This is the current revision of this page, as edited by GreenLipstickLesbian (talk | contribs) at 08:17, 17 May 2024 (removing close paraphrasing from https://www.eurekaselect.com/article/95541). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 08:17, 17 May 2024 by GreenLipstickLesbian (talk | contribs) (removing close paraphrasing from https://www.eurekaselect.com/article/95541)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)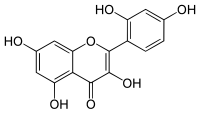
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2′,3,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Aurantica Al-Morin Morin hydrate Calico Yellow Toxylon pomiferum Bois d'arc Osage orange extract | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.858 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C15H10O7 |
| Molar mass | 302.238 g·mol |
| Density | 1.799 g/mL |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Morin is a yellow chemical compound that can be isolated from Maclura pomifera (Osage orange), Maclura tinctoria (old fustic), and from leaves of Psidium guajava (common guava). In a preclinical in vitro study, morin was found to be a weak inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with an IC50 of 2.33 μM. Morin was also found to inhibit amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide (or amylin) and disaggregate amyloid fibers.
Morin can be used to test for the presence of aluminium or tin in a solution, since it forms characteristically fluorescent coordination complexes with them under UV light.
Glycosides
- Morin-3-O-arabinoside
- Morin-3-O-lyxoside
References
- ^ Rattanachaikunsopon, Pongsak; Phumkhachorn, Parichat (2007). "Bacteriostatic effect of flavonoids isolated from leaves of Psidium guajava on fish pathogens". Fitoterapia. 78 (6): 434–436. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2007.03.015. PMID 17553634.
- Tian, Wei-Xi (2006). "Inhibition of Fatty Acid Synthase by Polyphenols". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (8): 967–977. doi:10.2174/092986706776361012. PMID 16611078.
- Noor, Harris; Cao, Ping; Raleigh, Daniel P. (2012). "Morin hydrate inhibits amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide and disaggregates amyloid fibers". Protein Science. 21 (3): 373–382. doi:10.1002/pro.2023. PMC 3375438. PMID 22238175.
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |