This is the current revision of this page, as edited by DMacks (talk | contribs) at 12:03, 30 December 2023 (→External links: ChemID now part of PubChem, which is linked in Chembox). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 12:03, 30 December 2023 by DMacks (talk | contribs) (→External links: ChemID now part of PubChem, which is linked in Chembox)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) See also: 1,4-Dioxin; Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds; and Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins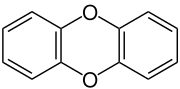
| |

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Oxanthrene | |
| Other names
Dibenzodioxin, Dibenzo-p-dioxin, Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 143227 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.432 |
| EC Number |
|
| Gmelin Reference | 280302 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H8O2 |
| Molar mass | 184.194 g·mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 122 °C (252 °F; 395 K) |
| Boiling point | 283.5 °C (542.3 °F; 556.6 K) |
| Solubility in water | 0.901 g/L (25 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H411 |
| Precautionary statements | P264, P270, P273, P301+P312, P330, P391, P501 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | polychlorinated dibenzodioxins ("dioxin"), dioxins and dioxin-like compounds |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, also dibenzodioxin or dibenzo-p-dioxin (dibenzo-para-dioxin), is a polycyclic heterocyclic organic compound in which two benzene rings are connected by a 1,4-dioxin ring. Its molecular formula is C12H8O2. The two oxygen atoms occupy opposite (para-) positions in the six-membered dioxin ring.
Dibenzodioxin is the carbon skeleton of the poisonous polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), often called dioxins. The most harmful PCDD is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD). Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds is a category of pollutants that includes PCDDs and other compounds that have similar structure, toxicity, and persistence. Dibenzodioxin is also the skeleton of the polybrominated dibenzodioxins.
Isomer
The general name dibenzodioxin usually refers to dibenzo-p-dioxin.
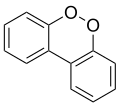
The isomeric compound dibenzo-o-dioxin (dibenzo-ortho-dioxin) or dibenzo-1,2-dioxin, like the unstable 1,2-dioxin, has two adjacent oxygen atoms (ortho-). No detailed information is available on this isomer, but it is expected to be highly unstable, with peroxide-like characteristics.
See also
- Thianthrene, the sulfur analog of dibenzodioxin
References
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 216. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-00130. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.