This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 99.65.239.69 (talk) at 01:56, 24 July 2024. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:56, 24 July 2024 by 99.65.239.69 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Main airport serving Houston, Texas, United States "Intercontinental Airport" and "Intercontinental airport" redirect here. For other such airports, see International airport. "Bush airport" redirects here. For simple airfields known as "bush airfields", see Bush flying.
| George Bush Intercontinental Airport | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Houston Airport System | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Greater Houston | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Houston, Texas, U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | June 8, 1969; 55 years ago (1969-06-08) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for | United Airlines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating base for | Spirit Airlines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | CST (UTC−06:00) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Summer (DST) | CDT (UTC−05:00) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 30 m / 97 ft | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 29°59′04″N 095°20′29″W / 29.98444°N 95.34139°W / 29.98444; -95.34139 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
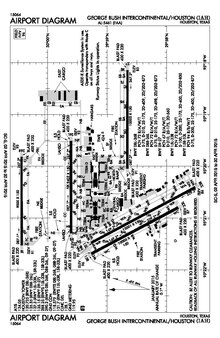 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2023) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sources: Fly2Houston.com and Federal Aviation Administration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
George Bush Intercontinental Airport (IATA: IAH, ICAO: KIAH, FAA LID: IAH) is an international airport in Houston, Texas, United States, serving the Greater Houston metropolitan area. Initially named Houston Intercontinental Airport upon its opening in 1969, it was renamed in honor of George H. W. Bush, the 41st president of the United States and a resident of Houston, in 1997.
Located about 23 miles (37 km) north of Downtown Houston between Interstate 45 and Interstate 69/U.S. Highway 59 with direct access to the Hardy Toll Road expressway, George Bush Intercontinental Airport has scheduled flights to a large number of domestic and international destinations covering five continents. It is the busiest airport in Texas for international passenger traffic and a number of international destinations, the second-busiest airport in Texas as of 2021 and the 15th busiest in the United States for total passenger traffic as of 2022
IAH covers 10,000 acres (40 km) of land and has five runways. Houston Intercontinental is one of the largest passenger hubs for United Airlines.
IAH is also a former hub of Continental and Texas International.
History
20th century

A group of Houston businessmen purchased the site for Bush Intercontinental Airport in 1957 to preserve it until the city of Houston could formulate a plan for a new airport as a replacement for William P. Hobby Airport (at the time known as Houston International Airport). The holding company for the land was named the Jet Era Ranch Corporation, but a typographical error transformed the words "Jet Era" into "Jetero" and the airport site subsequently became known as the Jetero airport site. Although the name Jetero was no longer used in official planning documents after 1961, the airport's eastern entrance was named Jetero Boulevard. Most of Jetero Boulevard was later renamed Will Clayton Parkway.
The City of Houston annexed the Intercontinental Airport area in 1965. This annexation, along with the 1965 annexations of the Bayport area, the Fondren Road area, and an area west of Sharpstown, resulted in a gain of 51,251 acres (20,741 ha) of land for the city limits.
Houston Intercontinental Airport, which was the original name for the airport, opened in June 1969. The airport's IATA code of IAH derived from the stylization of the airport's name as "Intercontinental Airport of Houston." All scheduled passenger airline service formerly operated from William P. Hobby Airport moved to Intercontinental upon the airport's completion. Hobby remained open as a general aviation airport and was once again used for scheduled passenger airline jet service two years later when Southwest Airlines initiated intrastate airline service nonstop between Hobby and Dallas Love Field in 1971.
In the late 1980s, Houston City Council considered a plan to rename the airport after Mickey Leland—an African-American U.S. Congressman who died in an aviation accident in Ethiopia. Instead of renaming the whole airport, the city named Mickey Leland International Arrivals Building, which would later become Mickey Leland Terminal D, after the congressman. In April 1997, Houston City Council unanimously voted to rename the airport George Bush Intercontinental Airport/Houston, after George H. W. Bush, the 41st president of the United States. The name change took effect on May 2, 1997.
On August 28, 1990, Continental Airlines agreed to build its maintenance center at George Bush Intercontinental Airport; Continental agreed to do so because the city of Houston agreed to provide city-owned land near the airport.
At the time of the opening of IAH in 1969, domestic scheduled passenger airline flights were being operated by American Airlines, Braniff International Airways, Continental Airlines, Delta Air Lines, Eastern Air Lines, National Airlines and Houston-based Texas International Airlines, which had formerly operated as Trans-Texas Airways. International flights at this time were being flown by Pan American World Airways with ten nonstop flights a week operated with Boeing 707 jetliners to Mexico City; KLM Royal Dutch Airlines operating Douglas DC-8 jets four days a week to Amsterdam via an intermediate stop in Montreal; Braniff International with Boeing 727 services several times a week to Panama City, Panama; and Aeronaves de Mexico (now Aeroméxico) flying Douglas DC-9 jets to Monterrey, Guadalajara, Puerto Vallarta, Acapulco and Mexico City several days a week. Texas International was also operating direct services to Mexico at this time with Douglas DC-9 jets to Monterrey and Convair 600 turboprop flights to Tampico and Veracruz.
KLM introduced Boeing 747 services in 1971 and by 1974 Air France was operating four nonstop Boeing 747 flights a week to both Paris and Mexico City. Also in 1974, Continental, Pan Am, and National were operating McDonnell Douglas DC-10 wide body jetliners into IAH while Delta was flying Lockheed L-1011 TriStar wide body jets with both types being operated on respective domestic routes from the airport by these airlines; with National also operating Boeing 747s on a Miami–Houston–Los Angeles routing.
By the late 1970s, Cayman Airways had begun nonstop flights between Grand Cayman in the Caribbean and Intercontinental with BAC One-Eleven jets. Cayman Airways served the airport for many years, operating a variety of aircraft including Boeing 727-200, Boeing 737-200, Boeing 737-300, Boeing 737-400 and Douglas DC-8 jetliners into IAH in addition to the BAC One-Eleven. In 1977, British Caledonian, commenced nonstop flights between London's Gatwick Airport and Houston with Boeing 707 service, and later with DC-10 and Boeing 747-200 service. British Airways continued operating the route, when in December 1987, BA took over B-Cal increasing its frequency on the route to double-daily.
By July 1983, the number of domestic and international air carriers serving Intercontinental had grown substantially. American, Continental, Delta and Eastern had been joined by Piedmont Airlines, Southwest Airlines, TWA, United Airlines, USAir and Western Airlines. Western was operating daily McDonnell Douglas DC-10 wide body jet services nonstop to Salt Lake City at this time, with this flight also offering one-stop services to Anchorage, Alaska. International services were being operated by Air Canada, Aviateca, British Caledonian Airways, Continental Airlines, Eastern Air Lines, SAHSA, South African Airways, TACA, TWA and Viasa in addition to Pan Am, KLM, Air France, Aeroméxico and Cayman Airways. Several commuter and regional airlines were also operating passenger services at this time from IAH including Emerald Air (operating as Pan Am Express), Metro Airlines, Rio Airways and Royale Airlines. Metro Airlines was operating "cross-town" shuttle services with de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter turboprops with up to seventeen round trip flights a day between IAH and the Clear Lake City STOLport located near the NASA Johnson Space Center and also up to nine round trip flights a day between the airport and Sugar Land Regional Airport as well as other flights to regional destinations in Texas and Louisiana. In addition, at this same time the airport had scheduled helicopter airline services operated by Executive Helicopters with Bell 206L LongRanger helicopters to four Houston-area heliports with up to 36 round trip flights a day.
21st century
Ground transportation
From Downtown Houston one can travel to George Bush Intercontinental by taking Interstate 69/U.S. Route 59 (Eastex Freeway) to Beltway 8 or to Will Clayton Parkway, and access the airport from either road. From Downtown one could also take Interstate 45 (North Freeway), connect to Beltway 8, and enter the airport from the Beltway. The Hardy Toll Road has an exit from the north or south to the airport.
The Metropolitan Transit Authority of Harris County, Texas, or METRO, offers bus services available at the south side of Terminal C. The 102 Bush IAH Express serves the airport. Previously, METRO also operated an express bus service known as Airport Direct, launched in the summer of 2008, which traveled from Downtown Houston to Terminal C via the HOV lane of the Eastex Freeway (I-69)/(US 59). In 2010, in an effort to increase ridership and maximize revenue, METRO reduced the fare of Airport Direct and closed a dedicated passenger plaza for the service in Downtown Houston; instead, the bus stopped at several downtown hotels. The fare each way was reduced from $15 to $4.50. The fare change increased ridership levels but reduced cash flow. METRO consistently provided the service at an operational loss. However, in the summer of 2011, METRO announced it was discontinuing the Airport Direct service, while the Route 102 local service (which serves the greater Greenspoint business and residential district before traveling on I-45 to access downtown) continued to operate.
As of 2016 the Taiwanese airline EVA Air operates a shuttle bus service from Bush IAH to Richardson in the Dallas-Fort Worth area so DFW based customers may fly on its services to and from Houston. Previously China Airlines, also a Taiwanese carrier, provided a shuttle bus service to Sugar Land and the Southwest Houston Chinatown. It ended in 2008 when China Airlines ended its Houston passenger service.
Carriers provide scheduled bus and shuttle services to locations from IAH to NRG Park/NRG Astrodome, Downtown Houston, Uptown, Greenway Plaza, the Texas Medical Center, hotels in the Westchase and Energy Corridor business districts, the city of College Station and William P. Hobby Airport. Super Shuttle uses shared vans to provide services from George Bush Intercontinental Airport to the surrounding communities.
Artwork

Ed Carpenter's "Light Wings", a multicolored glass sculpture suspended below a skylight, adorns the Terminal A North Concourse. In Terminal A, South Concourse stands Terry Allen's "Countree Music." Allen's piece is a cast bronze tree that plays instrumental music by Joe Ely and David Byrne, though the music is normally turned off. The corridor leading to Terminal A displays Leamon Green's "Passing Through," a 200-foot (61 m) etched glass wall depicting airport travelers.
The elevators in Terminal B are cased in stainless steel accordion shaped structures designed by Rachel Hecker. The corridor leading to Terminal B has Dixie Friend Gay's "Houston Bayou." This work is composed of an 8 ft × 75 ft (2.4 m × 22.9 m) Byzantine glass mosaic mural depicting scenes from Houston's bayous and wetlands, several bronze animals embedded in the floor, and five mosaic columns.
"Lights Spikes," designed by Jay Baker, was created for the 1990 G7 Summit when it was hosted by President George H. W. Bush in Houston. The sculpture was relocated to the airport outside E Terminal after the meetings, from its original location in front of the George R. Brown Convention Center. The columns lean at a ten-degree angle toward a central point that represents Houston. The distance between each "spike" and this point is relative to the distance between Houston and the capitals of the countries the flags represent. The countries represented are the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Japan, Canada, Italy and Germany, as well as the European community. The airport has a display of lighted modern sculptures between terminals C and D.
Radiant Fountains, LED-illuminated towers on JFK Boulevard, is the most prominent sculpture around the airport.
Other facilities
The airport houses an on-site hotel, a Marriott, between Terminals B and C and is accessible via the landside inter-terminal train which runs every 3 minutes from 3:30 am to 12:30 am every day. The hotel has 573 rooms, one restaurant and bar, a concierge lounge, a coffee shop, health club, sundry shop and a conference center.
A VOR station, identified as IAH, is located on the airport property, south of runway 33L.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
Cargo
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (December 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Statistics
Top destinations
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Los Angeles, California | 799,000 | American, Spirit, United |
| 2 | Denver, Colorado | 793,000 | Frontier, Southwest, Spirit, United |
| 3 | Atlanta, Georgia | 709,000 | Delta, Spirit, United |
| 4 | Chicago–O'Hare, Illinois | 668,000 | American, Spirit, United |
| 5 | Las Vegas, Nevada | 627,000 | Frontier, Southwest, Spirit, United |
| 6 | Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas | 607,000 | American, United |
| 7 | Orlando, Florida | 580,000 | Frontier, Southwest, Spirit, United |
| 8 | Newark, New Jersey | 571,000 | Spirit, United |
| 9 | San Francisco, California | 554,000 | United |
| 10 | New York–LaGuardia, New York | 462,000 | American, Delta, Spirit, United |
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 888,909 | Aeroméxico, United, Viva Aerobus, Volaris | |
| 2 | 838,138 | Frontier, Spirit, Sun Country, United | |
| 3 | 775,279 | Avianca El Salvador, Spirit, United, Volaris El Salvador | |
| 4 | 506,698 | British Airways, United | |
| 5 | 463,065 | Spirit, United, Viva Aerobus | |
| 6 | 363,478 | Lufthansa, United | |
| 7 | 344,208 | Spirit, United | |
| 8 | 328,830 | United, Viva Aerobus, Volaris | |
| 9 | 303,679 | United, WestJet | |
| 10 | 289,238 | Air Canada, United |
Airline market share
| Rank | Airline | Passengers | Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United Airlines | 33,387,750 | 72.28% |
| 2 | Spirit Airlines | 2,931,004 | 6.35% |
| 3 | American Airlines | 2,179,192 | 4.72% |
| 4 | Delta Airlines | 1,967,765 | 4.26% |
| 5 | Southwest Airlines | 1,189,075 | 2.57% |
| 6 | Other Airlines | 4,537,713 | 9.82% |
Annual traffic
| Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
| Year | Passengers | % Change | Year | Passengers | % Change | Year | Passengers | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 33,913,759 | — | 2012 | 39,890,756 | 2022 | 40,979,422 | ||
| 2003 | 34,208,217 | 2013 | 39,799,414 | 2023 | 46,192,499 | |||
| 2004 | 36,513,098 | 2014 | 41,257,384 | |||||
| 2005 | 39,716,583 | 2015 | 43,023,224 | |||||
| 2006 | 42,550,432 | 2016 | 41,692,372 | |||||
| 2007 | 42,998,040 | 2017 | 40,372,190 | |||||
| 2008 | 41,708,580 | 2018 | 43,807,720 | |||||
| 2009 | 40,007,354 | 2019 | 45,276,595 | |||||
| 2010 | 40,479,569 | 2020 | 18,217,426 | |||||
| 2011 | 40,187,442 | 2021 | 33,677,118 |
Accidents and incidents
- February 1, 1975: a Douglas DC-3 N15HC of Horizon Properties crashed on approach when the port wing collided with an electricity pylon. The aircraft was on a domestic non-scheduled passenger flight from Lawton Municipal Airport, Oklahoma, to Huntsville Regional Airport, Texas. The flight was diverted to Houston for weather. Of the 16 occupants, two crew and three passengers were killed.
- August 23, 1990: a Grumman Gulfstream I operated by Rowan Drilling Company; power loss in an engine after take-off resulted in a failed attempt to regain altitude en route to New Orleans International Airport. The aircraft crashed on departure from Runway 15L and came to rest midfield along a parallel taxiway. There were three fatalities.
- On September 11, 1991, Continental Express Flight 2574 was on descent to the airport when it suffered a structural failure because of improper maintenance, killing all 14 people on board.
- February 19, 1996: a Continental Airlines McDonnell Douglas DC-9-32 operating as Continental Airlines Flight 1943 from Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport, arriving in Houston, landed with its landing gear in the stowed position on Runway 27. The aircraft slid for 6,915 feet (2,108 m) on its belly before stopping on the runway 140 feet (43 m) left of the runway centerline approximately at the departure end of the runway. There were no fatalities and only minor injuries. The aircraft was written off.
- January 13, 1998, a Learjet 25 operated by American Corporate Aviation crashed 2 miles (3.2 km) east of IAH descending below the glideslope. Both occupants were killed.
- February 23, 2019: Atlas Air Flight 3591, a Boeing 767-300ERF operated for Amazon Air crashed into Trinity Bay while on approach, 30 miles (48 km) southeast of the airport. All three crewmembers were killed.
In popular culture
Part of the My 600-lb Life episode, "Maja's Story", is filmed at Bush Airport in Terminal C, when Maja and her boyfriend travel to Houston to meet Dr. Younan Nowzaradan (Dr. Now) for an appointment. In one of the show's most infamous scenes, Maja falls out of the loaner car onto the parking lot pavement because the rental company failed to give her the correctly-sized vehicle she needed due to her severe obesity, then proceeded to throw a temper tantrum inside the airport at the rental car kiosk.
Notes
- Singapore service is a continuation of the Manchester service as the same flight number
References
- "IAH Airport Annual Data from HAS (Houston Airport System) Statistics Dashboard". fly2houston.com. Retrieved June 22, 2024.
- ^ FAA Airport Form 5010 for IAH PDF, effective June 13, 2024
- ^ "About George Bush Intercontinental Airport". Fly2Houston.com. Houston Airport System. Archived from the original on October 12, 2013. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- ^ Intercontinental Airport" Houston Airport System
- "IAH airport data at skyvector.com". skyvector.com. Retrieved August 18, 2022.
- Airports and terminal maps
- Lee, Renée C. (October 8, 2006). "Annexed Kingwood Split on Effects". Houston Chronicle. p. A21. Retrieved July 6, 2011.
- Jen, Robert (January 15, 2024). Trivia Why's. Vol. 2. Sebesta Enterprises. p. 55. ISBN 9780974900377.
- Godiwalla, Adil (January 15, 2024). "Rehabilitation of Runway 9-27 at the Intercontinental Airport of Houston". The 2020 Vision of Air Transportation. American Society of Civil Engineers. p. 325. ISBN 9780784405307.
- "History of Hobby". Fly2Houston.com. Houston Airport System. Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- "Airport Renamed for Bush". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press. April 18, 1997. Retrieved May 2, 2013.
- Jicha, Tom (May 2, 1997). "Houston Airport renamed after Bush". South Florida Sun-Sentinel. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- Bettelheim, Adriel (August 29, 1990). "Houston Gets Continental Hangars. Airline May Shift 1,000 Colo. Jobs to Texas". The Denver Post. Retrieved January 23, 2010.
- June 1, 1969, Official Airline Guide (OAG), Houston flight schedules
- "Pan American World Airways system timetables". June 1, 1969. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "Braniff International Airways system timetables". March 15, 1969. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "KLM Royal Dutch Airlines system timetable". June 15, 1969. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "Aeronaves de Mexico system timetable". June 1, 1969. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "Texas International Airlines system timetable". July 1, 1970. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "KLM Royal Dutch Airlines system timetable". May 15, 1971. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "Air France system timetable". April 1, 1974. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "Official Airline Guide (OAG), Houston (IAH) flight schedules". April 1, 1974. Retrieved August 25, 2015.
- "Cayman Airways system timetable". December 15, 1979. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "Official Airline Guide (OAG) editions, Houston (IAH) flight schedules". Deaprtedflights.com. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- "BCal Texas IAH Photos". british-caledonian.com. Retrieved April 23, 2018.
- ^ "Official Airline Guide (OAG), Houston (IAH) flight schedules". July 1, 1983. Retrieved August 25, 2015.
- "Official Airline Guide (OAG)". Departedflights.com. July 1, 1983. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- "International Official Airline Guide (OAG), Houston (IAH) flight schedules". July 1, 1983. Retrieved August 25, 2015.
- ^ Simons, Janet (October 11, 1992). "Airport Info Houston Intercontinental Airport". Rocky Mountain News. Denver. pp. 5T. Retrieved February 7, 2012.
- ^ "Ground Transportation". Fly2Houston.com. Houston Airport System. Archived from the original on April 24, 2013. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- "Use METRO's Airport Direct to Get to/from Houston Intercontinental Airport". Continental Airlines. Archived from the original on March 8, 2009. Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- "102 Bush IAH Express" (PDF). RideMetro.org. Metropolitan Transit Authority of Harris County, Texas. August 17, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2015.
- Moran, Chris (December 6, 2010). "Metro Cuts Fare and Reroutes Shuttle to IAH". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved December 7, 2010.
- Christian, Carol (June 6, 2011). "Metro Airport Link Gets Riders, but Not Revenue". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved June 6, 2011.
- Christian, Carol (July 26, 2011). "Metro Moves to Eliminate Airport Direct Service". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved July 26, 2011.
- "Dallas – Houston – Dallas Free Shuttle Service Schedule Archived September 5, 2015, at the Wayback Machine." EVA Air. Retrieved February 29, 2016.
- "Houston International Airport Bus Service," China Airlines
- Hensel, Bill, Jr. "2 foreign airlines curtailing Houston passenger service." Houston Chronicle. January 11, 2008. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- "Portfolio:North Concourse Sculpture" (Press release). Ed Carpenter. June 1, 2001. Retrieved December 30, 2006.
- "George Bush Intercontinental Airport Renovation" (Press release). Houston Arts Alliance. June 1, 2001. Archived from the original on February 9, 2007. Retrieved December 30, 2006.
- "George Bush Intercontinental Airport Renovation" (Press release). Houston Arts Alliance. June 1, 2001. Archived from the original on February 9, 2007. Retrieved December 30, 2006.
- "Airport Art". Fly2Houston.com. Houston Airport System. Archived from the original on April 23, 2013. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- Hardy, Michael (October 10, 2013). "SLIDESHOW: New IAH Art". Houstonia. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- "Houston Airport Marriott at George Bush Intercontinental". Marriott. Retrieved August 24, 2015.
- "AirNav: George Bush Intercontinental/Houston Airport". Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- "Houston, TX - G. Bush to Mexico City". aeromexico.com.
- "Flight Schedule". Archived from the original on April 6, 2017. Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Flight Schedules". Air Canada.
- "Air France flight schedule". Air France. Paris: Air France-KLM.
- "Flight Timetables - Flight information". Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- Airlines, Alaska. "Flight Timetable". Alaska Airlines. Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Timetables [International Routes]". Retrieved April 10, 2018.
- ^ "Flight schedules and notifications". Retrieved June 11, 2024.
- "Check itineraries". Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "British Airways - Timetables". Retrieved March 17, 2018.
- "Flight Schedules". Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Flight Schedules". Emirates.
- "Timetables". EVA Air.
- ^ "Frontier Airlines announces new service from Bush Airport | Houston Airport System". www.fly2houston.com.
- ^ "Frontier Airlines Announces 17 New Routes Across Multiple Airports, Spanning the U.S. and Caribbean".
- "Frontier Airlines Adds Another 6 Destinations from Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport; Summer Daily Departures to Increase 57% Versus a Year Ago".
- "Frontier Airlines Announces Nonstop Service from CLE to 10 Additional Destinations; Summer Daily Departures to Increase 38% Versus a Year Ago". Cleveland Hopkins Airport.
- "Frontier". Retrieved March 4, 2018.
- "JetBlue Airlines Timetable". Archived from the original on July 13, 2013. Retrieved January 29, 2017.
- "View the Timetable". KLM. Archived from the original on September 12, 2017. Retrieved March 19, 2018.
- "Timetable - Lufthansa Canada". Lufthansa. Archived from the original on November 9, 2017. Retrieved March 19, 2018.
- "Flight timetable". Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Flight schedules". Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- ^ "SOUTHWEST AIRLINES REPORTS FIRST QUARTER 2024 RESULTS". Southwest Airlines. April 25, 2024. Retrieved April 25, 2024.
- "Check Flight Schedules". Archived from the original on February 2, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2022.
- https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240305-nkmay24
- ^ "Spirit Airlines Aug – Oct 2024 Removed Routes Summary – 19MAY24". Aeroroutes. Retrieved May 21, 2024.
- ^ "Spirit Airlines Adds and Cancels Routes in Summer Schedule Update". Ishrion Aviation.
- https://atxjetsetter.com/post/spirit-expanding-in-dallas//
- "Where We Fly". Spirit Airlines. Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Online Flight Schedule". Turkish Airlines.
- Gonzales, Sofia (November 30, 2023). "United Airlines unveils first-ever nonstop service from Houston's IAH to Georgetown, Guyana". Houston Business Journal.
- https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240628-uanw24mde
- "United Debuts Direct Flights Between U.S. and Tulum". November 17, 2023. Retrieved November 17, 2023.
- ^ "Timetable". Retrieved June 11, 2024.
- ^ "United NS24 Removed Domestic Routes Summary – 05JAN24". AeroRoutes.
- "The Houston – Acapulco flight returns". Fidetur Acapulco (in Spanish). May 2024. Retrieved May 20, 2024.
- "Cherry Capital Airport Adds Direct Service to Houston". The Ticker | Traverse City News & Events.
- "Our Destination". Retrieved March 17, 2018.
- ^ "Volaris Flight Schedule". Archived from the original on February 27, 2017. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- "Flight schedules". Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Lufthansa Cargo begins A321 Stavanger Freighter Service". Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- "Atlas Air Schedule". Atlas Air. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- "CAL to add new Houston call as it targets oil and gas". June 19, 2019.
- "Turkish Cargo adds 7 destinations in Jan 2018".
- "Houston, TX: George Bush Intercontinental/Houston (IAH)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved March 25, 2024.
- "BTS Air Carriers : T-100 International Market (All Carriers)". Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- "flyhouston".
- "IAH Airport Annual Passengers 2002-Present Via Houston Airport System (HAS) Statistics Dashboard". fly2houston.com. Retrieved June 22, 2024.
- "Accident description". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved August 19, 2010.
- "Flight International". FlightGlobal. April 24, 1976. p. 1090. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- "ASN Aircraft accident Grumman G-159 Gulfstream I N80RD Houston–Intercontinental Airport, TX (IAH)". Aviation Safety Network. August 23, 1990. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- "ASN Aircraft accident McDonnell Douglas DC-9-32 N10556 Houston–Intercontinental Airport, TX (IAH)". Aviation Safety Network. February 19, 1996. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- Accident description for N627WS at the Aviation Safety Network
External links
- Houston Airport System – Bush Intercontinental Airport
- Houston Airport System – Houston Airports Today television show
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective December 26, 2024
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KIAH
- ASN accident history for IAH
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KIAH
- FAA current IAH delay information
| Houston area airports | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Houston Airport System | |||
| Others in Harris County |
| ||
| Brazoria County | |||
| Chambers County |
| ||
| Fort Bend County |
| ||
| Galveston County | |||
| Liberty County | |||
| Montgomery County | |||
| Waller County | |||
| Micropolitan statistical areas |
| ||
| See also: List of airports in the Greater Houston Area | |||
| Major airports in the United States | |
|---|---|
| |
| Statistics |

