This is the current revision of this page, as edited by KormiSK (talk | contribs) at 14:43, 1 October 2024 (biosynthetic relevance). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 14:43, 1 October 2024 by KormiSK (talk | contribs) (biosynthetic relevance)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)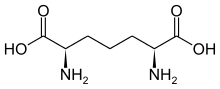 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (2R,6S)-2,6-Diaminoheptanedioic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.660 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| MeSH | Diaminopimelic+acid |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H14N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 190.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Density | 1.344 g/mL |
| Melting point | 295 °C (563 °F; 568 K) |
| Boiling point | 426.7 °C (800.1 °F; 699.8 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Diaminopimelic acid (DAP) is an amino acid, representing an epsilon-carboxy derivative of lysine. meso-α,ε-Diaminopimelic acid is the last intermediate in the biosynthesis of lysine and undergoes decarboxylation by diaminopimelate decarboxylase to give the final product.
DAP is a characteristic of certain cell walls of some bacteria. DAP is often found in the peptide linkages of NAM-NAG chains that make up the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. When provided, they exhibit normal growth. When in deficiency, they still grow but with the inability to make new cell wall peptidoglycan.
This is also the attachment point for Braun's lipoprotein.
See also
- Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in DAP synthesis
- Peptidoglycan
- Pimelic acid
Images
References
- Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith G. (2011). Biochemistry (4th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1072–1075. ISBN 978-0-470-57095-1. OCLC 690489261.
- Brooks, George H.; Geo F. Brooks (2007). Jawetz, Melnick & Adelberg's medical microbiology. McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 85. ISBN 978-0-07-147666-9.
- Seltmann, Guntram; Holst, Otto (2002). The Bacterial Cell Wall. Berlin: Springer. pp. 81–82. ISBN 3-540-42608-6.
| Microbiology: Bacteria | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical microbiology | |||||||
| Biochemistry and ecology |
| ||||||
| Shape | |||||||
| Structure |
| ||||||
| Taxonomy and evolution | |||||||
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |