This is the current revision of this page, as edited by KoIobok (talk | contribs) at 13:00, 18 September 2023 (Added Category:Glutamic acids). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 13:00, 18 September 2023 by KoIobok (talk | contribs) (Added Category:Glutamic acids)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)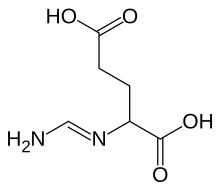
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name N-(aminomethylidene)-L-glutamic acid | |
| Other names FIGLU | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.308 |
| MeSH | Formiminoglutamic+acid |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H10N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 174.156 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Formiminoglutamic acid (FIGLU; conjugate base, formiminoglutamate) is an intermediate in the catabolism of L-histidine to L-glutamic acid. It thus is also a biomarker for intracellular levels of folate. The FIGLU test is used to identify vitamin B₁₂ deficiency, folate deficiency, and liver failure or liver disease. It is elevated with folate trapping, where it is accompanied by decreased methylmalonic acid, increased folate and a decrease in homocysteine.
See also
- Formiminotransferase cyclodeaminase
- Glutamate-1-semialdehyde
- Glutamic acid
- Imidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid
References
- Lascelles, P. T.; Donaldson, D. (1989). "Formiminoglutamic Acid (FIGLU) Test". Diagnostic Function Tests in Chemical Pathology. pp. 59–60. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-1846-7_31. ISBN 978-0-7462-0107-7.
- FIGLU+Test at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Scott, JohnM.; Weir, DonaldG. (15 August 1981). "THE METHYL FOLATE TRAP: A physiological response in man to prevent methyl group deficiency in kwashiorkor (methionine deficiency) and an explanation for folic-acid-induced exacerbation of subacute combined degeneration in pernicious anaemia". The Lancet. 318 (8242): 337–340. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(81)90650-4. ISSN 0140-6736. PMID 6115113. S2CID 29977127.
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This article about a base (chemistry) is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |