This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Marbletan (talk | contribs) at 14:35, 27 October 2023 (external links go last). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 14:35, 27 October 2023 by Marbletan (talk | contribs) (external links go last)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)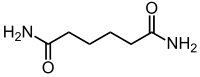
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Hexanediamide | |
| Other names Hexanedioic diamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 4-02-00-01972 |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.057 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Adipamide |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H12N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 144.174 g·mol |
| Appearance | powder |
| Melting point | 220 to 225 °C (428 to 437 °F; 493 to 498 K) |
| Solubility in water | 4.4 g/L (12 °C) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | hexanedioic acid hexanedihydrazide hexanedioyl dichloride hexanedinitrile |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Adipamide is the organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2C(O)NH2)2. It is a white solid. The dominant commercial interest in adipamides is related to their presence in nylons.
Adipamide is formed by treating dimethyl adipate with concentrated ammonia.
References
- Musser, M. T. (2005). "Adipic Acid". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_269. ISBN 3527306730.
- "Dimethyl Adipate". chemicalland21.com.
External links
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |