This is the current revision of this page, as edited by OAbot (talk | contribs) at 05:17, 15 August 2023 (Open access bot: doi updated in citation with #oabot.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 05:17, 15 August 2023 by OAbot (talk | contribs) (Open access bot: doi updated in citation with #oabot.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)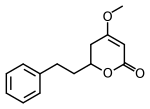
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 4-Methoxy-6-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one | |
| Other names
Dihydrokawain Marindinin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C14H16O3 |
| Molar mass | 232.27 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dihydrokavain is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant. It appears to contribute significantly to the anxiolytic effects of kava, based on a study in chicks.
Dihydrokavain bears some structural similarity to the strobilurins and has some fungicidal activity.
An analogue of the molecule was also shown to improve glycemic control by modulating AMPK target genes expression in fruit flies.
References
- Malani, Joji (2002-12-03). "Evaluation of the effects of Kava on the Liver" (PDF). Fiji School of Medicine. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-20. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- Feltenstein, MW; LC Lambdin; M Ganzera; H Ranjith; W Dharmaratne; NP Nanayakkara; IA Khan; KJ Sufka (March 2003). "Anxiolytic properties of Piper methysticum extract samples and fractions in the chick social-separation-stress procedure". Phytotherapy Research. 17 (3): 210–216. doi:10.1002/ptr.1107. PMID 12672148. S2CID 10548965.
- Zakharychev, Vladimir V; Kovalenko, Leonid V (1998-06-30). "Natural compounds of the strobilurin series and their synthetic analogues as cell respiration inhibitors". Russian Chemical Reviews. 67 (6): 535–544. Bibcode:1998RuCRv..67..535Z. doi:10.1070/rc1998v067n06abeh000426. ISSN 0036-021X. S2CID 95676421.
- Hadiza Muhammad Maiturare; Mudassir Aliyu Magaji; Muhammad Kabiru Dallatu; Kabir Magaji Hamid; Mustapha Umar Imam; Ibrahim Malami (2022). "5,6-dehydrokawain improves glycaemic control by modulating AMPK target genes in Drosophila with a high-sucrose diet-induced hyperglycaemia". Phytomedicine Plus. 2 (2): 100261–. doi:10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100261. ISSN 2667-0313. S2CID 247649601.
| Kava | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||||||
| Chemical composition |
| ||||||
| GABAA receptor positive modulators | |
|---|---|
| Alcohols | |
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents | |
| Monoureides | |
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
This article about an anxiolytic is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |