic | January 3, 2013 | D+19 | 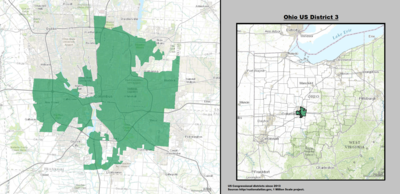
|
| 4th |  Jim Jordan (Urbana) |
Republican | January 3, 2007 | R+20 | 
|
| 5th |  Bob Latta (Bowling Green) |
Republican | December 11, 2007 | R+15 | 
|
| 6th |  Bill Johnson (Marietta) |
Republican | January 3, 2011 | R+24 | 
|
| 7th |  Bob Gibbs (Lakeville) |
Republican | January 3, 2011 | R+18 | 
|
| 8th |  Warren Davidson (Troy) |
Republican | June 7, 2016 | R+19 | 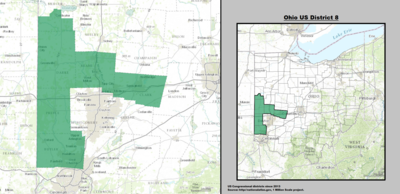
|
| 9th |  Marcy Kaptur (Toledo) |
Democratic | January 3, 1983 | D+9 | 
|
| 10th |  Mike Turner (Dayton) |
Republican | January 3, 2003 | R+5 | 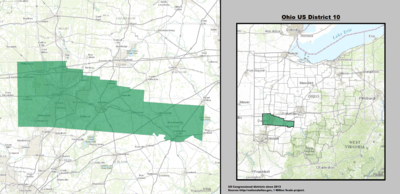
|
| 11th |  Shontel Brown (Warrensville Heights) |
Democratic | November 4, 2021 | D+30 | 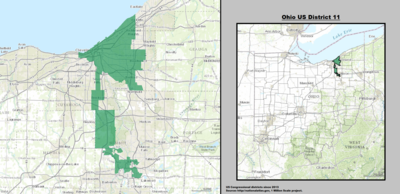
|
| 12th |  Troy Balderson (Zanesville) |
Republican | September 5, 2018 | R+6 | 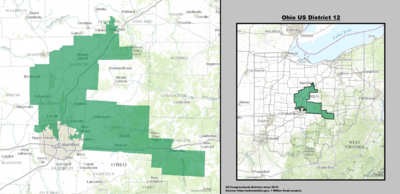
|
| 13th |  Tim Ryan (Warren) |
Democratic | January 3, 2003 | D+1 | 
|
| 14th |  Dave Joyce (Russell Township) |
Republican | January 3, 2013 | R+5 | 
|
| 15th |  Mike Carey (Columbus) |
Republican | November 4, 2021 | R+9 | 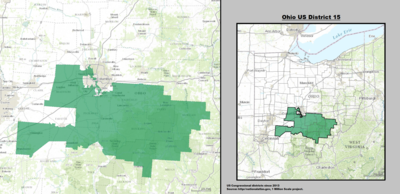
|
| 16th |  Anthony Gonzalez (Rocky River) |
Republican | January 3, 2019 | R+10 | 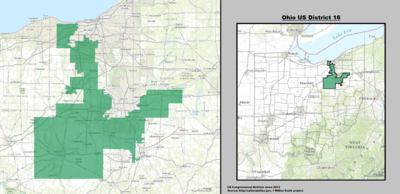
|
Historical district boundaries
Obsolete districts
- Ohio's at-large congressional district
- Ohio's 17th congressional district
- Ohio's 18th congressional district
- Ohio's 19th congressional district
- Ohio's 20th congressional district
- Ohio's 21st congressional district
- Ohio's 22nd congressional district
- Ohio's 23rd congressional district
- Ohio's 24th congressional district
See also
- List of United States congressional districts
- United States congressional delegations from Ohio
- History of 19th-century congressional redistricting in Ohio
References
- "The national atlas". nationalatlas.gov. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 22, 2014.
- Wang, Robert (2010-12-21). "Census costs Ohio two seats in Congress". The Canton Repository. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- Rosenberg, Gabe. "Ohio's Congressional Map Ruled Unconstitutional By Federal Court". radio.wosu.org. Retrieved 2019-05-03.
- ^ "U.S. Supreme Court tosses challenge to Republican-drawn Ohio congressional maps". Reuters. 2019-10-08. Retrieved 2020-04-04.
- Merica, Dan; Stark, Liz (April 26, 2021). "Census Bureau announces 331 million people in US, Texas will add two congressional seats". CNN. Retrieved April 26, 2021.
- ^ Balmert, Jessie. "Ohio Republicans propose congressional district maps advantaging the GOP. See them here". The Columbus Dispatch. Retrieved 2021-11-23.
- ^ "Ohio governor signs new congressional district map into law". ABC News. Retrieved 2021-11-23.
- "Federal lawsuit says Ohio's new state legislative, congressional maps discriminate against Black voters". cleveland.com. Retrieved December 7, 2021.
- Uniss, Kyle Anne (January 14, 2022). "Ohio Supreme Court invalidates GOP-drawn congressional districts". Courthouse News Service. Archived from the original on January 16, 2022. Retrieved January 16, 2022.
- Andy Chow (March 16, 2022). "Ohio Supreme Court March 16, 2022 ruling on state legislative maps". Scribd. Retrieved March 18, 2022.
- Michael Wines (March 17, 2022). "In Ohio, a Standoff Over Political Maps Threatens the Next Elections". New York Times. Retrieved March 18, 2022.
- Rosenberg, Gabe (May 3, 2019). "Federal Court Throws Out Ohio's Congressional Map". National Public Radio (NPR). Retrieved 5 May 2019.
- "Office of the Clerk, U.S. House of Representatives". clerk.house.gov. Retrieved 2022-01-06.
- "Introducing the 2021 Cook Political Report Partisan Voter Index". Cook Political Report. Retrieved 2022-01-06.
External links
- Rose Institute of State and Local Government, "Ohio: 2010 Redistricting Changes", Redistricting by State, Claremont, CA: Claremont McKenna College
| Ohio's congressional districts | |
|---|---|
|