This is the current revision of this page, as edited by 57.140.24.0 (talk) at 03:21, 17 June 2024. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 03:21, 17 June 2024 by 57.140.24.0 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)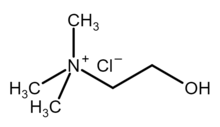
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethan-1-aminium chloride | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.596 |
| E number | E1001(iii) (additional chemicals) |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]Cl |
| Molar mass | 139.62 g·mol |
| Appearance | White hygroscopic crystals |
| Melting point | 302 °C (576 °F; 575 K) (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | very soluble (>650 g/L) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Signal word | Danger |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Choline chloride is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]Cl. It is a quaternary ammonium salt, consisting of choline cations ([(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]) and chloride anions (Cl). It is a bifunctional compound, meaning, it contains both a quaternary ammonium functional group and a hydroxyl functional group. The anion of this salt, choline, occurs in nature in living beings. Choline chloride is a white, water-soluble salt used mainly in animal feed.
Synthesis
In the laboratory, choline can be prepared by methylation of dimethylethanolamine with methyl chloride.
Choline chloride is mass-produced with world production estimated at 160 000 tons in 1999. Industrially, it is produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide, hydrogen chloride, and trimethylamine, or from the pre-formed salt:
Choline chloride can also be made by treating trimethylamine with 2-chloroethanol.
- (CH3)3N + ClCH2CH2OH → [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]Cl
Applications
It is an important additive in feed especially for chickens where it accelerates growth. It forms a deep eutectic solvent with urea, ethylene glycol, glycerol, and many other compounds.
It is also used as a clay control additive in fluids used for hydraulic fracturing.
Related salts
Other commercial choline salts are choline hydroxide and choline bitartrate. In foodstuffs, the compound is often present as phosphatidylcholine.
References
- "Chemical Safety Information from Intergovernmental Organizations - Choline Chloride" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-07-12.
- "Choline". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University. February 2015. Retrieved 11 November 2019.
- ^ Matthias Frauenkron; Johann-Peter Melder; Günther Ruider; Roland Rossbacher; Hartmut Höke (2002). "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_001. ISBN 3527306730.
- title=Johnson Matthey Process Technology - Choline chloride licensed process
- "Choline chloride" (PDF). Screening Information Data Set (SIDS) for High Production Volume Chemicals. IPCS INCHEM. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-07-12. Retrieved 2009-11-10.
- Kirk RE, et al. (2000). Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology. Vol. 6 (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 100–102. ISBN 9780471484943.
- "What Chemicals Are Used". FracFocus. Archived from the original on 2 July 2020. Retrieved 19 September 2014.