This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Sekio (talk | contribs) at 06:36, 24 July 2023 (Preparation is detailed in the section below, and uses modern IUPAC terminology.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 06:36, 24 July 2023 by Sekio (talk | contribs) (Preparation is detailed in the section below, and uses modern IUPAC terminology.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Cinnoline | |||
| Other names Benzopyridazine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.423 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C8H6N2 | ||
| Molar mass | 130.150 g·mol | ||
| Melting point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.64 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
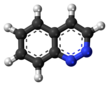
Cinnoline is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinoxaline, phthalazine and quinazoline.
Properties
The free base can be obtained as an oil by treatment of the hydrochloride with base. It co-crystallizes with one molecule of ether as white silky needles, (m.p. 24–25 °C) upon cooling ethereal solutions. The free base melts at 39 °C. It has a taste resembling that of chloral hydrate and leaves a sharp irritation for some time.
Discovery and synthesis
The compound was first obtained in impure form by cyclization of the alkyne o-C6H4(NH2)C≡CCO2H in water to give 4-hydroxycinnoline-3-carboxylic acid. This material could be decarboxylated and the hydroxyl group reductively removed to give the parent heterocycle. This reaction is called the Richter cinnoline synthesis. Improved methods exist for its synthesis. It can be prepared by dehydrogenation of dihydrocinnoline with freshly precipitated mercuric oxide. It can be isolated as the hydrochloride.
Cinnolines are cinnoline derivatives. A classic organic reaction for synthesizing cinnolines is the Widman–Stoermer synthesis, a ring-closing reaction of an α-vinyl- aniline with hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite:

The sodium nitrite is first converted to nitrous acid which then forms the electrophilic intermediate dinitrogen trioxide. The next intermediate is the stable nitrosamine with goes on to lose water forming the diazonium salt which then reacts with the vinyl group in the ring-closing step. A conceptually related reaction is the Bamberger triazine synthesis towards triazines.
Another cinnoline method is the Borsche cinnoline synthesis.
Safety
Cinnoline is toxic.
See also
References
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 212. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- Brown, H.C., et al., in Baude, E.A. and Nachod, F.C., Determination of Organic Structures by Physical Methods, Academic Press, New York, 1955.
- Victor von Richter (1883). "Über Cinnolinderivate". Chemische Berichte. 16: 677–683. doi:10.1002/cber.188301601154.
- Parrick, J.; Shaw, C. J. G.; Mehta, L. K. (2000). "Pyridazines, cinnolines, benzocinnolines and phthalazines". Rodd's Chemistry of Carbon Compounds. Vol. 4 (2nd ed.). pp. 1–69.
- Bradford P. Mundy; Michael G. Ellerd; Frank G. Jr. Favaloro (2005). Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic Synthesis. ISBN 0-471-22854-0.