This is the current revision of this page, as edited by JWBE (talk | contribs) at 15:41, 23 September 2024 (added Category:2-Methoxyphenyl compounds using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 15:41, 23 September 2024 by JWBE (talk | contribs) (added Category:2-Methoxyphenyl compounds using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (Ethane-1,2-diyl)bis | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.203.286 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C28H28O2P2 |
| Molar mass | 458.478 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
DIPAMP is an organophosphorus compound that is used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It is a white solid that dissolves in organic solvents. Work on this compound by W. S. Knowles was recognized with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. DIPAMP was the basis for one of the first industrial scale asymmetric hydrogenation, the synthesis of the drug L-DOPA.
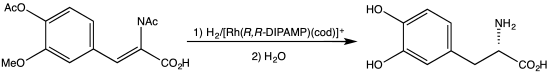
Synthesis of L-DOPA via hydrogenation with the C2-symmetric diphosphine DIPAMP.
DIPAMP is a C2-symmetric diphosphine. Each phosphorus centre, which is pyramidal, bears three different substituents - anisyl, phenyl, and the ethylene group. The ligand therefore exists as the enantiomeric (R,R) and (S,S) pair, as well as the achiral meso isomer.
DIPAMP was originally prepared by an oxidative coupling, starting from anisyl(phenyl)(methyl)phosphine.

References
- Knowles, William S. (2002). "Asymmetric Hydrogenations (Nobel Lecture) Copyright© The Nobel Foundation 2002. We thank the Nobel Foundation, Stockholm, for permission to print this lecture". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 41 (12): 1998. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20020617)41:12<1998::AID-ANIE1998>3.0.CO;2-8.
- Vineyard, B. D.; Knowles, W. S.; Sabacky, M. J.; Bachman, G. L.; Weinkauff, D. J. (1977). "Asymmetric hydrogenation. Rhodium chiral bisphosphine catalyst". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 99 (18): 5946–5952. doi:10.1021/ja00460a018.
- H.-J.Drexler; Songlin Zhang; Ailing Sun; A. Spannenberg; A. Arrieta; A. Preetz; D. Heller (2004). "Cationic Rh-bisphosphine-diolefin complexes as precatalysts for enantioselective catalysis––what information do single crystal structures contain regarding product chirality?". Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 15 (14): 2139–50. doi:10.1016/j.tetasy.2004.06.036.