This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Marbletan (talk | contribs) at 17:14, 18 July 2024. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 17:14, 18 July 2024 by Marbletan (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)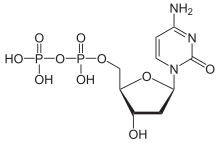
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2′-Deoxycytidine 5′-(trihydrogen diphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name methyl trihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Other names 2'-Deoxycytidine diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | deoxycytidine+diphosphate |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C9H15N3O10P2 |
| Molar mass | 387.178 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Deoxycytidine diphosphate is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is related to the common nucleic acid CTP, or cytidine triphosphate, with the -OH (hydroxyl) group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose removed (hence the deoxy- part of the name), and with one fewer phosphoryl group than CTP .
2'-Deoxycytidine diphosphate is abbreviated as dCDP.
Synthesis of cytidine nucleotides
Deoxycytidine diphosphate is synthesized through the oxidation-reduction reaction of cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine which is catalyzed by the presence of ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase. Additionally, ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase is capable of binding and catalyzing both the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotide.
See also
References
- MeSH term, accessed Dec. 31, 2012
- Kandeel, Mahmoud; Al-Taher, Abdulla (2020-11-01). "Metabolic drug targets of the cytosine metabolism pathways in the dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius) and blood parasite Trypanosoma evansi". Tropical Animal Health and Production. 52 (6): 3337–3358. doi:10.1007/s11250-020-02366-8. ISSN 1573-7438. PMID 32926292. S2CID 221722974.
- Torrents, Eduard (2014). "Ribonucleotide reductases: essential enzymes for bacterial life". Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 4: 52. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2014.00052. ISSN 2235-2988. PMC 4009431. PMID 24809024.
Further reading
- Kennedy, Eugene P.; Louise Fencil Borkenhagen; Sylvia Wagner Smith (1959). "Possible Metabolic Functions of Deoxycytidine Diphosphate Choline and Deoxycytidine Diphosphate Ethanolamine". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 234 (8): 1998–2000. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)69855-2. PMID 13673002.
- Reichard, Peter (1962). "Enzymatic Synthesis of Deoxyribonucleotides: I. FORMATION OF DEOXYCYTIDINE DIPHOSPHATE FROM CYTIDINE DIPHOSPHATE WITH ENZYMES FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 237: 3513–3519. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)70849-7. PMID 13973714..
| Nucleic acid constituents | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleobase | |||||||
| Nucleoside |
| ||||||
| Nucleotide (Nucleoside monophosphate) |
| ||||||
| Nucleoside diphosphate | |||||||
| Nucleoside triphosphate | |||||||