This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Entranced98 (talk | contribs) at 00:37, 23 January 2023 (Importing Wikidata short description: "Chemical compound"). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 00:37, 23 January 2023 by Entranced98 (talk | contribs) (Importing Wikidata short description: "Chemical compound")(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Pentifylline" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2019) |
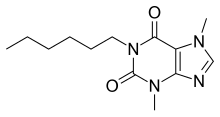 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1-Hexyltheophylline |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.584 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H20N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 264.329 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Pentifylline (marketed as Cosaldon) is a vasodilator.
References
- Bath PM, Bath-Hextall FJ (2004). "Pentoxifylline, propentofylline and pentifylline for acute ischaemic stroke". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD000162. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000162.pub2. PMID 15266424.
| Peripheral vasodilators (C04) | |
|---|---|
| Phenylethanolamine derivatives | |
| Alpha blockers |
|
| Nicotinic acid and derivatives | |
| Purine derivatives | |
| Ergot alkaloids | |
| Other peripheral vasodilators | |
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |