This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Shinkolobwe (talk | contribs) at 13:05, 16 February 2023 (→References: New section: == See also ==). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 13:05, 16 February 2023 by Shinkolobwe (talk | contribs) (→References: New section: == See also ==)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Not to be confused with Fluorene, Fluorenone, or Fluorine. | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3H-Xanthen-3-one | |
| Other names 3-Isoxanthone; 3-Oxo-3H-xanthene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C13H8O2 |
| Molar mass | 196.205 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
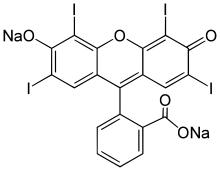
Fluorone is a heterocyclic chemical compound. It forms the core structure for various chemicals, most notably fluorone dyes, including fluorescein, erythrosine and rhodamine. It is an isomer of xanthone, sometimes referred to as an isoxanthone.
See also
References
- Shi, Jianmin; Zhang, Xianping; Neckers, Douglas C (1992). "Xanthenes: fluorone derivatives". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 57 (16): 4418–4421. doi:10.1021/jo00042a020.
This article about a heterocyclic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |