This is the current revision of this page, as edited by InternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs) at 16:40, 15 September 2024 (Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.5) (Whoop whoop pull up - 21247). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 16:40, 15 September 2024 by InternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs) (Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.5) (Whoop whoop pull up - 21247)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names Monoammonium phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.877 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E342(i) (antioxidants, ...) |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
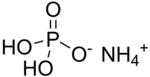
| Chemical formula | H6NO4P |
| Molar mass | 115.025 g·mol |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Odor | none |
| Density | 1.80 g/cm |
| Melting point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) |
| Solubility in water | (g/dL) 28 (10 °C) 36 (20 °C) 44 (30 °C) 56 (40 °C) 66 (50 °C) 81 (60 °C) 99 (70 °C) 118 (80 °C) 173 (100 °C) |
| Solubility | insoluble in ethanol insoluble in acetone |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.525 |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | tetragonal |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−1445.07 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 5750 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Ammonium phosphate Diammonium phosphate |
| Other cations | Monosodium phosphate Potassium dihydrogen phosphate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), also known as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)(H2PO4). ADP is a major ingredient of agricultural fertilizers and dry chemical fire extinguishers. It also has significant uses in optics and electronics.
Chemical properties
Monoammonium phosphate is soluble in water and crystallizes from it as the anhydrous salt in the tetragonal system, as elongated prisms or needles. It is practically insoluble in ethanol.
Solid monoammonium phosphate can be considered stable in practice for temperatures up to 200 °C, when it decomposes into gaseous ammonia NH
3 and molten phosphoric acid H
3PO
4. At 125 °C the partial pressure of ammonia is 0.05 mm Hg.
A solution of stoichometric monoammonium phosphate is acidic (pH 4.7 at 0.1% concentration, 4.2 at 5%).
Preparation
Monoammonium phosphate is industrially prepared by the exothermic reaction of phosphoric acid and ammonia in the correct proportions:
- NH
3 + H
3PO
4 → NH
4H
2PO
4
Crystalline MAP then precipitates.
Uses
Agriculture
The largest use of monoammonium phosphate by weight is in agriculture, as an ingredient of fertilizers. It supplies soil with the elements nitrogen and phosphorus in a form usable by plants. Its NPK label is 12-61-0 (12-27-0), meaning that it contains 12% by weight of elemental nitrogen and (nominally) 61% of phosphorus pentoxide P
2O
5, or 27% of elemental phosphorus.
Fire extinguishers
The compound is also a component of the ABC powder in some dry chemical fire extinguishers.
Optics
Monoammonium phosphate is a widely used crystal in the field of optics due to its birefringence properties. As a result of its tetragonal crystal structure, this material has negative uniaxial optical symmetry with typical refractive indices no = 1.522 and ne = 1.478 at optical wavelengths.
Electronics
Monoammonium phosphate crystals are piezoelectric, a property required in some active sonar transducers (the alternative being transducers that use magnetostriction). In the 1950s ADP crystals largely replaced the quartz and Rochelle salt crystals in transducers because they are easier to work than quartz and, unlike Rochelle salt, are not deliquescent.
Toys
Being relatively non-toxic, MAP is also a popular substance for recreational crystal growing, being sold as toy kits mixed with dyes of various colors.
Natural occurrence
The compound appears in nature as the rare mineral biphosphammite. It is formed in guano deposits. A related compound, that is the monohydrogen counterpart, is the even more scarce phosphammite.
References
- Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 4–40. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ Dejun Xu, Xing Xiong, Lin Yang, Zhiye Zhang, and Xinlong Wang (2016): "Determination of the Solubility of Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate in Water-Ethanol System at Different Temperatures from 283.2 to 343.2 K". Journal of Chemincal Engineering Data, volume 61, issue 1, pages 78–82. doi:10.1021/acs.jced.5b00224
- Chemical Book: "Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate". Accessed on 2018-08-14.
- National Bureau of Standards. Selected Values of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties. Technical note 270-3. 1968
- "Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)" (PDF). www.mosaicco.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- IPNI. "Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)" (PDF). www.ipni.net. International Plant Nutrition Institute. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Amnon Yariv, Pochi Yeh (1984). Optical Waves in Crystals. Wiley, Inc.
- ^ Willem Hackmann (1984). Seek and Strike: Sonar, Anti-Submarine Warfare and the Royal Navy, 1914–1954. Her Majesty's Stationery Office. ISBN 0-11-290423-8.
- G. O. Guerrant and D. E. Brown (196): "Thermal Decomposition of High-Analysis Fertilizers Based on Ammonium Phosphate". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, volume 13, issue 6, pages 493-497. doi:10.1021/jf60142a002
- John R Van Wazer (1958). Phosphorus And Its Compounds - Volume I: Chemistry. New York: Interscience Publishers, Inc. p. 503.
- Haifa Chemicals Ltd.: "Mono-Ammonium Phosphate 12-61-0 Archived 15 October 2022 at the Wayback Machine". Product fact sheet, accessed on 2018-08-13.
- Martin Bäckman, Martin Gunnarsson, Linnea Kollberg, Martin Müller, and Simon Tallvod (2016): "Production of Monoammonium Phosphate at Yara AB Archived 18 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine". Technical Report, Lund University.
- "Biphosphammite".
- "List of Minerals". 21 March 2011.
- "Phosphammite".
- "List of Minerals". 21 March 2011.
| Phosphates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||