This is the current revision of this page, as edited by LegionMammal978 (talk | contribs) at 23:06, 4 May 2023 (add semisystematic name). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 23:06, 4 May 2023 by LegionMammal978 (talk | contribs) (add semisystematic name)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)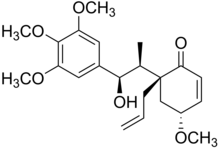
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (1′R,5′R,7R,8S)-7-Hydroxy-3,4,5,5′-methoxy-5′,6′-dihydro-2′H-8,1′-neolign-8′-en-2′-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (4R,6R)-6--4-methoxy-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)cyclohex-2-en-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C22H30O6 |
| Molar mass | 390.476 g·mol |
| Density | 1.242 g/cm |
| Melting point | 152 °C (306 °F; 425 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Megaphone is a cytotoxic neolignan obtained from Aniba megaphylla, a flowering plant of Laurel family which gave the compound its name. Megaphone has also been prepared synthetically.
Studies carried out in the 1960s demonstrated that an alcoholic extract of the ground root of Aniba megaphylla inhibited, in vitro, growth of cells derived from human carcinoma of the nasopharynx. In 1978, the active components of the extract were isolated using silica gel chromatography, characterized and named as megaphone (C22H30O6, solid), megaphone acetate (C24H32O7, oily liquid) and megaphyllone acetate (C23H28O7, oily liquid). For comparison, megaphone acetate was also produced synthetically by reacting megaphone with acetic anhydride at 50 °C for 6 hours. Stirring an alcoholic solution of megaphone (megaphone acetate), with added palladium catalyst, in hydrogen atmosphere, followed by evaporation of the solvent yields tetrahydromegaphone (tetrahydromegaphone acetate) as an oil. Millimeter-sized crystals of megaphone can be grown from an ether-chloroform solution. They have monoclinic symmetry with space group P21, lattice constants a = 0.8757 nm, b = 1.1942 nm and c = 1.0177 nm and two formula units per unit cell. Megaphone and megaphone acetate molecules are chiral and the reported extraction and synthesis procedures yielded their racemic mixtures. Megaphone acetate was also isolated from the root of Endlicheria dysodantha, another plant of Laurel family, using chromatography of ethanolic solution. It showed inhibitory activity against cells of crown gall tumor and human lung, breast and colon carcinomas.
References
- Zoretic, P (1983). "Total synthesis of d,l-megaphone". Tetrahedron Letters. 24 (11): 1125–1128. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)86382-0.
- Tomioka, Kiyoshi; Kawasaki, Hisashi; Iitaka, Yoichi; Koga, Kenji (1985). "Enantiospecific total synthesis of (-)-megaphone by a highly controlled consecutive 1,4- and 1,3-asymmetric induction". Tetrahedron Letters. 26 (7): 903–906. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)61960-3.
- Buechi, George; Chu, Ping-Sun (1981). "The Synthesis of Megaphone". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 103 (10): 2718. doi:10.1021/ja00400a039.
- ^ SM Kupchan; KL Stevens; EA Rohlfing; BR Sickles; AT Sneden; RW Miller; RF Bryan (1978). "Tumor inhibitors. 126. New cytotoxic neolignans from Aniba megaphylla Mez". J. Org. Chem. 43 (4): 586–590. doi:10.1021/jo00398a013.
- Ma, WW; Kozlowski, JF; McLaughlin, JL (1991). "Bioactive neolignans from Endlicheria dysodantha". Journal of Natural Products. 54 (4): 1153–8. doi:10.1021/np50076a045. PMID 1665173.